
Nicaragua is a country in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Costa Rica and Honduras. Nicaragua is the largest country in Central America in square kilometers.

The term "United States," when used in the geographical sense, refers to the contiguous United States, the state of Alaska, the island state of Hawaii, the five insular territories of Puerto Rico, Northern Mariana Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam, and American Samoa, and minor outlying possessions. The United States shares land borders with Canada and Mexico and maritime borders with Russia, Cuba, The Bahamas, and many other countries, mainly in the Caribbeanin addition to Canada and Mexico. The northern border of the United States with Canada is the world's longest bi-national land border.

A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest, is a generally tropical or subtropical, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud cover, usually at the canopy level, formally described in the International Cloud Atlas (2017) as silvagenitus. Cloud forests often exhibit an abundance of mosses covering the ground and vegetation, in which case they are also referred to as mossy forests. Mossy forests usually develop on the saddles of mountains, where moisture introduced by settling clouds is more effectively retained.
The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.
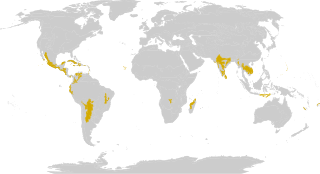
The tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest is a habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature and is located at tropical and subtropical latitudes. Though these forests occur in climates that are warm year-round, and may receive several hundred centimeters of rain per year, they have long dry seasons that last several months and vary with geographic location. These seasonal droughts have great impact on all living things in the forest.

The Sonoran Desert is a desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States. It is the hottest desert in both Mexico and the United States. It has an area of 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi).

The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
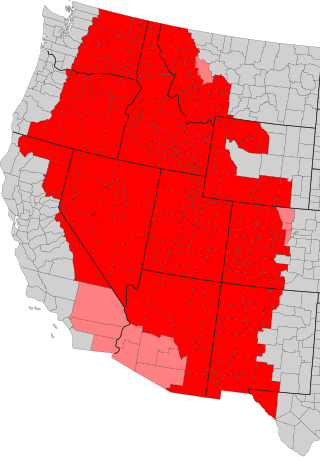
The Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the Rocky Mountain Front on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the west.

Bayaluseeme or Bayalu Seeme is the area lying to the east of Malenadu, a region of Karnataka state in India. The area is largely open plain, with few hillocks. It includes the districts of Bangalore, Bagalkot, Bijapur, Chitradurga, Davanagere, Dharwad, Gadag, Hassan, Haveri, Mandya, Mysore, and Tumkur.

The Alto Paraná Atlantic forests, also known as the Paraná-Paraíba interior forests, is an ecoregion of the tropical moist forests biome, and the South American Atlantic Forest biome. It is located in southern Brazil, northeastern Argentina, and eastern Paraguay.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine–oak forests is a tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion in Southern Mexico.
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

The Central Mexican matorral is an ecoregion of the deserts and xeric shrublands biome of central Mexico. It is the southernmost ecoregion of the Nearctic realm.

The Sierra Madre del Sur pine–oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion in the Sierra Madre del Sur mountain range of southern Mexico.

Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply.
The Sierra de Tamaulipas is an isolated, semi-tropical mountain range in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas. Its highest point is 1,260 m (4,130 ft). There are no cities or towns in the Sierra and the small population is largely agricultural. The higher elevations of the Sierra have forests of oak and pine, contrasting with the semi-arid brush that dominates at lower altitudes. Several archaeological sites establish that the Sierra de Tamaulipas was the northern outpost of the agricultural Mesoamerican peoples of eastern Mexico.

The Jalisco dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in southwestern Mexico.

The Southern Pacific dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico.

The Yucatán dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico. It includes the dry forests of the northwestern Yucatán Peninsula.

















