Related Research Articles

Benjamin Banneker was an American naturalist, mathematician, astronomer and almanac author. A landowner, he also worked as a surveyor and farmer.

An almanac is a regularly published listing of a set of current information about one or multiple subjects. It includes information like weather forecasts, farmers' planting dates, tide tables, and other tabular data often arranged according to the calendar. Celestial figures and various statistics are found in almanacs, such as the rising and setting times of the Sun and Moon, dates of eclipses, hours of high and low tides, and religious festivals. The set of events noted in an almanac may be tailored for a specific group of readers, such as farmers, sailors, or astronomers.

Edward Pococke was an English Orientalist and biblical scholar.

Poor Richard's Almanack was a yearly almanac published by Benjamin Franklin, who adopted the pseudonym of "Poor Richard" or "Richard Saunders" for this purpose. The publication appeared continually from 1732 to 1758. It sold exceptionally well for a pamphlet published in the Thirteen Colonies; print runs reached 10,000 per year.

John Partridge was an English astrologer, the author and publisher of a number of astrological almanacs and books.

Whitaker's is a reference book, published annually in the United Kingdom. It was originally published by J. Whitaker & Sons from 1868 to 1997, next by HM Stationery Office until 2003 and then by A. & C. Black, which became a wholly owned subsidiary of Bloomsbury Publishing in 2011. The publication was acquired by Rebellion Publishing in 2020, with the 153rd edition appearing on 15 April 2021. In mid-2022, Rebellion announced that there would not be a 2022 edition and no further editions have appeared since then.

Wisden Cricketers' Almanack, or simply Wisden, colloquially the Bible of Cricket, is a cricket reference book published annually in the United Kingdom. The description "Bible of cricket" has been applied to Wisden since the early 1900s.

Nettlebed is a village and civil parish in Oxfordshire in the Chiltern Hills about 4+1⁄2 miles (7 km) north-west of Henley-on-Thames and 6 miles (10 km) south-east of Wallingford. The parish includes the hamlet of Crocker End, about 1⁄2 mile (800 m) east of the village. The 2011 Census recorded a parish population of 727.

Old Moore's Almanack is an astrological almanac which has been published in Britain since 1697.

The Old Farmer's Almanac is an almanac containing weather forecasts, planting charts, astronomical data, recipes, and articles. Topics include gardening, sports, astronomy, folklore, and predictions on trends in fashion, food, home, technology, and living for the coming year. Published every September, The Old Farmer's Almanac has been published continuously since 1792, making it the oldest continuously published periodical in North America. The publication follows in the heritage of American almanacs such as Benjamin Franklin’s Poor Richard's Almanack.

Old Moore's Almanac is an almanac which has been published for nearly two and a half centuries. Its founder, Theophilus Moore, ran a classical academy at Milltown which was then a village near Dublin. A teacher of Irish, English, Greek and Latin, he became known as a clever mathematician and a wizard of astrology, gaining the nickname 'The Irish Merlin'. He published his Old Moore's Almanac for the first time in 1764, and received such support that the other Irish almanacs gradually dwindled away. Theophilus Moore is now buried in the Drumcondra Churchyard, in Dublin, but the tradition of Old Moore's Almanac continues unbroken to this day.

Samuel Danforth (1626–1674) was a Puritan minister, preacher, poet, and astronomer, the second pastor of The First Church in Roxbury and an associate of the Rev. John Eliot of Roxbury, Massachusetts, known as the “Apostle to the Indians.”
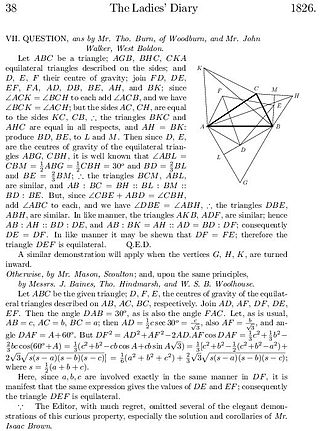
The Ladies' Diary: or, Woman's Almanack appeared annually in London from 1704 to 1841 after which it was succeeded by The Lady's and Gentleman's Diary. It featured material relating to calendars etc. including sunrise and sunset times and phases of the moon, as well as important dates, and a chronology of remarkable events.
Poor Robin was an English 17th and 18th-century satirical almanac series, appearing as Poor Robin's Almanack from 1663. Other similar writings by the pseudonymous Poor Robin were published later, in America and into the 19th century.

Ames' Almanack (almanac) was the first almanac printed in the British North American colonies. While Benjamin Franklin's Poor Richard's Almanack is more widely known, the Ames' Almanack had a much larger readership. Franklin's publication had a circulation of 10,000 copies compared to 60,000 for the Ames' Almanack.
Melbourne Punch was an Australian illustrated magazine founded by Edgar Ray and Frederick Sinnett, and published from August 1855 to December 1925. The magazine was modelled closely on Punch of London which was founded fifteen years earlier. A similar magazine, Adelaide Punch, was published in South Australia from 1878 to 1884.
William Abel Pantin was a historian of medieval England who spent most of his academic life at the University of Oxford.

North Leigh Roman Villa was a Roman courtyard villa in the Evenlode Valley about 0.5 miles (800 m) north of the hamlet of East End in North Leigh civil parish in Oxfordshire. It is a scheduled monument in the care of English Heritage and is open to the public.
A tradition of almanacs published for the purposes of North America began in New England in the 17th century. A New World's dwelling would seldom be found without the latest print of North American almanac and The Pilgrim's Progress.
References
- 1 2 Hibbert, Christopher, ed. (1988). "Oxford Almanacks". The Encyclopaedia of Oxford . Macmillan. pp. 298–299. ISBN 0-333-39917-X.
- ↑ @OxUniPress (2 January 2020). "Hi, unfortunately there isn't an Oxford Almanack for 2020. The University of Oxford and OUP have agreed to stop producing the Almanack from 2020 onwards due to dwindling interest" (Tweet) – via Twitter.