
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist.
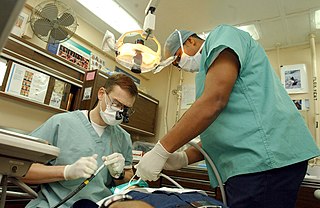
A dentist, also known as a dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists.
The American Dental Association (ADA) is an American professional association established in 1859 which has more than 161,000 members. Based in the American Dental Association Building in the Near North Side of Chicago, the ADA is the world's largest and oldest national dental association. The organization lobbies on behalf of the American dental profession and provides dental accreditation.
Cosmetic dentistry is generally used to refer to any dental work that improves the appearance of teeth, gums and/or bite. It primarily focuses on improvement in dental aesthetics in color, position, shape, size, alignment and overall smile appearance. Many dentists refer to themselves as "cosmetic dentists" regardless of their specific education, specialty, training, and experience in this field. This has been considered unethical with a predominant objective of marketing to patients. The American Dental Association does not recognize cosmetic dentistry as a formal specialty area of dentistry. However, there are still dentists that promote themselves as cosmetic dentists.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity (mouth), head and neck, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery/facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.

A dental hygienist or oral hygienist is a licensed dental professional, registered with a dental association or regulatory body within their country of practice. Prior to completing clinical and written board examinations, registered dental hygienists must have either an associate's or bachelor's degree in dental hygiene from an accredited college or university. Once registered, hygienists are primary healthcare professionals who work independently of or alongside dentists and other dental professionals to provide full oral health care. They have the training and education that focus on and specialize in the prevention and treatment of many oral diseases.

Chapin Aaron HarrisA.M., MD, D.D.S. was an American physician and dentist and dentistry school founder.

Lucy Hobbs Taylor was an American dentist, known for being the first woman to graduate from dental school.
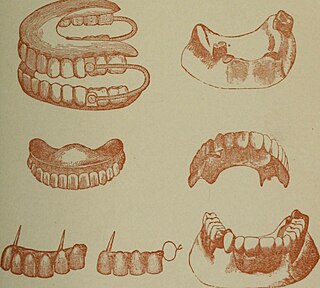
A denturist in the United States and Canada, clinical dental technologist in the United Kingdom and Ireland, dental prosthetist in Australia, or a clinical dental technician in New Zealand is a member of the oral health care team and role as primary oral health care provider who provides an oral health examination, planning treatment, takes impressions of the surrounding oral tissues, constructs and delivers removable oral prosthesis treatment directly to the patient.

The Ohio State University College of Dentistry is one of the graduate and professional schools of Ohio State University. The college is the fourth largest public dental school in the U.S. and consists of nine academic divisions representing all major dental specialties. In addition to the Doctor of Dental Surgery (D.D.S.) and Bachelor of Science in Dental Hygiene degrees, the Ohio State College of Dentistry offers specialty training programs, advanced training programs, MS programs, and a Ph.D. program in Oral Biology. Outreach and Engagement activities include over 60 active programs and more than 42 extramural sites, which continue to expand.
Special needs dentistry, also known as special care dentistry, is a dental specialty that deals with the oral health problems of geriatric patients, patients with intellectual disabilities, and patients with other medical, physical, or psychiatric issues.
Howard University College of Dentistry is a school of dentistry located in the United States city of Washington, D.C. It is the only dental school in Washington, D.C..

John Miller Hyson, Jr. was the former curator, director of curatorial services, and director of archives and history at the National Museum of Dentistry, an affiliate of the Smithsonian Institution located in Baltimore, Maryland. He was also the author of many articles and books on the history of dentistry and was a practicing dentist for nearly 50 years.

The University of Michigan School of Dentistry is the dental school of the University of Michigan, a public research university located in Ann Arbor, Michigan. Established in 1875, the School of Dentistry engages in oral and craniofacial health care education, research, patient care and community service.

There is a long history of women in dentistry in the United States.

There is a long history of women in dentistry. Women are depicted as assistant dentists in the Middle Ages. Prior to the 19th century, dentistry was largely not yet a clearly defined and regulated profession with formal educational requirements. Individual female dentists are known from the 18th century. When the profession was regulated in the 19th century, it took a while before women achieved the formal education and permission to engage in dentistry.
The Pierre Fauchard Academy is a volunteer-run, non-profit dental organization that was founded by Dr. Elmer S. Best, a dentist from Minnesota in 1936. The objective is the independence from commercial interests in dental research and its publications. Dr. Best endeavored to raise the professional standards. The academy is named after Pierre Fauchard (1678-1761), a French dentist who is considered the "Father of modern dentistry". Fauchard wrote a book entitled Le Chirurgien dentiste, ou Traité des dents, the first dental textbook of modern times.
Esther Mae Wilkins was an American dental hygienist, dentist and author of the first comprehensive book on dental hygiene, Clinical Practice of the Dental Hygienist. The dental instrument known as the Wilkins/Tufts Explorer was named after her.

John C. Greene was an American dentist and public health administrator. He was a rear admiral in the U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, and served as the Deputy Surgeon General of the United States under President Carter from 1978 to 1981. He was the Acting Surgeon General from January to May 1981 under Ronald Reagan. He was the highest ranking non-physician public health officer in the history of the U.S. government.
Jessica Ann Rickert became the first female American Indian dentist in America upon graduating with a DDS from the University of Michigan School of Dentistry in 1975. She was one of only six women in a class of 140 students. She is a member of the Prairie Band Potawatomi Nation, and a direct descendant of the Indian chief Wahbememe (Whitepigeon).













