Antidepressants are medications used to treat major depressive disorder, some anxiety disorders, some chronic pain conditions, and to help manage some addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is a slight increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. A discontinuation syndrome can occur after stopping any antidepressant which resembles recurrent depression.
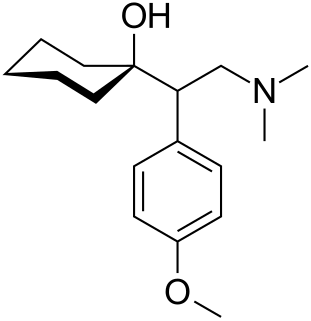
Escitalopram, sold under the brand names Cipralex and Lexapro, among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. Escitalopram is mainly used to treat major depressive disorder or generalized anxiety disorder. It is taken by mouth. It is available commercially exclusively as the oxalate salt.

Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant drugs that treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the more widely used selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act upon serotonin only.

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).

Dextromethorphan, often referred to as DXM, is a medication most often used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is a term used in clinical psychiatry to describe a condition that affects people with major depressive disorder (MDD) who do not respond adequately to a course of appropriate antidepressant medication within a certain time. Typical definitions of TRD vary, and they do not include a resistance to psychological therapies. Inadequate response has traditionally been defined as no clinical response whatsoever. However, many clinicians consider a response inadequate if the person does not achieve full remission of symptoms. People with treatment-resistant depression who do not adequately respond to antidepressant treatment are sometimes referred to as pseudoresistant. Some factors that contribute to inadequate treatment are: early discontinuation of treatment, insufficient dosage of medication, patient noncompliance, misdiagnosis, and concurrent psychiatric disorders. Cases of treatment-resistant depression may also be referred to by which medications people with TRD are resistant to. In TRD adding further treatments such as psychotherapy, lithium, or aripiprazole is weakly supported as of 2019.

Azelastine, sold under the brand name Optivar among others, is a medication primarily used as a nasal spray to treat allergic rhinitis and as eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis. Other uses may include asthma and skin rashes for which it is taken by mouth. Onset of effects is within minutes when used in the eyes and within an hour when used in the nose. Effects last for up to 12 hours.

Desvenlafaxine, sold under the brand name Pristiq among others, is a medication used to treat depression. It is recommended that the need for further treatment be occasionally reassessed. It may be less effective than its parent compound venlafaxine, although some studies have found comparable efficacy. It is an antidepressant of the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class and is taken by mouth.
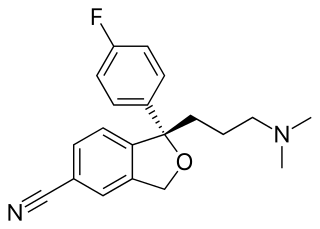
Esketamine, also known as (S)-ketamine or S(+)-ketamine, is the S(+) enantiomer of ketamine, is a dissociative hallucinogen medication used as a general anesthetic and as an antidepressant for treatment of depression. It is sold under the brand names Spravato and Ketanest, among others. Esketamine is the active enantiomer of ketamine in terms of NMDA receptor antagonism and is more potent than racemic ketamine.

Vilazodone, sold under the brand name Viibryd among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. While it was being studied for generalized anxiety disorder, such research had stopped as of 2017. It is taken by mouth.
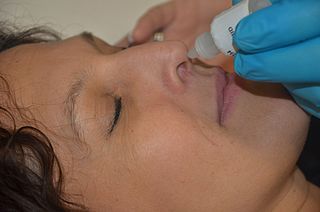
Nasal administration, popularly known as snorting, is a route of administration in which drugs are insufflated through the nose. It can be a form of either topical administration or systemic administration, as the drugs thus locally delivered can go on to have either purely local or systemic effects. Nasal sprays are locally acting drugs such as decongestants for cold and allergy treatment, whose systemic effects are usually minimal. Examples of systemically active drugs available as nasal sprays are migraine drugs, rescue medications for overdose and seizure emergencies, nicotine replacement, and hormone treatments. Recently, the nasal route has been proposed to direct drugs and antibodies directed against SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 to prevent viral loads and minimize neuroinvasion by the virus. The nasal route for Targeting other microbes as the " Brain-eating amoeba " has been also been hinted as the nasal cavity is the natural route of the Naegleria fowleri to the brain.

Vortioxetine, sold under the brand names Trintellix and Brintellix among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. Effectiveness is viewed as similar to that of other antidepressants. In the United Kingdom, it is only recommended in people who have not improved sufficiently on two other antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

Aticaprant is a selective antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) which was originally developed by Eli Lilly and is now under development by Janssen Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of major depressive disorder and smoking withdrawal.

Apimostinel is an antidepressant, acting as a selective partial agonist of an allosteric site of the glycine site of the NMDA receptor complex, which is under investigation by Naurex and Allergan for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). As of 2015, an intravenous formulation of apimostinel is in a phase II clinical trial for MDD, and an oral formulation is concurrently in phase I trials for MDD.
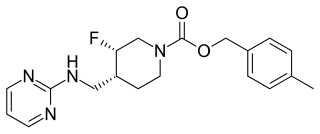
Rislenemdaz is an orally-active, selective NMDA receptor subunit 2B (NR2B) antagonist which is under development by Cerecor in the United States as an adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). In November 2013, phase II clinical trials were initiated, and in the same month, rislenemdaz received Fast Track Designation from the Food and Drug Administration for TRD.

4-Androstadienol, also known as 4,16-androstadien-3β-ol, is a pherine which is under development by VistaGen Therapeutics, Inc. in a nasal spray formulation (PRN) for the acute treatment of social anxiety disorder. It is also being investigated by VistaGen Therapeutics for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The pherine is a positional isomer of the endogenous pheromone androstadienol. As of 2020, it is in phase III clinical trials for social anxiety disorder.
Pherines, also known as vomeropherines, are odorless synthetic neuroactive steroids that engage nasal chemosensory receptors and induce dose-dependent and reversible pharmacological and behavioral effects. Pherines target human chemosensory receptors and possibly other receptors such as the GABAA receptor and influence central nervous system activity.

L-4-Chlorokynurenine is an orally active small molecule prodrug of 7-chlorokynurenic acid, a NMDA receptor antagonist. It was investigated as a potential rapid-acting antidepressant.

Synthetic oxytocin, sold under the brand name Pitocin among others, is a medication made from the peptide oxytocin. As a medication, it is used to cause contraction of the uterus to start labor, increase the speed of labor, and to stop bleeding following delivery. For this purpose, it is given by injection either into a muscle or into a vein.

















