
IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet without connecting wires.

A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link desktop and laptop computers, tablet computers, smartphones, smart TVs, printers, and smart speakers together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries and airports to provide the public Internet access for mobile devices.

Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. "Free space" means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable.
Atmel Corporation was a designer and manufacturer of semiconductors before being acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. It was founded in 1984. The company focuses on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products include microcontrollers radio frequency (RF) devices including Wi-Fi, EEPROM, and flash memory devices, symmetric and asymmetric security chips, touch sensors and controllers, and application-specific products. Atmel supplies its devices as standard products, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), or application-specific standard product (ASSPs) depending on the requirements of its customers.

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications.
Netgear, Inc. is a multinational computer networking company based in San Jose, California, with offices in about 25 other countries. It produces networking hardware for consumers, businesses, and service providers. The company operates in three business segments: retail, commercial, and as a service provider.

High-speed multimedia radio (HSMM) is the implementation of high-speed wireless TCP/IP data networks over amateur radio frequency allocations using commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware such as 802.11 Wi-Fi access points. This is possible because the 802.11 unlicensed frequency bands partially overlap with amateur radio bands and ISM bands in many countries. Only licensed amateur radio operators may legally use amplifiers and high-gain antennas within amateur radio frequencies to increase the power and coverage of an 802.11 signal.
Qualcomm Atheros is a developer of semiconductor chips for network communications, particularly wireless chipsets. Founded under the name T-Span Systems in 1998 by experts in signal processing and VLSI design from Stanford University, the University of California, Berkeley and private industry. The company was renamed Atheros Communications in 2000 and it completed an initial public offering in February 2004 trading on NASDAQ under the symbol ATHR.
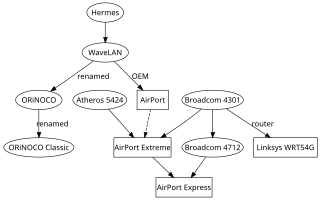
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.
Cambium Networks is a wireless infrastructure provider that offers fixed wireless and Wi-Fi to broadband service providers and enterprises to provide Internet access. An American telecommunications infrastructure company, it provides wireless technology, including Enterprise WiFi, switching solutions, Internet of Things, and fixed wireless broadband and Wi-Fi for enterprises. Publicly traded on the NASDAQ stock exchange, it spun out of Motorola in October 2011.

Proxim Wireless Corporation is a San Jose, California-based company that builds scalable broadband wireless networking systems for communities, enterprises, governments, and service providers. It offers wireless LAN, point-to-multipoint and point-to-point products through a channel network. The company is a product of many mergers and acquisitions over the years.
Airspan Networks is an American telecommunications company headquartered in Boca Raton, Florida, developing Radio Access Network technology including the Sprint 'Magic Box' and both small cells and macro cells for the Rakuten virtualized network.
IEEE 802.11b-1999 or 802.11b is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking specification that extends throughput up to 11 Mbit/s using the same 2.4 GHz band. A related amendment was incorporated into the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard.
IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended throughput to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/s. This specification under the marketing name of Wi-Fi has been implemented all over the world. The 802.11g protocol is now Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard, and Clause 19 of the published IEEE 802.11-2012 standard.
There are several uses of the 2.4 GHz band. Interference may occur between devices operating at 2.4 GHz. This article details the different users of the 2.4 GHz band, how they cause interference to other users and how they are prone to interference from other users.

Silicon Laboratories, Inc. is a fabless global technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductors, other silicon devices and software, which it sells to electronics design engineers and manufacturers in Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure, industrial automation, consumer and automotive markets worldwide.

Ubiquiti Inc. is an American technology company founded in San Jose, California, in 2003. Now based in New York City, Ubiquiti manufactures and sells wireless data communication and wired products for enterprises and homes under multiple brand names.
Digital Ocean, Inc., was a maker of wireless products from 1992 to 1998.
IEEE 802.11ah is a wireless networking protocol published in 2017 called Wi-Fi HaLow as an amendment of the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard. It uses 900 MHz license-exempt bands to provide extended range Wi-Fi networks, compared to conventional Wi-Fi networks operating in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. It also benefits from lower energy consumption, allowing the creation of large groups of stations or sensors that cooperate to share signals, supporting the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT). The protocol's low power consumption competes with Bluetooth and has the added benefit of higher data rates and wider coverage range.










