Related Research Articles
A flight surgeon is a military medical officer practicing in the clinical field of aviation medicine. Although the term "flight surgery" is considered improper by purists, it may occasionally be encountered.
A physician assistant (PA) is a type of mid-level health care provider. PAs may diagnose illnesses, develop and manage treatment plans, prescribe medications, and may serve as a principal healthcare provider. PAs are required in nearly all states to have a direct agreement with a physician for supervision and collaboration.

The U.S. Army Medical Command (MEDCOM) is a direct reporting unit of the U.S. Army that formerly provided command and control of the Army's fixed-facility medical, dental, and veterinary treatment facilities, providing preventive care, medical research and development and training institutions. On 1 October 2019, operational and administrative control of all military and veteran medical facilities transitioned to the Defense Health Agency.

A combat support hospital is a type of modern United States Army field hospital. The CSH is transportable by aircraft and trucks and is normally delivered to the Corps Support Area in standard military-owned demountable containers (MILVAN) cargo containers. Once transported, it is assembled by the staff into a tent hospital to treat patients. Depending upon the operational environment, a CSH might also treat civilians and wounded enemy soldiers. The CSH is the successor to the mobile army surgical hospital.

A field hospital is a temporary hospital or mobile medical unit that takes care of casualties on-site before they can be safely transported to more permanent facilities. This term was initially used in military medicine, but it is inherited to be used in disasters and other emergency situations.

The Combat Medic/Healthcare Specialist is responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at a point of wounding in a combat or training environment, as well as primary care, and health protection and evacuation from a point of injury or illness. Additionally, medics may also be responsible for the creation, oversight, and execution of long-term patient care plans in consultation with or in the absence of a readily available physician or advanced practice provider. Combat medics may be utilized in hospitals and clinics where they have the opportunity to work in additional roles such as operating medical and laboratory equipment, performing and assisting with procedures, and beyond.

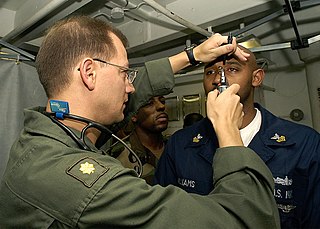
A hospital corpsman is an enlisted medical specialist of the United States Navy, who may also serve in a U.S. Marine Corps unit. The corresponding rating within the United States Coast Guard is health services technician (HS).

The Army Medical Department of the U.S. Army (AMEDD), formerly known as the Army Medical Service (AMS), encompasses the Army's six medical Special Branches. It was established as the "Army Hospital" in July of 1775 to coordinate the medical care required by the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War. The AMEDD is led by the Surgeon General of the U.S. Army, a lieutenant general.

The Medical Corps (MC) of the U.S. Army is a staff corps of the U.S. Army Medical Department (AMEDD) consisting of commissioned medical officers – physicians with either an M.D. or a D.O. degree, at least one year of post-graduate clinical training, and a state medical license.

The 67th Combat Support Hospital was the only forward deployed combat support hospital in Europe with both warfighter support and community service missions. Medical readiness was the primary concern for the unit. Located in the heart of the European theater, the 67th Combat Support Hospital stood ready to provide Echelon III health care around the globe.
In the United States Army and Marine Corps, a battalion aid station is a medical section within a battalion's support company. As such, it is the forwardmost medically staffed treatment location.

The Surgeon General of the United States Army is the senior-most officer of the U.S. Army Medical Department (AMEDD). By policy, the Surgeon General (TSG) serves as Commanding General, U.S. Army Medical Command (MEDCOM) as well as head of the AMEDD. The surgeon general's office and staff are known as the Office of the Surgeon General (OTSG) and are located in Falls Church, Virginia.

The Madigan Army Medical Center, located on Joint Base Lewis-McChord just outside Lakewood, Washington, is a key component of the Madigan Healthcare System and one of the largest military hospitals on the West Coast of the United States.

The 115th Field Hospital is a field hospital of the United States Army formed in 1917 and perpetuated until today. The hospital has participated in World War I, World War II, Desert Storm, Operation Iraqi Freedom and Operation Enduring Freedom (Afghanistan). As of March 2019, the 115th Combat Support Hospital reorganized and re-designated as a field hospital and is now a component unit of the 32d Hospital Center.

The structure of the United States Army is complex, and can be interpreted in several different ways: active/reserve, operational/administrative, and branches/functional areas.

The 28th Combat Support Hospital was a Combat Support Hospital of the United States Army. It was first constituted in 1943 and served in China during World War II. During the Gulf War in 1990, it was the first Army hospital unit established and deployed into Iraq with combat forces of the XVIII Airborne Corps. More recently it has been involved in relief operations following natural disasters and has undertaken several recent deployments to Iraq. The unit fell under the command of the 44th Medical Brigade and was based at Fort Bragg, North Carolina.

The 10th Field Hospital is a Field Hospital of the United States Army first constituted on 23 June 1942 in the Army of the United States as the 10th Field Hospital.
68W is the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) for the United States Army's Combat Medic. 68Ws are primarily responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at point of wounding on the battlefield, limited primary care, and health protection and evacuation from a point of injury or illness. This specialty is open to males and females with minimum line scores of 107 GT and 101 ST on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery.
In the United States Army, a medical brigade is a unit providing command and control for assigned or attached medical units at Corps level. One MED BDE is typically assigned to one Army Corps and a typical Headquarters and Headquarters Detachment (HHD) for a MED BDE consists of about 65 personnel.

The 14th Combat Support Hospital is a combat support hospital of the United States Army. It participated in World War II, the Korean War and, more recently, deployed to Afghanistan. Additionally, it was involved in the relief operations following Hurricane Katrina. The unit currently falls under the command of the 44th Medical Brigade and is based at Fort Benning, Ga and relocating to Fort Stewart, GA during FY 2020.
References
- Gillett, Mary C. (1995), The Army Medical Department, 1865-1917, Washington, DC: Center of Military History, United States Army. (Series: Army Historical Series)
- Hume, Edgar Erskine (1943), Victories of Army Medicine: Scientific Accomplishments of the Medical Department of the United States Army, Philadelphia: Lippincott.
- Tobey, James A. (1927), The Medical Department of the Army: Its History, Activities and Organization, Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press; Reprint: New York City: AMS Press, 1974.
- This article also contains information that originally came from US Government publications and websites and is in the public domain. The External links is where most information is resourced