
Lower Saxony is a German state (Land) situated in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with 47,624 km2 (18,388 sq mi), and fourth-largest in population among the 16 Länder federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, but the number of speakers is declining.

Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of 18,413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants.

Thuringia, officially the Free State of Thuringia, is a state of Germany.

Saxony-Anhalt (German: Sachsen-Anhalt is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of 20,447.7 square kilometres and has a population of 2.2 million inhabitants, making it the 8th-largest state in Germany by area and the 11th-largest by population. Its capital is Magdeburg and its largest city is Halle.

Svealand, Swealand or Sweden proper is the historical core region of Sweden. It is located in south central Sweden and is one of three historical lands of Sweden, bounded to the north by Norrland and to the south by Götaland. Deep forests, Tiveden, Tylöskog, and Kolmården, separated Svealand from Götaland. Historically, its inhabitants were called Svear, from which is derived the English Swedes.
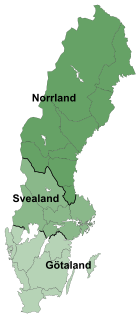
The lands of Sweden are three traditional parts, each consisting of several provinces, in Sweden. The division into lands goes back to the foundation of modern Sweden, when Götaland, the land of the Geats, merged with Svealand, the land of the Swedes, to form the country, while Norrland and Österland were added later. The lands have no administrative function but are still seen by many Swedes as an important part of their identity.
Altenburger Land is a district in Thuringia, Germany. It is bounded by the district of Greiz, the Burgenlandkreis (Saxony-Anhalt), and the districts Leipzig, Mittelsachsen and Zwickau in Saxony. The district is a member of the Central German Metropolitan Region.

Föhrpronunciation (help·info) is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German coast of the North Sea. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Föhr is the second-largest North Sea island of Germany and a popular destination for tourists. A town and eleven distinct municipalities are located on the island. The climate is oceanic with moderate winters and relatively cool summers.

The House of Wettin is a dynasty of German counts, dukes, prince-electors and kings that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany.

Albert II, the Degenerate was a Margrave of Meissen, Landgrave of Thuringia and Count Palatine of Saxony. He was a member of the House of Wettin.

The Saxon Eastern March was a march of the Holy Roman Empire from the 10th until the 12th century. The term "eastern march" stems from the Latin term marchia Orientalis and originally could refer to either a march created on the eastern frontier of the East Frankish duchy of Saxony or another on the eastern border of the Duchy of Bavaria: the Bavarian marchia Orientalis, corresponding to later Austria.

The Margraviate of Landsberg was a march of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 13th to the 14th century under the rule of the Wettin dynasty. It was named after Landsberg Castle in present-day Saxony-Anhalt.

The March or Margraviate of Lusatia was as an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast Marca Geronis. Ruled by several Saxon margravial dynasties, among them the House of Wettin, the lordship was contested by the Polish kings as well as by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg. The remaining territory was finally incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown in 1367.

Dunsum is a municipality located on the western shore of Föhr in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is composed of the districts of Greater and Lesser Dunsum.

The Division of Altenburg was the plan for the division of the Meissen lands agreed upon by the two hostile Wettin brothers Elector Frederick II of Saxony and William III on 16 July 1445 at Altenburg. The brothers had attempted to reconcile, but eventually the division led the Saxon Fratricidal War, which began in 1446 and lasted for five years, until the Peace of Naumburg was negotiated in 1451. Following the peace, the subsequent Treaty of Eger in 1459, and the deaths of Frederick II and Wilhelm III, the two sons of Frederick II eventually gained control of the land of both their father and William III.
Orientalis, oriental in Latin, may refer to :
Wilhelm II, the Rich was the second son of Margrave Frederick the Strict of Meissen and Catherine of Henneberg.
A Very Big Child is a 1952 West German comedy film directed by Paul Verhoeven and starring Georg Thomalla, Angelika Hauff and Gardy Granass.












