
Cuitláhuac or Cuitláhuac was the 10th Huey Tlatoani (emperor) of the Aztec city of Tenochtitlan for 80 days during the year Two Flint (1520). He is credited with leading the resistance to the Spanish and Tlaxcalteca conquest of the Mexica Empire, following the death of his kinsman Moctezuma II.

Cuauhtémoc, also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler (tlatoani) of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, making him the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle", and is commonly rendered in English as "Descending Eagle", as in the moment when an eagle folds its wings and plummets down to strike its prey. This is a name that implies aggressiveness and determination.

Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca was a Spanish conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the king of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas.

Moctezuma I, also known as Moteuczomatzin Ilhuicamina, Huehuemoteuczoma or Montezuma I, was the second Aztec emperor and fifth king of Tenochtitlan. During his reign, the Aztec Empire was consolidated, major expansion was undertaken, and Tenochtitlan started becoming the dominant partner of the Aztec Triple Alliance. Often mistaken for his popular descendant, Moctezuma II, Moctezuma I greatly contributed to the famed Aztec Empire that thrived until Spanish arrival, and he ruled over a period of peace from 1440 to 1453. Moctezuma brought social, economical, and political reform to strengthen Aztec rule, and Tenochtitlan benefited from relations with other cities.

Motecuhzoma Xocoyotzin, referred to retroactively in European sources as Moctezuma II, was the ninth Emperor of the Aztec Empire, reigning from 1502 or 1503 to 1520. Through his marriage with Queen Tlapalizquixochtzin of Ecatepec, one of his two wives, he was also king consort of that altepetl.

Tenochtitlan, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican altepetl in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521.

Aztec mythology is the body or collection of myths of the Aztec civilization of Central Mexico. The Aztecs were Nahuatl-speaking groups living in central Mexico and much of their mythology is similar to that of other Mesoamerican cultures. According to legend, the various groups who were to become the Aztecs arrived from the north into the Anahuac valley around Lake Texcoco. The location of this valley and lake of destination is clear – it is the heart of modern Mexico City – but little can be known with certainty about the origin of the Aztec. There are different accounts of their origin. In the myth the ancestors of the Mexica/Aztec came from a place in the north called Aztlan, the last of seven nahuatlacas to make the journey southward, hence their name "Azteca." Other accounts cite their origin in Chicomoztoc, "the place of the seven caves", or at Tamoanchan.

The Aztecs were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (altepetl), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca, Texcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Aztec and Aztecs have long been the topic of scholarly discussion ever since German scientist Alexander von Humboldt established its common usage in the early 19th century.

Acamapichtli was the first Tlatoani, or king, of the Aztecs of Tenochtitlan, and founder of the Aztec imperial dynasty. Chronicles differ as to the dates of his reign: according to the Codex Chimalpahin, he reigned from 1367 to 1387; according to the Codex Aubin, he reigned from 1376 to 1395; and according to the Codex Chimalpopoca, he reigned from 1350 to 1403.

Jaguar warriors or jaguar knights, ocēlōtlNahuatl pronunciation:[oˈseːloːt͡ɬ] (singular) or ocēlōmeh (plural) were members of the Aztec military elite. They were a type of Aztec warrior called a cuāuhocēlōtl. They were an elite military unit similar to the eagle warriors.

Chimalpopoca or Chīmalpopōcatzin (1397–1427) was the third Emperor of Tenochtitlan (1417–1427).

Juan Velázquez Tlacotzin was an Aztec leader in Tenochtitlan, during the final decades of the Aztec Empire. He then was the first post-Spanish conquest indigenous ruler of Tenochtitlan from 1525 to 1526.

The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance was an alliance of three Nahua city-states: Mexico-Tenochtitlan, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan. These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish conquistadores and their native allies who ruled under Hernán Cortés defeated them in 1521.

The Aztec sun stone is a late post-classic Mexica sculpture housed in the National Anthropology Museum in Mexico City, and is perhaps the most famous work of Mexica sculpture. It measures 3.6 metres (12 ft) in diameter and 98 centimetres (39 in) thick, and weighs 24,590 kg (54,210 lb). Shortly after the Spanish conquest, the monolithic sculpture was buried in the Zócalo, the main square of Mexico City. It was rediscovered on 17 December 1790 during repairs on the Mexico City Cathedral. Following its rediscovery, the sun stone was mounted on an exterior wall of the cathedral, where it remained until 1885. Early scholars initially thought that the stone was carved in the 1470s, though modern research suggests that it was carved some time between 1502 and 1521.

The Aztec religion is a polytheistic and monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of teotl was construed as the supreme god Ometeotl, as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the Aztec Empire's state religion sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies.

Don Andrés de Tapia Motelchiuh Huitznahuatlailótlac, also known as Motelchiuhtzin, was the ruler of Tenochtitlan (1525–1530).

Don Luis de Santa María Nanacacipactzin, also known as Cipac, was the last tlatoani ("king") of the Nahua altepetl of Tenochtitlan, as well as its governor (gobernador) under the colonial Spanish system of government. The previous ruler Cristóbal de Guzmán Cecetzin having died in 1562, Nanacacipactzin was installed on September 30, 1563, and ruled until his death on December 27, 1565.
Martín Ocelotl was an Aztec indigenous priest (shaman) who was put on trial during New Spain’s Inquisition. He was ultimately banished to Spain.
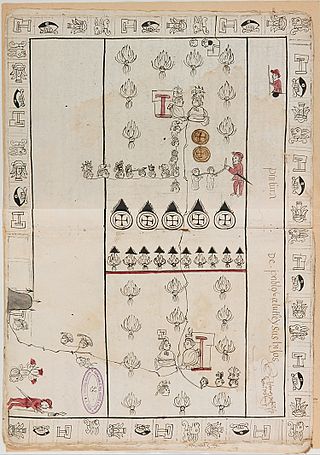
Pièce du Procès de Pablo Ocelotl et ses Fils is a colonial Mexican indigenous pictorial manuscript, originally used in a 1565 court case between the Matlatzinca Alonso González and the Nahua Pablo Ocelotl.

Atotoztli or Huitzilxochtzin was an Aztec princess and possible regent. She was a daughter of the Aztec emperor Moctezuma I and Chichimecacihuatzin I, the daughter of Cuauhtototzin, the ruler of Cuauhnahuac.



















