
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. It was first deployed in Finland in December 1991. By the mid-2010s, it became a global standard for mobile communications achieving over 90% market share, and operating in over 193 countries and territories.
Amstrad was a British electronics company, founded in 1968 by Alan Sugar at the age of 21. The name is a contraction of Alan Michael Sugar Trading. It was first listed on the London Stock Exchange in April 1980. During the late 1980s, Amstrad had a substantial share of the PC market in the UK. Amstrad was once a FTSE 100 Index constituent, but since 2007 has been wholly owned by Sky UK. As of 2006, Amstrad's main business was manufacturing Sky UK interactive boxes. In 2010, Sky integrated Amstrad's satellite division as part of Sky so they could make their own set-top boxes in-house.

Citizens band radio, used in many countries, is a land mobile radio system, a system allowing short-distance person-to-many persons bidirectional voice communication among individuals, using two way radios operating on 40 channels near 27 MHz (11 m) in the high frequency band. Citizens band is distinct from other personal radio service allocations such as FRS, GMRS, MURS, UHF CB and the Amateur Radio Service. In many countries, CB operation does not require a license, and it may be used for business or personal communications. Like many other land mobile radio services, multiple radios in a local area share a single frequency channel, but only one can transmit at a time. The radio is normally in receive mode to receive transmissions of other radios on the channel; when users want to talk they press a "push to talk" button on their radio, which turns on their transmitter. Users on a channel must take turns talking. Transmitter power is limited to 4 watts in the US and the EU. CB radios have a range of about 3 miles (4.8 km) to 20 miles (32 km) depending on terrain, for line of sight communication; however, various radio propagation conditions may intermittently allow communication over much greater distances.

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications.
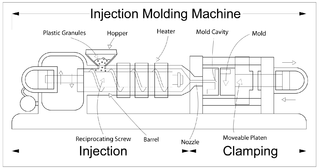
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers that do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

A walkie-talkie, more formally known as a handheld transceiver (HT), is a hand-held, portable, two-way radio transceiver. Its development during the Second World War has been variously credited to Donald Hings, radio engineer Alfred J. Gross, Henryk Magnuski and engineering teams at Motorola. First used for infantry, similar designs were created for field artillery and tank units, and after the war, walkie-talkies spread to public safety and eventually commercial and jobsite work.

Kyocera Corporation is a Japanese multinational ceramics and electronics manufacturer headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It was founded as Kyoto Ceramic Company, Limited in 1959 by Kazuo Inamori and renamed in 1982. It manufactures industrial ceramics, solar power generating systems, telecommunications equipment, office document imaging equipment, electronic components, semiconductor packages, cutting tools, and components for medical and dental implant systems.

Yaesu, founded as Yaesu Musen Co., Ltd. in 1959 by a Japanese radio amateur Sako Hasegawa with call sign JA1MP in the Tokyo neighborhood of Yaesu, is a Japanese brand of commercial and amateur radio equipment.
Sepura Limited is a British telecommunications equipment provider that designs, manufactures and supplies digital mobile radio products, systems and applications for business and critical communications. The company specialises in Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA) technology.
VTech is a global supplier of electronic learning products from infancy to preschool.

GSM-R, Global System for Mobile Communications – Railway or GSM-Railway is an international wireless communications standard for railway communication and applications.

Arburg GmbH + Co KG is a German machine manufacturing company. It is owned by the Hehl and Keinath families and, with its electric, hybrid and hydraulic plastic injection moulding machines, turnkey systems and its industrial additive manufacturing system, is among the industry leaders worldwide. With approximately 2,500 employees in Germany and a further 500 worldwide, Arburg serves sales markets for machines with clamping forces ranging from 125 to 6,500 kN.

A wireless microphone, or cordless microphone, is a microphone without a physical cable connecting it directly to the sound recording or amplifying equipment with which it is associated. Also known as a radio microphone, it has a small, battery-powered radio transmitter in the microphone body, which transmits the audio signal from the microphone by radio waves to a nearby receiver unit, which recovers the audio. The other audio equipment is connected to the receiver unit by cable. In one type the transmitter is contained within the handheld microphone body. In another type the transmitter is contained within a separate unit called a "bodypack", usually clipped to the user's belt or concealed under their clothes. The bodypack is connected by wire to a "lavalier microphone" or "lav", a headset or earset microphone, or another wired microphone. Most bodypack designs also support a wired instrument connection. Wireless microphones are widely used in the entertainment industry, television broadcasting, and public speaking to allow public speakers, interviewers, performers, and entertainers to move about freely while using a microphone without requiring a cable attached to the microphone.
In-mould labelling is the use of paper or plastic labels during the manufacturing of containers by blow molding, injection molding, or thermoforming processes. The label serves as the integral part of the final product, which is then delivered as pre-decorated item. Combining the decoration process with the moulding process cuts the total cost, but can increase the manufacturing time. The technology was first developed by Owens-Illinois in cooperation with Procter & Gamble to supply pre-labelled bottles that could be filled on the product filling line. This was first applied to Head & Shoulders shampoo bottles.
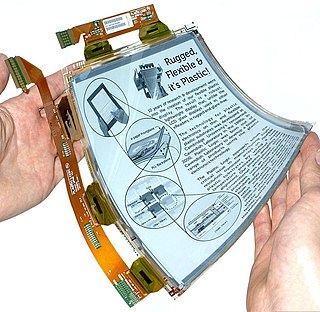
Plastic Logic Germany develops and manufactures electrophoretic displays (EPD), based on organic thin-film transistor (OTFT) technology, in Dresden, Germany.
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. is a manufacturer of electric wire and optical fiber cables. Its headquarters are in Chūō-ku, Osaka, Japan. The company's shares are listed in the first section of the Tokyo, Nagoya Stock Exchanges, and the Fukuoka Stock Exchange. In the period ending March 2021, the company reported consolidated sales of US$26,5 billion.

Chen Hsong Holdings Limited is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic injection moulding equipment and systems. The company was established by Dr. Chiang Chen in a small village workshop in Hong Kong in 1958. The following half-century has been a period of growth and expansion both locally and internationally. Today Chen Hsong has a customer base covering more than 80 countries worldwide including China, Taiwan, the United States, Canada, France, the United Kingdom, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico and most Southeast Asian countries.
Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co KG is an international electronics group specializing in the fields of electronic test equipment, broadcast & media, cybersecurity, radiomonitoring and radiolocation, and radiocommunication. The company provides products for the wireless communications, broadcast & media, cybersecurity and electronics industry, aerospace and defense, homeland security and critical infrastructures.
Huawei SingleRAN is a radio access network (RAN) technology offered by Huawei that allows mobile telecommunications operators to support multiple mobile communications standards and wireless telephone services on a single network. The technology incorporates a software-defined radio device, and is designed with a consolidated set of hardware components, allowing operators to purchase, operate and maintain a single telecommunications network and set of equipment, while supporting multiple mobile communications standards.
Sidel is a manufacturing company providing equipment and services for packaging liquids such as water; carbonated and non-carbonated soft drinks; sensitive beverages such as milk, liquid dairy products, juices, tea, coffee, isotonics and beer; food and home and personal care.











