Related Research Articles

Assistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for people with disabilities and the elderly. Disabled people often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, or even with assistance. ADLs are self-care activities that include toileting, mobility (ambulation), eating, bathing, dressing, grooming, and personal device care. Assistive technology can ameliorate the effects of disabilities that limit the ability to perform ADLs. Assistive technology promotes greater independence by enabling people to perform tasks they were formerly unable to accomplish, or had great difficulty accomplishing, by providing enhancements to, or changing methods of interacting with, the technology needed to accomplish such tasks. For example, wheelchairs provide independent mobility for those who cannot walk, while assistive eating devices can enable people who cannot feed themselves to do so. Due to assistive technology, disabled people have an opportunity of a more positive and easygoing lifestyle, with an increase in "social participation", "security and control", and a greater chance to "reduce institutional costs without significantly increasing household expenses." In schools, assistive technology can be critical in allowing students with disabilities to access the general education curriculum. Students who experience challenges writing or keyboarding, for example, can use voice recognition software instead. Assistive technologies assist people who are recovering from strokes and people who have sustained injuries that affect their daily tasks.

A keyset or chorded keyboard is a computer input device that allows the user to enter characters or commands formed by pressing several keys together, like playing a "chord" on a piano. The large number of combinations available from a small number of keys allows text or commands to be entered with one hand, leaving the other hand free. A secondary advantage is that it can be built into a device that is too small to contain a normal-sized keyboard.

A pointing device is a human interface device that allows a user to input spatial data to a computer. Graphical user interfaces (GUI) and CAD systems allow the user to control and provide data to the computer using physical gestures by moving a hand-held mouse or similar device across the surface of the physical desktop and activating switches on the mouse. Movements of the pointing device are echoed on the screen by movements of the pointer and other visual changes. Common gestures are point and click and drag and drop.

In computing, a Control keyCtrl is a modifier key which, when pressed in conjunction with another key, performs a special operation. Similarly to the Shift key, the Control key rarely performs any function when pressed by itself. The Control key is located on or near the bottom left side of most keyboards, with many featuring an additional one at the bottom right.

An electronic keyboard, portable keyboard, or digital keyboard is an electronic musical instrument based on keyboard instruments. Electronic keyboards include synthesizers, digital pianos, stage pianos, electronic organs and digital audio workstations. In technical terms, an electronic keyboard is a rompler-based synthesizer with a low-wattage power amplifier and small loudspeakers.
Computer accessibility refers to the accessibility of a computer system to all people, regardless of disability type or severity of impairment. The term accessibility is most often used in reference to specialized hardware or software, or a combination of both, designed to enable the use of a computer by a person with a disability or impairment.

In computing, a keyboard shortcut is a software-based assignment of an action to one or more keys on a computer keyboard. Most operating systems and applications come with a default set of keyboard shortcuts, some of which may be modified by the user in the settings.

Beatmania IIDX (IIDX) is a series of rhythm video games, that was first released by Konami in Japan on 26 February 1999. Beatmania IIDX has since spawned 32 arcade releases and 14 console releases on the Sony PlayStation 2. It is the sequel to the beatmania game series, and is part of the Bemani line of music games.

A keychain is a small ring or chain of metal to which several keys, or fobs can be attached. The terms keyring & keychain are often used interchangeably to mean both the individual ring, or a combined unit of a ring and fob.
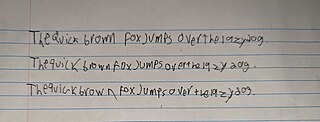
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder and learning disability that concerns impairments in written expression, which affects the ability to write, primarily handwriting, but also coherence. It is a specific learning disability (SLD) as well as a transcription disability, meaning that it is a writing disorder associated with impaired handwriting, orthographic coding and finger sequencing. It often overlaps with other learning disabilities and neurodevelopmental disorders such as speech impairment, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or developmental coordination disorder (DCD).

Arrow keys or cursor movement keys are keys on a computer keyboard that are either programmed or designated to move the cursor in a specified direction.

The word "manual" is used instead of the word "keyboard" when referring to any hand-operated keyboard on a keyboard instrument that has a pedalboard, such as an organ; or when referring to one of the keyboards on an instrument that has more than one hand-operated keyboard, such as a two- or three-manual harpsichord.

The microKORG is a MIDI-capable digital synthesizer/vocoder from Korg featuring DSP-based analog modelling. The synthesizer is built in such a way that it is essentially a Korg MS-2000 with a programmable step arpeggiator, a less advanced vocoder, lack of motion sequencing, lack of an XLR microphone input, and in a smaller case with fewer real-time control knobs.

Japanese input methods are used to input Japanese characters on a computer.
The Windows shell is the graphical user interface for the Microsoft Windows operating system. Its readily identifiable elements consist of the desktop, the taskbar, the Start menu, the task switcher and the AutoPlay feature. On some versions of Windows, it also includes Flip 3D and the charms. In Windows 10, the Windows Shell Experience Host interface drives visuals like the Start Menu, Action Center, Taskbar, and Task View/Timeline. However, the Windows shell also implements a shell namespace that enables computer programs running on Windows to access the computer's resources via the hierarchy of shell objects. "Desktop" is the top object of the hierarchy; below it there are a number of files and folders stored on the disk, as well as a number of special folders whose contents are either virtual or dynamically created. Recycle Bin, Libraries, Control Panel, This PC and Network are examples of such shell objects.

A front panel was used on early electronic computers to display and allow the alteration of the state of the machine's internal registers and memory. The front panel usually consisted of arrays of indicator lamps, digit and symbol displays, toggle switches, dials, and push buttons mounted on a sheet metal face plate. In early machines, CRTs might also be present. Prior to the development of CRT system consoles, many computers such as the IBM 1620 had console typewriters.

A mouse button is an electric switch on a computer mouse which can be pressed (“clicked”) to select or interact with an element of a graphical user interface. Mouse buttons are most commonly implemented as miniature snap-action switches.

A computer keyboard is a peripheral input device modeled after the typewriter keyboard which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches. Replacing early punched cards and paper tape technology, interaction via teleprinter-style keyboards have been the main input method for computers since the 1970s, supplemented by the computer mouse since the 1980s.

In computing, an input device is a piece of equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include keyboards, computer mice, scanners, cameras, joysticks, and microphones.

A keyboard layout is any specific physical, visual, or functional arrangement of the keys, legends, or key-meaning associations (respectively) of a computer keyboard, mobile phone, or other computer-controlled typographic keyboard.
References
- ↑ P. Blenkhorn, "Switch, overlay keyboard and touch screen software for children and adults with profound and multiple disabilities", Feb. 24, 1998, accessed Sept. 22, 2007
- ↑ "Everything You Need to Know about Overlay Keyboards", accessed 29 July 2009