Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria.
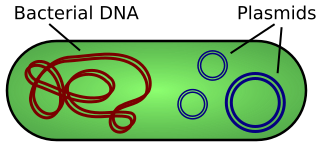
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation.

The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including bacteria and archaea. It extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. In eukaryotes, it is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements.

Cytokinesis is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and meiosis. During cytokinesis the spindle apparatus partitions and transports duplicated chromatids into the cytoplasm of the separating daughter cells. It thereby ensures that chromosome number and complement are maintained from one generation to the next and that, except in special cases, the daughter cells will be functional copies of the parent cell. After the completion of the telophase and cytokinesis, each daughter cell enters the interphase of the cell cycle.

Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42-kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm.

FtsZ is a protein encoded by the ftsZ gene that assembles into a ring at the future site of bacterial cell division. FtsZ is a prokaryotic homologue of the eukaryotic protein tubulin. The initials FtsZ mean "Filamenting temperature-sensitive mutant Z." The hypothesis was that cell division mutants of E. coli would grow as filaments due to the inability of the daughter cells to separate from one another. FtsZ is found in almost all bacteria, many archaea, all chloroplasts and some mitochondria, where it is essential for cell division. FtsZ assembles the cytoskeletal scaffold of the Z ring that, along with additional proteins, constricts to divide the cell in two.
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division.

The nucleoid is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions needing it to be compacted in order to fit. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Instead, the nucleoid forms by condensation and functional arrangement with the help of chromosomal architectural proteins and RNA molecules as well as DNA supercoiling. The length of a genome widely varies and a cell may contain multiple copies of it.

A tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium, including A. tumefaciens, A. rhizogenes, A. rubi and A. vitis.

RecA is a 38 kilodalton protein essential for the repair and maintenance of DNA. A RecA structural and functional homolog has been found in every species in which one has been seriously sought and serves as an archetype for this class of homologous DNA repair proteins. The homologous protein is called RAD51 in eukaryotes and RadA in archaea.
Crescentin is a protein which is a bacterial relative of the intermediate filaments found in eukaryotic cells. Just as tubulins and actins, the other major cytoskeletal proteins, have prokaryotic homologs in, respectively, the FtsZ and MreB proteins, intermediate filaments are linked to the crescentin protein. Some of its homologs are erroneously labelled Chromosome segregation protein ParA. This protein family is found in Caulobacter and Methylobacterium.
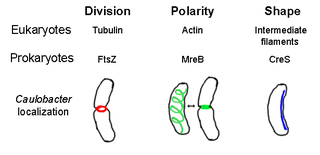
The prokaryotic cytoskeleton is the collective name for all structural filaments in prokaryotes. It was once thought that prokaryotic cells did not possess cytoskeletons, but advances in visualization technology and structure determination led to the discovery of filaments in these cells in the early 1990s. Not only have analogues for all major cytoskeletal proteins in eukaryotes been found in prokaryotes, cytoskeletal proteins with no known eukaryotic homologues have also been discovered. Cytoskeletal elements play essential roles in cell division, protection, shape determination, and polarity determination in various prokaryotes.
Segrosomes are protein complexes that ensure accurate segregation (partitioning) of plasmids or chromosomes during bacterial cell division.
In molecular cloning, a vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to artificially carry foreign genetic material into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed. A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids. Common to all engineered vectors have an origin of replication, a multicloning site, and a selectable marker.
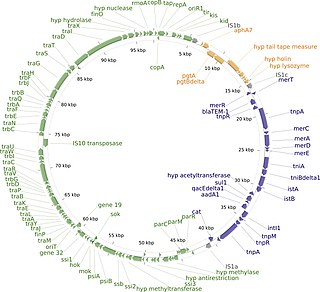
The R1 Plasmid is a plasmid that was first isolated from Salmonella paratyphi bacteria in 1963. It is a short plasmid, composed of 97,566 nucleotides and 120 genes, that belongs to the IncFII plasmid group.
ParM is a prokaryotic actin homologue which provides the force to drive copies of the R1 plasmid to opposite ends of rod shaped bacteria before cytokinesis.

A prokaryote is a typically unicellular organism that lacks a nuclear membrane-enclosed nucleus. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό and κάρυον. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. But in the three-domain system, based upon molecular analysis, prokaryotes are divided into two domains: Bacteria and Archaea. Organisms with nuclei are placed in a third domain, Eukaryota. In the study of the origins of life, prokaryotes are thought to have arisen before eukaryotes.

A toxin-antitoxin system is a set of two or more closely linked genes that together encode both a "toxin" protein and a corresponding "antitoxin". Toxin-antitoxin systems are widely distributed in prokaryotes, and organisms often have them in multiple copies. When these systems are contained on plasmids – transferable genetic elements – they ensure that only the daughter cells that inherit the plasmid survive after cell division. If the plasmid is absent in a daughter cell, the unstable antitoxin is degraded and the stable toxic protein kills the new cell; this is known as 'post-segregational killing' (PSK).
The parABS system is a broadly conserved molecular mechanism for plasmid partitioning and chromosome segregation in bacteria. Originally identified as a genetic element required for faithful partitioning of low-copy-number plasmids, it consists of three components: the ParA ATPase, the ParB DNA-binding protein, and the cis-acting parS sequence. The parA and parB genes are typically found in the same operon, with parS elements located within or adjacent to this operon. Collectively, these components function to ensure accurate partitioning of plasmids or whole chromosomes between bacterial daughter cells prior to cell division.
A plasmid partition system is a mechanism that ensures the stable inheritance of plasmids during bacterial cell division. Each plasmid has its independent replication system which controls the number of copies of the plasmid in a cell. The higher the copy number is, the more likely the two daughter cells will contain the plasmid. Generally, each molecule of plasmid diffuses randomly, so the probability of having a plasmid-less daughter cell is 21−N, where N is the number of copies. For instance, if there are 2 copies of a plasmid in a cell, there is a 50% chance of having one plasmid-less daughter cell. However, high-copy number plasmids have a cost for the hosting cell. This metabolic burden is lower for low-copy plasmids, but those have a higher probability of plasmid loss after a few generations. To control vertical transmission of plasmids, in addition to controlled-replication systems, bacterial plasmids use different maintenance strategies, such as multimer resolution systems, post-segregational killing systems, and partition systems.












