The PaleozoicEra is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 541 to 251.902 million years ago, and is subdivided into six geologic periods : the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian. The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era.

Rodinia was a Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.1–0.9 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. Valentine & Moores 1970 were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by McMenamin & McMenamin 1990 who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent.

The Proterozoic is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 541 million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon." It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided into three geologic eras : the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic, and Neoproterozoic.
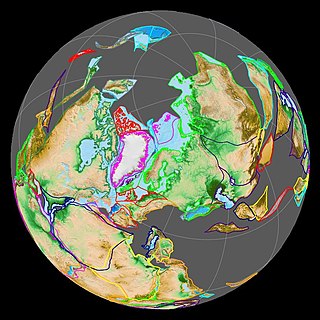
Laurasia, was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around 335 to 175 million years ago (Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana 215 to 175 Mya during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean c. 56 Mya. The name is a blend of Laurentia and Asia.

Pannotia, also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontinent that formed at the end of the Precambrian during the Pan-African orogeny, during the Cryogenian period and broke apart 560 Ma with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean, in the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian. Pannotia formed when Laurentia was located adjacent to the two major South American cratons, Amazonia and Río de la Plata. The opening of the Iapetus Ocean separated Laurentia from Baltica, Amazonia, and Río de la Plata.

Atlantica is an ancient continent that formed during the Proterozoic about 2,000 million years ago from various 2 Ga cratons located in what is now West Africa and eastern South America. The name, introduced by Rogers 1996, was chosen because the parts of the ancient continent are now located on opposite sides of the South Atlantic Ocean.
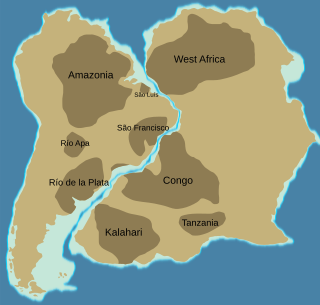
The Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago.

The supercontinent cycle is the quasi-periodic aggregation and dispersal of Earth's continental crust. There are varying opinions as to whether the amount of continental crust is increasing, decreasing, or staying about the same, but it is agreed that the Earth's crust is constantly being reconfigured. One complete supercontinent cycle is said to take 300 to 500 million years. Continental collision makes fewer and larger continents while rifting makes more and smaller continents.

Mirovia or Mirovoi was a hypothesized superocean which may have been a global ocean surrounding the supercontinent Rodinia in the Neoproterozoic Era, about 1 billion to 750 million years ago. Mirovia may be essentially identical to, or the precursor of, the hypothesized Pan-African Ocean, which followed the rifting of Rodinia. The Panthalassa (proto-Pacific) Ocean developed in the Neoproterozoic Era by subduction at the expense of the global Mirovia ocean.
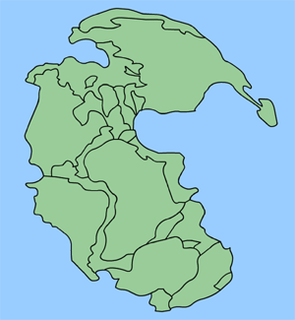
A superocean is an ocean that surrounds a supercontinent. It is less commonly defined as any ocean larger than the current Pacific Ocean. Named global superoceans include Mirovia, which surrounded the supercontinent Rodinia, and Panthalassa, which surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea. Pannotia and Columbia, along with landmasses before Columbia, were also surrounded by superoceans.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.

Pangaea or Pangea was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from earlier continental units approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 175 million years ago. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the Equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.
The West African Craton (WAC) is one of the five cratons of the Precambrian basement rock of Africa that make up the African Plate, the others being the Kalahari craton, Congo craton, Saharan Metacraton and Tanzania Craton. Cratons themselves are tectonically inactive, but can occur near active margins, with the WAC extending across 14 countries in Western African, coming together in the late Precambrian and early Palaeozoic eras to form the African continent. It consists of two Archean centers juxtaposed against multiple Paleoproterozoic domains made of greenstone belts, sedimentary basins, regional granitoid-tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG) plutons, and large shear zones. The craton is overlain by Neoproterozoic and younger sedimentary basins. The boundaries of the WAC are predominantly defined by a combination of geophysics and surface geology, with additional constraints by the geochemistry of the region. At one time, volcanic action around the rim of the craton may have contributed to a major global warming event.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.
The Pharusian Ocean is an ancient ocean that existed from 800 to 635 million years ago, between the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent and the start of formation of the Gondwana supercontinent.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.

The Terra Australis Orogen (TAO) was the oceanic southern margin of Gondwana which stretched from South America to Eastern Australia and encompassed South Africa, West Antarctica, New Zealand and Victoria Land in East Antarctica.
The geology of Central African Republic (CAR) is part of the broader geology of Africa. CAR occupies a swath of ancient rocks, dating back billions of years that record significant aspects of Earth history and yield minerals vital to the country's small economy.










