
The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan (non-Austronesian) speaking Melanesians as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.
Indo-Pacific is a hypothetical language macrofamily proposed in 1971 by Joseph Greenberg and now believed to be spurious. It grouped together the Papuan languages of New Guinea and Melanesia with the languages of the Andaman Islands and, tentatively, the languages of Tasmania, both of which are remote from New Guinea. The valid cognates Greenberg found turned out to be reflexes of the less extensive Trans–New Guinea family. Recently the Kusunda language, which is generally seen as a language isolate, is also included in the Indo-Pacific proposal. Greenberg did not include "Australian" in his original 1971 proposal.

The Trans-Fly – Bulaka RiverakaSouth-Central Papuan languages form a hypothetical family of Papuan languages. They include many of the languages west of the Fly River in southern Papua New Guinea into southern Indonesian West Papua, plus a pair of languages on the Bulaka River a hundred km further west.

The Eastern Trans-Fly languages are a small independent family of Papuan languages spoken in the Oriomo Plateau to the west of the Fly River in New Guinea.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ." Languages with statutory recognition are Tok Pisin, English, Hiri Motu, and Papua New Guinean Sign Language. Tok Pisin, an English-based creole, is the most widely spoken, serving as the country's lingua franca. Papua New Guinean Sign Language became the fourth officially recognised language in May 2015, and is used by the deaf population throughout the country.
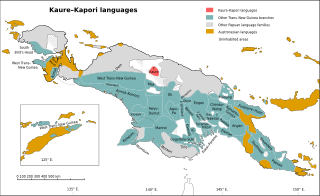
The Kaure–Kosare or Nawa River languages are a small family spoken along the Nawa River in West Papua, near the northern border with Papua New Guinea. The languages are Kaure and Kosare.

The Bosavi or Papuan Plateau languages are a family of the Trans–New Guinea languages in the classifications of Malcolm Ross and Timothy Usher. The family is named after Mount Bosavi and the Papuan Plateau.

The East Strickland or Strickland River languages are a family of Papuan languages.
The Koiarian languages Koiari are a small family of Trans–New Guinea languages spoken in the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea. They are classified within the Southeast Papuan branch of Trans–New Guinea.
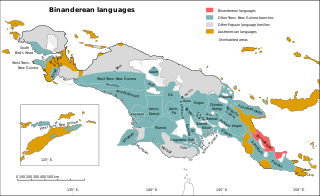
The Greater Binanderean or Guhu-Oro languages are a language family spoken along the northeast coast of the Papuan Peninsula – the "Bird's Tail" of New Guinea – and appear to be a recent expansion from the north. They were classified as a branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages by Stephen Wurm (1975) and Malcolm Ross (2005), but removed by Timothy Usher (2020). The Binandere family proper is transparently valid; Ross connected it to the Guhu-Semane isolate based on pronominal evidence, and this has been confirmed by Smallhorn (2011). Proto-Binanderean has been reconstructed in Smallhorn (2011).
The Demta–Sentani languages form a language family of coastal Indonesian Papua near the Papua New Guinea border.
The Trans-Fly languages are a small family of Papuan languages proposed by Timothy Usher, that are spoken in the region of the Fly River.

Kaluli is a language spoken in Papua New Guinea. It is a developing language with 3,100 speakers. Some people refer to this language as Bosavi, however the people themselves refer to the language as Kaluli. There are four dialects, Ologo, Kaluli, Walulu, and Kugenesi. The differences between the dialects are not clear. Their writing system uses the Latin script. Kaluli belongs to the Trans-New Guinea language family. Kaluli was first analyzed by Murray Rule in 1964 who wrote a preliminary phonological and morphological analysis. A dictionary of Kaluli has been compiled by Schieffelin and Feld (1998).
Wipi, also known as Gidra, Jibu or Oriomo, is a Papuan language of New Guinea. It is a member of the Eastern Trans-Fly family, the other languages of this family being Gizrra, Meriam Mir and Bine. The family has influenced the neighbouring Kiwai language as well as Kalau Lagau Ya.
Tirio is Papuan language of Western Province, Papua New Guinea. The Giribam 'dialect' may be a distinct language.
Bine, also known as Pine, Kunini, Masingara or Oriomo, is a Papuan language of New Guinea. Glottolog lists the following varieties: Boze-Giringarede, Irupi-Drageli, Kunini, Masingle, Sebe, Sogal and Tate.
Bitur is Papuan language of Western Province, Papua New Guinea.

The Oriomo River is located in southern Papua New Guinea. Originating on the Oriomo Plateau, it enters the sea near the town of Daru.

Oriomo-Bituri Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Western Province, Papua New Guinea. Eastern Trans-Fly languages are spoken in the LLG.










