Related Research Articles

Venezuela is a country in South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, between Colombia and Guyana. It is situated on major sea and air routes linking North and South America. Located at the northernmost end of South America, Venezuela has a total area of 912,050 km2 (352,140 sq mi) and a land area of 882,050 km2 (340,560 sq mi). It is the 32nd largest country and is slightly smaller than Egypt, or half the size of Mexico. Shaped roughly like an inverted triangle, the country has a 2,800 km (1,700 mi) long coastline. It is bound on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the east by Guyana, on the south by Brazil, and on the west by Colombia. It has the 55th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 471,507 km2 (182,050 sq mi). Its maritime territory borders Trinidad and Tobago, Dominica, the Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and the United States. Venezuela also claims the region of Guayana Esequiba, currently under the control of Guyana.

The Orinoco is one of the longest rivers in South America at 2,250 kilometres (1,400 mi). Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers 989,000 km2 (382,000 sq mi), with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the world by discharge volume of water. The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the Llanos of Colombia. The environment and wildlife in the Orinoco's basin are extremely diverse.

The Guiana Shield is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate. It is a 1.7 billion-year-old Precambrian geological formation in northeast South America that forms a portion of the northern coast. The higher elevations on the shield are called the Guiana Highlands, which is where the table-like mountains called tepuis are found. The Guiana Highlands are also the source of some of the world's most well-known waterfalls such as Angel Falls, Kaieteur Falls and Cuquenan Falls.

Amazonas State is one of the 23 states into which Venezuela is divided. It covers nearly a fifth of the area of Venezuela, but has less than 1% of Venezuela's population.

A blackwater river is a type of river with a slow-moving channel flowing through forested swamps or wetlands. As vegetation decays, tannins leach into the water, making a transparent, acidic water that is darkly stained, resembling black tea. Most major blackwater rivers are in the Amazon Basin and the Southern United States. The term is used in fluvial studies, geology, geography, ecology, and biology. Not all dark rivers are blackwater in that technical sense. Some rivers in temperate regions, which drain or flow through areas of dark black loam, are simply black due to the color of the soil; these rivers are black mud rivers. There are also black mud estuaries.

Hevea is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, with about ten members. It is also one of many names used commercially for the wood of the most economically important rubber tree, H. brasiliensis. The genus is native to tropical South America but is widely cultivated in other tropical countries and naturalized in several of them. It was first described in 1775.
The Pacaraima or Pakaraima Mountains are a mountain range primarily in southwestern Guyana, and into northern Brazil and eastern Venezuela.

Cerro Autana is a geological formation located at the western portion of the Guiana Shield in the Estado Amazonas, Venezuela near the Colombian border. It is characterized by a narrow base, a flat top and almost vertical walls. Its top is at approximately 1,220 metres (4,000 ft). It belongs to the formations known as tepuis which are characteristic flat-top mountains of the Guiana Shield. Cerro Autana plays the role of the "tree of life" in the oral history and lore of the Piaroa Indians which inhabit the region. The first Europeans to visit the region around Cerro Autana were Humboldt and Bonpland in 1800. During 1852-1854 Richard Spruce and Alfred Russel Wallace made numerous observations and botanical collections. Cerro Autana is the landmark of the region of Autana which encompasses the Cerro Autana itself, a smaller adjacent mountain often referred to as the “Autanita”, the Cuao, Autana and Umaj-ajé rivers and Lake Leopoldo. Cerro Autana was declared a Natural Monument in 1978, including part of the Autana River and Lake Leopoldo. The mountain is also known internationally for rock climbing and exotic BASE jumping.

The Cordillera de Mérida is a series of mountain ranges, or massif, in northwestern Venezuela. The Cordillera de Mérida is a northeastern extension of the Andes Mountains and the most important branch of the Venezuelan Andes. The ranges run southwest–northeast between the Venezuelan-Colombian border and the Venezuelan Coastal Ranges. The Táchira depression separates the Cordillera de Mérida from the Cordillera Oriental, which forms the Colombia-Venezuela border.

The Guayana Region is an administrative region of eastern Venezuela.

Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to confirm its existence, and it was dismissed as a myth along with the city. The search for Lake Parime led explorers to map the rivers and other features of southern Venezuela, northern Brazil, and southwestern Guyana before the lake's existence was definitively disproved in the early 19th century. Some explorers proposed that the seasonal flooding of the Rupununi savannah may have been misidentified as a lake. Recent geological investigations suggest that a lake may have existed in northern Brazil, but that it dried up some time in the 18th century. Both "Manoa" and "Parime" are believed to mean "big lake".

The Brazil–Venezuela border is the limit that separates the territories of Brazil and Venezuela. It was delimited by the Treaty of Limits and River Navigation of May 5, 1859 and ratified by the Protocol of 1929. The geographical boundary begins at the triple point between Brazil-Colombia-Venezuela at Cucuy Rock and continues up the Maturacá channel to the Huá waterfall; it then follows a straight line to the top of a mountain called Cerro Cupi. It then follows the crest of the drainage divide between the Orinoco and Amazon river basins up to the Brazil-Guyana-Venezuela border tripoint on top of Mount Roraima, thus covering a total of 2,199 kilometres through the Imeri, Tapirapecó, Curupira and Urucuzeiro mountain ranges, and the Parima, Auari, Urutanim and Pacaraima ranges, in the Guiana Shield.

The Serranía de la Neblina National Park is a national park of Venezuela.

The Guayana natural region also simply known as Guayana in Venezuela, is a large massif of approximately 441,726 km2 (170,551 sq mi) area, equivalent to 48.2% of the total continental territory of the country.

The Guianan savanna (NT0707) is an ecoregion in the south of Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname and the north of Brazil. It is in the Amazon biome. The savanna covers an area of rolling upland plains on the Guiana Shield between the Amazon and Orinoco basins. It includes forested areas, but these are shrinking steadily due to the effect of frequent fires, either accidental or deliberate. The ecoregion includes the Gran Sabana region of Venezuela.

The Negro–Branco moist forests (NT0143) is an ecoregion of tropical moist broadleaf forest to the east of the Andes in southern Venezuela, eastern Colombia and northern Brazil, in the Amazon biome. It lies on the watershed between the Orinoco and Rio Negro basins. It includes both blackwater and whitewater rivers, creating different types of seasonally flooded forest. The vegetation is more typical of the Guiana region than the Amazon.

The Guayanan Highlands moist forests (NT0124) is an ecoregion in the south of Venezuela and the north of Brazil and in Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana. It is in the Amazon biome. It encompasses an upland region with diverse fauna and flora, which contains dramatic tepuis, or sandstone table mountains. The region has been inaccessible in the past and is generally fairly intact, apart from the north and northeast where large scale agriculture, ranching and mining operations are steadily encroaching on the ecosystem. New roads are opening the interior to logging, and planned dams will have a drastic impact on the riparian zones.
The Alto Orinoco-Casiquiare Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO biosphere reserve in the Venezuelan Amazon biome.

The Guianan moist forests (NT0125) is an ecoregion in the east of Venezuela, north of Brazil and the Guyanas. It is in the Amazon biome. The climate is hot and humid, with two rainy seasons each year. As of 1996 the tropical rainforest habitat was relatively intact, although there were mounting threats from illegal logging and gold mining.
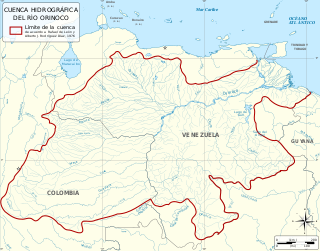
The Orinoco Basin is the part of South America drained by the Orinoco river and its tributaries. The Orinoco watershed covers an area of about 990000 km2, making it the third largest in South America, covering most of Venezuela and eastern part of Colombia.
References
- ↑ "Parima Mountains". Encyclopædia Britannica. February 9, 2007. Retrieved September 19, 2009.
- ↑ Otto Huber; Julian A. Steyermark; Ghillean T. Prance; Catherine Ales (984). "The Vegetation of the Sierra Parima, Venezuela-Brazil: Some Results of Recent Exploration". Brittonia. 36 (2): 104–139. ISSN 0007-196X. JSTOR 2806619.
Coordinates: 3°30′00″N64°15′00″W / 3.5000°N 64.2500°W