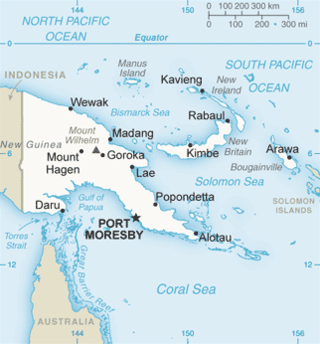
The geography of Papua New Guinea describes the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, the islands of New Ireland, New Britain and Bougainville, and smaller nearby islands. Together these make up the nation of Papua New Guinea in tropical Oceania, located in the western edge of the Pacific Ocean.

Solomon Islands is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, that lies east of Papua New Guinea.
Northern Province or North Province may refer to:

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.

A biogeographic realm is the broadest biogeographic division of Earth's land surface, based on distributional patterns of terrestrial organisms. They are subdivided into bioregions, which are further subdivided into ecoregions. A biogeographic realm is also known as "ecozone", although that term may also refer to ecoregions.

The Australasian realm is a biogeographic realm that is coincident with, but not the same as, the geographical region of Australasia. The realm includes Australia, the island of New Guinea, and the eastern part of the Indonesian archipelago, including the island of Sulawesi, the Moluccas, and the islands of Lombok, Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, and Timor, often known as the Lesser Sundas.

Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania.

Solomon Islands is a country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Papua New Guinea to the northwest, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna and Tuvalu to the east, Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 29,000 square kilometres, and a population of approximately 700,000. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands.

Malesia is a biogeographical region straddling the Equator and the boundaries of the Indomalayan and Australasian realms, and also a phytogeographical floristic region in the Paleotropical Kingdom. The original definition by the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions included Papuasia, but this was split off in its 2001 version.

The Malay Archipelago also called Insulindia or the Indo-Australian Archipelago is the archipelago between Mainland Southeast Asia and Australia. It has also been called the "Malay world," "Nusantara", "East Indies", and other names over time. The name was taken from the 19th-century European concept of a Malay race, later based on the distribution of Austronesian languages.

Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, Indonesian Papua, is the western, Indonesian half of the island of New Guinea. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua.
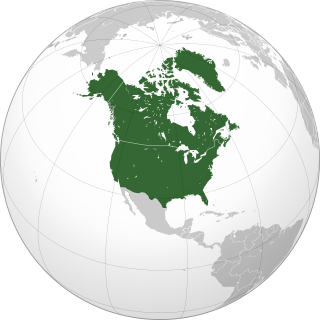
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America. Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States.

The flora consists of many unique varieties of tropical plants. Blessed with a tropical climate and roughly 17,000 islands, Indonesia is the nation with the second highest biodiversity in the world. The flora of Ind reflects an intermingling of Asian, Australian and unique, Indonesian lineages. This is due to the geography of Indonesia, located between the aforementioned continents. The archipelago consists of a variety of regions, from the tropical rain forests of the northern lowlands and the seasonal forests of the southern lowlands through the hill and mountain vegetation, to subalpine shrub vegetation. With the second longest coastline in the world, Indonesia also has many swamps and other varieties of coastal vegetation. Combined, these all give rise to a huge floral biodiversity. There are about 28,000 species of flowering plants documented in Indonesia, including 2500 orchids, 122 species of bamboo, over 350 species of rattan and 400 species of Dipterocarpus, including ebony, sandalwood and teakwood. Indonesia is also home to some unusual species of carnivorous plants. One exceptional species is known as Rafflesia arnoldi, named after Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles and Dr. Thomas Arnold, who discovered the flower in the depths of Bengkulu, southwest Sumatra. This parasitic plant has the largest flower of any plant, does not produce leaves and grows only on one species of liana on the rainforest floor. Another unusual plant is Amorphophallus titanum from Sumatra. Numerous species of insect trapping pitcher plants can also be found in Borneo, Sumatra, and other islands of the Indonesian archipelago. There are a staggering 6000 traditional medicinal plants used as Jamu.,
The World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) is a biogeographical system developed by the international Biodiversity Information Standards (TDWG) organization, formerly the International Working Group on Taxonomic Databases. The WGSRPD standards, like other standards for data fields in botanical databases, were developed to promote "the wider and more effective dissemination of information about the world's heritage of biological organisms for the benefit of the world at large". The system provides clear definitions and codes for recording plant distributions at four scales or levels, from "botanical continents" down to parts of large countries. The codes may be referred to as TDWG geographical codes. Current users of the system include the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), and Plants of the World Online (POWO).

The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul, Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and Eastern hemispheres. The name "Sahul" takes its name from the Sahul Shelf, which is a part of the continental shelf of the Australian continent. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other nearby islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The name "New Guinea" was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.

Eastern Asia is one of the regions of temperate Asia defined in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD) for use in recording the distribution of plants. It is very much smaller than common definitions of East Asia. It consists of the Korean Peninsula, Japan, and Taiwan. Some islands belonging to Japan politically, such as Marcus Island (Minami-Tori-shima), have greater floristic affinity with similar Pacific islands and are placed in the botanical continent of the Pacific.

The Cape Provinces of South Africa is a biogeographical area used in the World Geographical Scheme for Recording Plant Distributions (WGSRPD). It is part of the WGSRPD region 27 Southern Africa. The area has the code "CPP". It includes the South African provinces of the Eastern Cape, the Northern Cape and the Western Cape, together making up most of the former Cape Province.















