Related Research Articles

Naval Air Station Whidbey Island (NASWI) is a naval air station of the United States Navy located on two pieces of land near Oak Harbor, on Whidbey Island, in Island County, Washington.

The destroyers-for-bases deal was an agreement between the United States and the United Kingdom on September 2, 1940, according to which 50 Caldwell, Wickes, and Clemson-class US Navy destroyers were transferred to the Royal Navy from the US Navy in exchange for land rights on British possessions.

Saint George, officially the Parish of Saint George, is a parish of Antigua and Barbuda on the island of Antigua. Saint George borders Saint Peter to the southeast, and Saint John to the west and south. Saint George is mostly farmland and savanna in the south, dense forest in the Blackman's Peninsula area, marshland in the Fitches Creek area, and dense forest in the northwest. It is the smallest parish in Antigua and Barbuda, and the parish capital is Fitches Creek. The largest city in the parish is Piggotts. Saint George is the newest parish, and split from the parish of Saint Peter in 1725. It had a population of 7,976 in 2011.

Saint Philip, officially the Parish of Saint Philip, is a civil parish of Antigua and Barbuda, on the easternmost portion of Antigua island. Its capital is the village of St. Philip's. Saint Philip borders Saint Peter and Saint Paul. Saint Philip faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Philip is surrounded by various islands and islets. It had a population of 3,347 in 2011, which makes it the least populous parish of Antigua and Barbuda.

Saint Paul, officially the Parish of Saint Paul, is a parish of Antigua and Barbuda on the island of Antigua. Saint Paul borders Saint Peter and Saint John to the north, Saint Mary to the west, and Saint Philip to the east. Saint Paul is dominated by farmland in the north, with various creeks and Potworks Dam marking its northern border, and low-lying hills to the south, defining its western border with Saint Mary. The largest city fully within the parish is Liberta, the fourth largest city in the country. The parish capital, and the location of the parish church, is Falmouth. The main economic and tourism hub of the parish is English Harbour. Saint Paul was created with the other five original parishes on 11 January 1692. It had a population of 9,004 in 2018.
Puget Sound Bridge and Dredging Company was a major shipbuilding and construction company, located in Seattle, Washington, on the southwestern corner of Harbor Island, an artificial island in Elliott Bay. The Bridge and Dredging Company created the island, completing its construction in 1909. It established itself in 1898 and engaged in construction projects around the United States and shipbuilding for the U.S. Navy during and after World War II. During the war it also operated under the name Associated Shipbuilders in a joint venture with the nearby Lake Union Dry Dock Company. In 1959 Lockheed purchased the shipyard and it became the Lockheed Shipbuilding and Construction Company. The Yard was permanently closed in 1987.

Marine Corps Air Station Kaneohe Bay or MCAS Kaneohe Bay is a United States Marine Corps (USMC) airfield located within the Marine Corps Base Hawaii complex, formerly known as Marine Corps Air Facility (MCAF) Kaneohe Bay or Naval Air Station (NAS) Kaneohe Bay. It is located two miles northeast of the central business district of Kaneohe, in Honolulu County, Hawaii, United States. The airfield has one runway (4/22) with a 7,771 x 200 ft asphalt surface.

Old Road, officially known as Old Road Town, is a town located on a roadstead in the parish of Saint Mary, Antigua and Barbuda. It is overlooked by Boggy Peak, which lies to its northwest. Old Road was founded in the 1700s, and in the 1850s was still a tiny settlement of 96, smaller than its neighbour to the west, Urlings. Old Road has since grown to a population of 1,251 in 2011, and is now the tenth largest settlement in the country. Old Road is smaller than Willikies, but is larger than Montclear, Skyline, and Potters Village. Old Road is separated from the rest of Antigua by the Shekerley Mountains. The village is located on Andy Roberts Drive which to the east, merges onto Fig Tree Drive leading to John Hughes, and to the west, continues through Urlings, Crabs Hill, and Johnsons Point before merging onto Valley Road in Ffryes village.

Naval Station Pearl Harbor is a United States naval base on the island of Oahu, Hawaii. In 2010, as part of the recommendations of the Base Realignment and Closure (BRAC) commission, the naval station was consolidated with the United States Air Force's Hickam Air Force Base to form Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam. Since 1940, Pearl Harbor has been the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet.

US Naval Advance Bases were built globally by the United States Navy during World War II to support and project U.S. naval operations worldwide. A few were built on Allied soil, but most were captured enemy facilities or completely new. Advance bases provided the fleet with support to keep ships tactically available with repair and supply depots of facilities, rather than return them to the continental United States. Before Japan declared war on the United States the U.S. Navy had a single fleet-sized advanced base in the Territory of Hawaii at Naval Station Pearl Harbor. During the war the U.S. Navy Seabees built over 400 advance bases categorized by size. Naval bases were either Lions or Cubs while airfields were either Oaks or Acorns. Lions and Oaks were major facilities while Cubs and Acorns were minor. PT Boats typically would get a Cub and airfields with single runways were Acorns. The larger bases could do refueling and overhaul; loading of troopship and cargo ships; and preparing amphibious assault ships. Some became major repair depots. The Seabees developed auxiliary floating drydocks were able to repair battle damage and do regular maintenance in the field saving ships trans-pacific trips for repair. A few bases also were developed to be R and R for all U.S. personnel. Most Advance Bases were built by the US Navy's Seabees in Naval Construction Battalions (CBs). At the start of the war civilian contractors were employed in construction. The Seabees in World War II built most of the airfields used by the United States Army Air Forces and United States Marine Corps, as they had the ships and cranes needed to transport the vast amount of equipment needed at the advance bases. The US Army and United States Coast Guard also operated out of many of these facilities. Seabees could build new or repair damaged runways, and with advancements in heavy bomber technology lengthen runways as needed. A few Naval Advance Bases were built for the Korean War and Vietnam War.

Naval Base Trinidad, also called NAS Trinidad, NAS Port-of-Spain, was a large United States Navy Naval base built during World War II to support the many naval ships fighting and patrolling the Battle of the Atlantic. The fighting in the area became known as the Battle of the Caribbean. Naval Base Trinidad was located on the Island of Trinidad in West Indies of the Caribbean Sea.

Naval Base Manila, Naval Air Base Manila was a major United States Navy base south of the City of Manila, on Luzon Island in the Philippines. Some of the bases dates back to 1898, the end of the Spanish–American War. Starting in 1938 civilian contractors were used to build new facilities in Manila to prepare for World War II. Work stopped on December 23, 1941, when Manila was declared not defendable against the Empire of Japan southward advance, which took over the city on January 2, 1942, after the US declared it an open city. US Navy construction and repair started in March 1945 with the taking of Manila in the costly Battle of Manila ending on March 2, 1945. Naval Base Manila supported the Pacific War and remained a major US Naval Advance Base until its closure in 1971.

Naval Base Okinawa, now Naval Facility Okinawa, is a number of bases built after the Battle of Okinawa by United States Navy on the Okinawa Island of Japan. The naval bases were built to support the landings on Okinawa on April 1, 1945, and the troops fighting on Okinawa. The Navy repaired and did expansion of the airfields on Okinawa. United States Navy Seabees built or repaired the facilities on the island. The bases on Okinawa put the United States Armed Forces only 350 miles from Japan's home islands. Most facilities closed after the war, but some are still in use today in all branches of the United States Armed Forces.

Naval Base Brisbane was a major United States Navy base built in the early part of World War II at Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. At first, operated as a base for patrol aircraft and convoy escort aircraft to protect the last leg of the Pacific War to the Southwest Pacific. As the US Navy expanded in the island hopping campaign, Naval Base Brisbane expanded to include a submarine base, repair depot, seaplane base and other facilities. US Navy operations started on April 14, 1942, and ended after the war in 1945.

Naval Base Lingayen was a United States Navy base built during World War II at Lingayen Gulf on the northwestern Island of Luzon in the Philippines. The base was founded after the Invasion of Lingayen Gulf on January 9, 1945 at Lingayen city and the surrounding gulf. The Naval base was used to support the later operations at Manila and the rest of Luzon Island and then at Okinawa. Lingayen Gulf offered excellent fleet anchorage.

U.S. Naval Base Australia comprised several United States Navy bases in Australia during World War II. Australia entered World War II on 3 September 1939, being a self-governing nation within the British Empire. The United States formally entered the war on 7 December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Following this attack Japanese forces quickly took over much of the western and central Pacific Ocean. The United States lost key naval bases including Naval Base Manila and Naval Base Subic Bay as a result of the 1941 Japanese invasion of the Philippines, along with Guam and Wake Island. The Allied forces needed new bases in the South West Pacific to stage attacks on Japan's southern empire, and these were built in Australia.

US Naval Base Philippines was number of United States Navy bases in the Philippines Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Most were built by the US Navy Seabees, Naval Construction Battalions, during World War II. The US Naval Bases in Philippines were lost to the Empire of Japan in December 1941 during the Philippines campaign of 1941–1942. In February 1945 the United States Armed Forces retook the Philippines in the Battle of Manila in 1945. Before the captured US bases on Luzon were retaken the US Navy Seabees built a new large base, Leyte-Samar Naval Base, on the Philippine Island of Leyte, starting in October 1944.
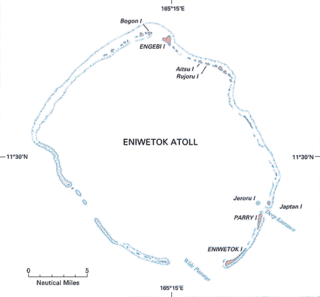
Naval Base Eniwetok was a major United States Navy base located at Enewetak Atoll in the Marshall Islands, during World War II. The base was built to support the island-hopping strategy used by allied nations fighting the Empire of Japan in the Pacific War. During 1944-5 Eniwetok was one of the busiest naval bases in the world with over 488 ships.

References
- ↑ Crabbs Peninsula bucknell.edu
- ↑ US Bases US Navy
- ↑ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 2023-02-10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-02-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ↑ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 2023-02-10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-02-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ↑ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 2023-02-10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-02-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ↑ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 2023-02-10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-02-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ↑ "Wayback Machine" (PDF). 2023-02-10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-02-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
17°07′37″N61°45′18″W / 17.127°N 61.755°W