
The National Defense Education Act (NDEA) was signed into law on September 2, 1958, providing funding to United States education institutions at all levels.

Debt consolidation is a form of debt refinancing that entails taking out one loan to pay off many others. This commonly refers to a personal finance process of individuals addressing high consumer debt, but occasionally it can also refer to a country's fiscal approach to consolidate corporate debt or government debt. The process can secure a lower overall interest rate to the entire debt load and provide the convenience of servicing only one loan or debt.

A student loan is a type of loan designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and the associated fees, such as tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses. It may differ from other types of loans in the fact that the interest rate may be substantially lower and the repayment schedule may be deferred while the student is still in school. It also differs in many countries in the strict laws regulating renegotiating and bankruptcy. This article highlights the differences of the student loan system in several major countries.
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is a form completed by current and prospective college students in the United States to determine their eligibility for student financial aid.
Student financial aid in the United States is funding that is available exclusively to students attending a post-secondary educational institution in the United States. This funding is used to assist in covering the many costs incurred in the pursuit of post-secondary education. Financial aid is available from federal and state governments, educational institutions, and private organizations. It can be awarded in the form of grants, loans, work-study, and scholarships. In order to apply for federal financial aid, students must first complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
A Federal Perkins Loan, or Perkins Loan, was a need-based student loan part of the Federal Direct Student Loan Program, offered by the U.S. Department of Education to assist American college students in funding their post-secondary education. The program was named after Carl D. Perkins, a former member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Kentucky.
A Stafford Loan was a student loan offered from the United States Department of Education to eligible students enrolled in accredited American institutions of higher education to help finance their education. The terms of the loans are described in Title IV of the Higher Education Act of 1965, which guarantees repayment to the lender if a student defaults. As of July 1, 2010, Stafford Loans are no longer being offered, having been replaced with the William D. Ford Federal Direct Student Loan Program.
The Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program was a system of private student loans which were subsidized and guaranteed by the United States federal government. The program issued loans from 1965 until it was ended in 2010. Similar loans are now provided under the Federal Direct Student Loan Program, which are federal loans issued directly by the United States Department of Education.
The William D. Ford Federal Direct Loan Program provides "low-interest loans for students and parents to help pay for the cost of a student's education after high school. The lender is the U.S. Department of Education ... rather than a bank or other financial institution." It is the largest single source of federal financial aid for students and their parents pursuing post-secondary education and for many it is the first financial obligation they incur, leaving them with debt to be paid over a period of time that can be a decade or more as the average student takes 19.4 years.
A private student loan is a financing option for higher education in the United States that can supplement, but should not replace, federal loans, such as Stafford loans, Perkins loans and PLUS loans. Private loans, which are heavily advertised, do not have the forbearance and deferral options available with federal loans. In contrast with federal subsidized loans, interest accrues while the student is in college, even if repayment does not begin until after graduation. While unsubsidized federal loans do have interest charges while the student is studying, private student loan rates are usually higher, sometimes much higher. Fees vary greatly, and legal cases have reported collection charges reaching 50% of amount of the loan. Since 2011, most private student loans are offered with zero fees, effectively rolling the fees into the interest rates.
Federal Student Aid (FSA), an office of the U.S. Department of Education, is the largest provider of student financial aid in the United States. Federal Student Aid provides student financial assistance in the form of grants, loans, and work-study funds. FSA is a Performance-Based Organization, and was the first PBO to be established in the US government.
Graduate PLUS is a type of federal student aid, in the form of student loans, which is available to graduate and professional students. Similar to the Parent PLUS loan for parents of dependent undergraduate students, the Graduate PLUS loan is an unsubsidized federally guaranteed education loan with no annual or aggregate limits. It has no grace period and it goes into repayment as soon as the funds are disbursed to the borrower. It has the same deferment and forbearance options as the federal Stafford loan program. As such, graduate and professional students can postpone repayment using in-school deferment while enrolled at least half-time in a degree or certificate program of study.
In the United States, the Federal Direct Student Loan Program (FDLP) includes consolidation loans that allow students to consolidate Stafford Loans, PLUS Loans, and Federal Perkins Loans into one single debt. This results in reduced monthly repayments and a longer term for the loan. Unlike the other loans, consolidation loans have a fixed interest rate for the life of the loan.
Government sponsored Student Loans in Canada was designed to help post-secondary students pay for their education in Canada. The federal government funds the Canada Student Loan Program (CSLP) and the provinces may fund their own programs or be integrated with the CSLP. In addition, Canadian banks offer commercial loans targeted for students in professional programs.
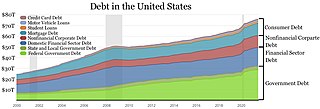
Student loans in the United States are a form of financial aid intended to help students access higher education. In 2018, 70 percent of higher education graduates had used loans to cover some or all of their expenses. With notable exceptions, student loans must be repaid, in contrast to other forms of financial aid such as scholarships, which are not repaid, and grants, which rarely have to be repaid. Student loans may be discharged through bankruptcy, but this is difficult.
Income-based repayment or income-driven repayment (IDR) is a student loan repayment program in the United States that regulates the amount that one needs to pay each month based on one's current income and family size.
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program is a United States government program that was created under the College Cost Reduction and Access Act of 2007 (CCRAA) to provide indebted professionals a way out of their federal student loan debt burden by working full-time in public service. The program permits Direct Loan borrowers who make 120 qualifying monthly payments under a qualifying repayment plan, while working full-time for a qualifying employer, to have the remainder of their balance forgiven. The earliest time in which borrowers could receive forgiveness under the program was after October 1, 2017. The Department of Education reported that 2,215 borrowers had the remainder of their respective student loans forgiven under the program as of April 30, 2020.

The Bipartisan Student Loan Certainty Act of 2013 was a bill signed into law by President Barack Obama on August 9, 2013, which, after more than a month of contentious debate between both parties about higher education and how the government should distribute loans, sets federal student loan rates to financial markets on all DIRECT student loans disbursed on or after July 1, 2013. There are maximum rate caps for Undergrad, Graduate PLUS and Parent PLUS loans. Democrats had originally planned to extend the low 3.4% rate for another 1–2 years but the bill, sponsored by Sen. Jack Reed (D-RI), was filibustered. Republicans in the House created a market-based approach, and the two sides eventually reconciled, after Sen. Joe Manchin (D-WV) and Sen. Angus King (I-ME) broke away from the Democratic Caucus to side up with the Republican bill, to prevent undesired gridlock.
Pay As You Earn (PAYE) is a federal student loan relief program signed into law on December 21, 2012, by President Barack Obama.
A repayment plan is a structured repaying of funds that have been loaned to an individual, business or government over either a standard or extended period of time, typically alongside a payment of interest. Repayment plans are prominent within the financial industry of a national economy where liquid funds are in high demand to assist in investment opportunities, governmental expenditure or personal finance. The term first saw prominence with its use by the International Monetary Fund to describe its form of financial loan repayment from individual nations. Typically, the term "repayment plan" refers to the system of Federal Student Aid in the United States of America, which assists in covering tertiary education expenses of domestic students.


