Overview
The standard, codified by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN, German Institute for Standardization), is DIN 40430. Panzergewinde sizes are named with the prefix PG plus a nominal number which approximately corresponds to the maximum cable diameter (in millimeters) that can be passed through the conduit.
Because the walls of the conduit are usually relatively thin, the thread depth is limited. Thus a thread angle of 80° is used. The Verband der Elektrotechnik, Elektronik und Informationstechnik (VDE) (which began as a trade association for standardization in electrical engineering) originally standardized (and named) the thread for use with conduit and cable glands that were made of steel, although today the thread is used with both steel (typically plated with combinations of nickel, zinc, or tin to resist rusting) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Beginning in 2000, the VDE standard for cable glands (VDE 0619) was formally replaced by EN 50262. After a transitional period of several years during which it could still be used, it was replaced in 2003 by a final metric fine thread with 1.5 mm (0.0591 in) pitch. Similarly, conduit threads were replaced by EN 60423.
Even today, Panzergewinde cable glands are still often found on chemical reactors and bioreactors (for example, PG13.5 thread for screwing in sensors) and various other equipment, enclosures, junction boxes, and connectors.

British Standards (BS) are the standards produced by the BSI Group which is incorporated under a royal charter. The BSI Group produces British Standards under the authority of the charter, which lays down as one of the BSI's objectives to:
Set up standards of quality for goods and services, and prepare and promote the general adoption of British Standards and schedules in connection therewith and from time to time to revise, alter and amend such standards and schedules as experience and circumstances require.
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardization can help maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality. It can also facilitate commoditization of formerly custom processes. In social sciences, including economics, the idea of standardization is close to the solution for a coordination problem, a situation in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by making mutually consistent decisions. Standardization is creating emotional balance, conventional detail, a universal familiarity and natural definition to a concept based on physical or emotional comfort and acceptance by changing societal behaviors and developments.

A 19-inch rack is a standardized frame or enclosure for mounting multiple electronic equipment modules. Each module has a front panel that is 19 inches (482.6 mm) wide. The 19 inch dimension includes the edges or "ears" that protrude from each side of the equipment, allowing the module to be fastened to the rack frame with screws. Common uses include computer servers, telecommunications equipment and networking hardware, audiovisual production gear, and scientific equipment.

American National Standard Pipe Thread standards, often called national pipe thread (NPT) standards for short, are U.S. national technical standards for screw threads used on threaded pipes and pipe fittings. They include both tapered and straight thread series for various purposes including rigidity, pressure-tight sealing, or both. The various types are each named with a symbol and a full name; examples of the symbols include NPT, NPS, NPTF, NPSC, and others.

A washer is a thin plate with a hole that is normally used to distribute the load of a threaded fastener, such as a bolt or nut. Other uses are as a spacer, spring, wear pad, preload indicating device, locking device, and to reduce vibration. Washers often have an outer diameter (OD) about twice their inner diameter (ID), but this can vary quite widely.

Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.

A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener.
The VDE e. V. is one of Europe’s largest technical-scientific associations with 36,000 members, including 1,300 corporate and institutional members and 8,000 students.
British Standard Whitworth (BSW) is an imperial-unit-based screw thread standard, devised and specified by Joseph Whitworth in 1841 and later adopted as a British Standard. It was the world's first national screw thread standard, and is the basis for many other standards, such as BSF, BSP, BSCon, and BSCopper.
British Standard Pipe (BSP) is a set of technical standards for screw threads that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting and sealing pipes and fittings by mating an external (male) thread with an internal (female) thread. It has been adopted as standard in plumbing and pipe fitting, except in North America, where NPT and related threads are used.

A bayonet mount or bayonet connector is a fastening mechanism consisting of a cylindrical male side with one or more radial pins, and a female receptor with matching L-shaped slot(s) and with spring(s) to keep the two parts locked together. The slots are shaped like a capital letter L with serif ; the pin slides into the vertical arm of the L, rotates across the horizontal arm, then is pushed slightly upwards into the short vertical "serif" by the spring; the connector is no longer free to rotate unless pushed down against the spring until the pin is out of the "serif".
The ISO metric screw thread is the most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread worldwide. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was set up in 1947.

Edison screw (ES) is a standard lightbulb socket for electric light bulbs. It was developed by Thomas Edison, patented in 1881, and was licensed in 1909 under General Electric's Mazda trademark. The bulbs have right-hand threaded metal bases (caps) which screw into matching threaded sockets. For bulbs powered by AC current, the thread is generally connected to neutral and the contact on the bottom tip of the base is connected to the "live" phase.

A screw and a bolt are similar types of fastener typically made of metal, and characterized by a helical ridge, known as a male thread. Screws and bolts are used to fasten materials by the engagement of the screw thread with a similar female thread in the matching part.

Strut channel, often referred to colloquially by one of several manufacturer trade names, is a standardized formed structural system used in the construction and electrical industries for light structural support, often for supporting wiring, plumbing, or mechanical components such as air conditioning or ventilation systems.
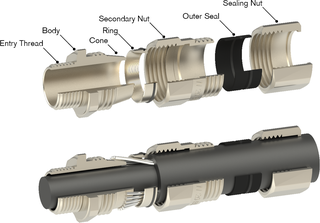
A cable gland is a device designed to attach and secure the end of an electrical cable to the equipment. A cable gland provides strain-relief and connects by a means suitable for the type and description of cable for which it is designed—including provision for making electrical connection to the armour or braid and lead or aluminium sheath of the cable, if any. Cable glands may also be used for sealing cables passing through bulkheads or gland plates. Cable glands are mostly used for cables with diameters between 1 mm and 75 mm.
Knuckle threads or round threads are an unusual highly rounded thread form. The large space between the rounded crests and roots provides space for debris to be shifted to not interfere with the thread, making this form resistant to debris and thread damage.

An electrical conduit is a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical conduit may be made of metal, plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid, but flexible conduit is used for some purposes.
The Löwenherz thread is a largely obsolete metric thread form designed in the late nineteenth century and frequently applied in precision instruments. It is named after Dr. Leopold Löwenherz, who was the director of the metrology institute Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt in Berlin.













