Rodinia was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). Valentine & Moores 1970 were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named "Pangaea I." It was renamed "Rodinia" by McMenamin & McMenamin 1990, who also were the first to produce a plate reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent.

Pannotia, also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontinent that formed at the end of the Precambrian during the Pan-African orogeny, during the Cryogenian period and broke apart 560 Ma with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean, in the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian. Pannotia formed when Laurentia was located adjacent to the two major South American cratons, Amazonia and Río de la Plata. The opening of the Iapetus Ocean separated Laurentia from Baltica, Amazonia, and Río de la Plata. A 2022 paper argues that Pannotia never fully existed, reinterpreting the geochronological evidence: "the supposed landmass had begun to break up well before it was fully assembled". However, the assembly of the next supercontinent Pangaea is well established.
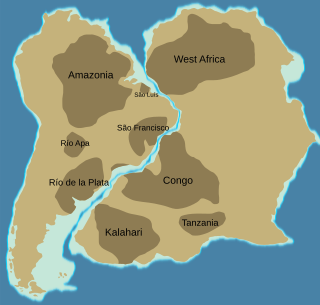
The Congo Craton, covered by the Palaeozoic-to-recent Congo Basin, is an ancient Precambrian craton that with four others makes up the modern continent of Africa. These cratons were formed between about 3.6 and 2.0 billion years ago and have been tectonically stable since that time. All of these cratons are bounded by younger fold belts formed between 2.0 billion and 300 million years ago.

The Rio de la Plata Craton (RPC) is a medium-sized continental block found in Uruguay, eastern Argentina and southern Brazil. During its complex and protracted history it interacted with a series other blocks and is therefore considered important for the understanding of the amalgamation of West Gondwana. Two orogenic cycles have been identified in the RPC: a 2000 Ma-old western domain representing the old craton and a 700–500 Ma-old eastern domain assigned to the Brasiliano Cycle. It is one of the five cratons of the South American continent. The other four cratons are: Amazonia, São Francisco, Río Apa and Arequipa–Antofalla.

Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and the Hebridean Terrane in northwest Scotland. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of early Proterozoic orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today.
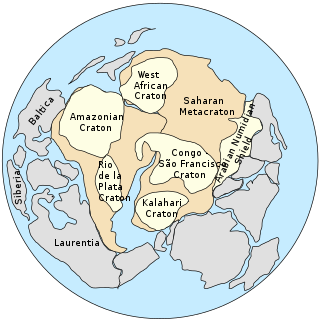
The Saharan Metacraton is a large area of continental crust in the north-central part of Africa. Whereas a craton is an old and stable part of the lithosphere, the term "metacraton" is used to describe a craton that has been remobilized during an orogenic event, but where the characteristics of the original craton are still identifiable. The geology of the continent has only been partially explored, and other names have been used to describe the general area that reflect different views of its nature and extent. These include "Nile Craton", "Sahara Congo Craton", "Eastern Saharan Craton" and "Central Saharan Ghost Craton". This last term is because the older rocks are almost completely covered by recent sediments and desert sands, making geological analysis difficult.

The Tuareg Shield is a geological formation lying between the West African craton and the Saharan Metacraton in West Africa. Named after the Tuareg people, it has complex a geology, reflecting the collision between these cratons and later events. The landmass covers parts of Algeria, Niger and Mali.
The Pharusian Ocean is an ancient ocean that existed on Earth from 800 to 635 million years ago, between the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent and the start of formation of the Pannotia supercontinent.

The Mozambique Belt is a band in the Earth's crust that extends from East Antarctica through East Africa up to the Arabian-Nubian Shield. It formed as a suture between plates during the Pan-African orogeny, when Gondwana was formed.
The Mwembeshi Shear Zone is a ductile shear zone about 550 million years old that extends ENE-WSW across Zambia. In Zambia, it separates the Lufilian Belt to the northwest from the Zambezi Belt to the southeast. It is associated with a sinistral strike slip movement.

The Lufilian Arc is part of a system of orogenic belts in southern Africa formed during the Pan-African orogeny, a stage in the formation of the Gondwana supercontinent. It extends across eastern Angola, the Katanga Province of the southern Democratic Republic of the Congo and the northwest of Zambia. The arc is about 800 kilometres (500 mi) long. It has global economic importance owing to its rich deposits of copper and cobalt.
The Kibaran orogeny is a term that has been used for a series of orogenic events, in what is now Africa, that began in the Mesoproterozoic, around 1400 Ma and continued until around 1000 Ma when the supercontinent Rodinia was assembled. The term "Kibaran" has often been used for any orogenic rocks formed during this very extended period. Recently, it has been proposed that the term should be used in a much narrower sense for an event around 1375 Ma and a region in the southeast of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
The Zambezi Belt is an area of orogenic deformation in southern Zambia and northern Zimbabwe. It is a segment of a broader belt lying between the Congo Craton and the Kalahari Craton, which also includes the Lufilian Arc and the Damaran Belt. The eastern margin of the belt interacts with the north-south Eastern African orogen.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.
The Damara orogeny was part of the Pan-African orogeny. The Damara orogeny occurred late in the creation of Gondwana, at the intersection of the Congo and the Kalahari cratons.

Brasiliano orogeny or Brasiliano cycle refers to a series of orogenies from the Neoproterozoic era, exposed chiefly in Brazil but also in other parts of South America. The Brasiliano orogeny is a regional name for the larger Pan-African/Brasiliano orogeny that extended not only in South America but across most of Gondwana. In a wide sense the Brasiliano orogeny includes also the Pampean orogeny. Almeida et al. coined the term Brasiliano Orogenic Cycle in 1973. The orogeny led to the closure of several oceans and aulacogens including the Adamastor Ocean, the Goianides Ocean, the Puncoviscana Ocean and the Peri-Franciscano Ocean.
The Adamastor Ocean was a "proto-Atlantic" ocean that formed with the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent c. 780–750 Ma. It separated the Río de la Plata Craton from the Congo Craton. The inversion of the Adamastor Ocean began about 640 Ma with the development of a large back-arc basin along the western margin of the Kalahari Craton, and the ocean closed when Río de la Plata collided with Kalahari about 545 Ma along the sinistral Sierra Ballena Shear Zone. The São Francisco Craton and the Río de la Plata Craton amalgamated 630–620 Ma, closing the Adamastor Ocean on the South American side and forming the Mantiqueira Mountains around 600 Ma.

The Aravalli Mountain Range is a northeast-southwest trending orogenic belt in the northwest part of India and is part of the Indian Shield that was formed from a series of cratonic collisions. The Aravalli Mountains consist of the Aravalli and Delhi fold belts, and are collectively known as the Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt. The whole mountain range is about 700 km long. Unlike the much younger Himalayan section nearby, the Aravalli Mountains are believed much older and can be traced back to the Proterozoic Eon. They are arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth. The collision between the Bundelkhand craton and the Marwar craton is believed to be the primary mechanism for the development of the mountain range.

The Owambo Basin is a sedimentary basin located on the Congo Craton in Southern Africa that extends from southern Angola into Namibia and includes the Etosha Pan. It is bound on the southern and western sides by the Damara Belt in Northern Namibia, and by the Cubango River to the East. The northern boundary is scientifically disputed, but is currently mapped by most stratigraphers to include southern Angola with the boundary set at the Kunene River. The Owambo Basin is host to two famous regions: Tsumeb, a major Namibian city and site of a formerly active copper mine with exceptional mineralogical variability producing museum quality rare specimens, and Etosha National Park, the largest protected wildlife sanctuary in Namibia centered around Etosha Pan.











