
South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian (eastern) coast. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

KwaZulu-Natal is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the government merged the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu and Natal Province.

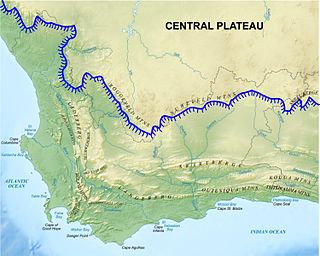
The Drakensberg is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – 2,000 to 3,482 metres within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho.

Veld, also spelled veldt, is a type of wide open rural landscape in Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe and Botswana. A certain sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa has been officially defined as the Bushveld by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Trees are not abundant—frost, fire and grazing animals allow grass to grow, but prevent the build-up of dense foliage.

The Karoo is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its extent is also not precisely defined. The Karoo is partly defined by its topography, geology and climate, and above all, its low rainfall, arid air, cloudless skies, and extremes of heat and cold. The Karoo also hosted a well-preserved ecosystem hundreds of million years ago which is now represented by many fossils.

The Highveld is the portion of the South African inland plateau which has an altitude above roughly 1,500 m (4,900 ft), but below 2,100 m (6,900 ft), thus excluding the Lesotho mountain regions to the south-east of the Highveld. It is home to some of the country's most important commercial farming areas, as well as its largest concentration of metropolitan centres, especially the Gauteng conurbation, which accommodates one-third of South Africa's population.
Mont-aux-Sources is a mountain in Southern Africa, forming one of the highest portions of the Drakensberg Range. It is mostly within Lesotho, with parts in the KwaZulu-Natal and Free State provinces of South Africa.

Sani Pass is a mountain pass located in the West of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa on the road between Himeville, KwaZulu-Natal and Mokhotlong, Lesotho. The pass traverses the Great Escarpment of southern Africa in its highest region, the Drakensberg Mountains, which reach an elevation of over 3,000 meters.

The Karoo National Park is a wildlife reserve in the Great Karoo area of the Western Cape, South Africa near Beaufort West. This semi-desert area covers an area of 750 square kilometres (290 sq mi). The Nuweveld portion of the Great Escarpment runs through the Park. It is therefore partly in the Lower Karoo, at about 850 m above sea level, and partly in the Upper Karoo at over 1300 m altitude.

The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a period of about 120 million years.
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mountains near Bahía Blanca in Argentina, the Pensacola Mountains, the Ellsworth Mountains and the Hunter-Bowen orogeny in eastern Australia. The rocks involved are generally sandstones and shales, with the shales persisting in the valley floors while the erosion resistant sandstones form the parallel ranges, the Cape Fold Mountains, which reach a maximum height of 2325 m at Seweweekspoortpiek.

Table Mountain Sandstone (TMS) is a group of rock formations within the Cape Supergroup sequence of rocks. Although the term "Table Mountain Sandstone" is still widely used in common parlance, the term TMS is no longer formally recognized; the correct name is the "Peninsula Formation Sandstone", which is part of the Table Mountain Group. The designation "Table Mountain Sandstone" will, however, in deference to the title, continue to be used in the rest of this article. The name is derived from the famous landmark in Cape Town, Table Mountain.

The Stormberg Group is one of the four geological groups that comprises the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. It is the uppermost geological group representing the final phase of preserved sedimentation of the Karoo Basin. The Stormberg Group rocks are considered to range between Lower Triassic (Olenekian) to Lower Jurassic (Pliensbachian) in age. These estimates are based on means of geological dating including stratigraphic position, lithostratigraphic and biostratigraphic correlations, and palynological analyses.

Matatiele Municipality is a local municipality within the Alfred Nzo District Municipality, in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It adjoins Lesotho to the north, Elundini to the south-west, and Greater Kokstad to the east and its 4,352 km² makes the Matatiele Municipality largest of four municipalities in the district at almost half of its geographical area. According to the South African National Census of 2011, its 203,483 residents and 49,527 households makes Matatiele Municipality the second largest populated area in the Alfred Nzo District Municipality behind Mbizana.

The geology of South Africa is highly varied including cratons, greenstone belts, large impact craters as well as orogenic belts. The geology of the country is the base for a large mining sector that extracts gold, diamonds, iron and coal from world-class deposits. The geomorphology of South Africa consists of a high plateau rimmed to west, south and southeast by the Great Escarpment, and the rugged mountains of the Cape Fold Belt. Beyond this there is strip of narrow coastal plain.

The Lesotho Highlands are formed by the Drakensberg and Maloti mountain ranges in the east and central parts of the country of Lesotho. Foothills form a divide between the lowlands and the highlands. Snow is common in the highlands in the winter.
The geology of Lesotho is built on ancient crystalline basement rock up to 3.6 billion years old, belonging to the Kaapvaal Craton, a section of stable primordial crust. Most of the rocks in the country are sedimentary or volcanic units, belonging to the Karoo Supergroup. The country is notable for large fossil deposits and intense erosion due to high rainfall and a rare case of southern African glaciation during the last ice age. Lesotho has extensive diamonds and other natural resources and has the highest concentration of kimberlite pipes anywhere in the world.

The Drakensberg Group is a geological group named after the Drakensberg mountain range where in its uppermost sections the rocks are found. The Drakensberg Group lies over most of Lesotho and localities in the Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal, and Free State provinces of South Africa. It forms part of the greater Karoo Igneous Province, which occurs over an extensive area of southern Africa.
Cleft Peak is a mountain peak in the Drakensberg in KwaZulu-Natal. It forms part of an escarpment of the Drakensberg on the border between South Africa and Lesotho. Cleft Peak is the second-highest peak in the northern part of the region, after Mont-aux-Sources, several meters higher.



















