
The geography of Mozambique consists mostly of coastal lowlands with uplands in its center and high plateaus in the northwest. There are also mountains in the western portion. The country is located on the east coast of southern Africa, directly west of the island of Madagascar. Mozambique has a tropical climate with two seasons, a wet season from October to March and a dry season from April to September.
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by WWF, the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". So, for example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.

The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.

The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The Eastern Highlands extend north and south for about 300 kilometres (190 mi) through Zimbabwe's Manicaland Province and Mozambique's Manica Province.

Chipinge District is a district in Manicaland Province of Zimbabwe. The administrative headquarters is Chipinge.
The Udzungwa Mountains are a mountain range in south-central Tanzania. The mountains are mostly within Iringa Region, south of Tanzania's capital Dodoma. The Udzungwa Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains, and are home to a biodiverse community of flora and fauna with large numbers of endemic species.
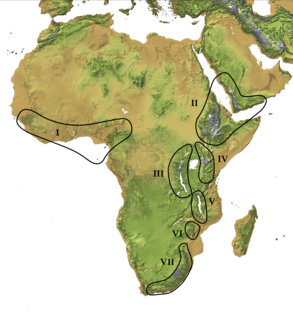
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

The South Malawi montane forest-grassland mosaic is an ecoregion of Malawi.
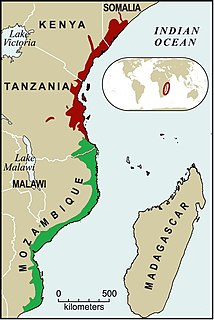
The Southern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic, also known as the Southern Swahili coastal forests and woodlands, is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. It is a southern variation of Northern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic. The ecoregion supports habitats of forest, savanna and swamps. The southern portion of the ecoregion is not as well studied due to the 1977-1992 civil war in Mozambique.
The Southern Highlands is a highland region in southwestern Tanzania, at the northern end of Lake Malawi. The highlands include portions of Mbeya, Njombe, Rukwa, Ruvuma, and Songwe regions, bordering Malawi, Mozambique, and Zambia. Mbeya is the largest city in the highlands.

The Zambezian and mopane woodlands is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of southeastern Africa.

The Eastern Arc forests is a montane tropical moist forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. The ecoregion comprises several separate highland areas above 800 meters in Kenya, and (mostly) Tanzania.

The Chimanimani Mountains are a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The mountains are in the southern portion of the Eastern Highlands, or Manica Highlands, a belt of highlands that extend north and south along the international border, between the Zambezi and Save rivers.

Mount Morrumbala, also known as Mount Tembe, is a mountain in Morrumbala District of Zambezia Province in central Mozambique.

The Cheringoma Plateau is a low plateau in Sofala Province of Mozambique. It lies mostly within Cheringoma, Muanza, and Marromeu districts.

The Umalila Mountains are a mountain range in southern Tanzania, on the border with Malawi. The Umalila Mountains are part of Tanzania's Southern Highlands.

The Rubeho Mountains are a mountain range in central Tanzania. The mountains in Dodoma and Morogoro regions, southeast of Tanzania's capital Dodoma. The Rubeho Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains, and are home to a biodiverse community of flora and fauna with large numbers of endemic species.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.

The Ukaguru Mountains are a mountain range in central Tanzania. The mountains are in Morogoro region, east of Tanzania's capital Dodoma. The mountains are named for the Kaguru people. The Ukaguru Mountains are part of the Eastern Arc Mountains, and are home to a biodiverse community of flora and fauna with large numbers of endemic species.















