
Meadowhall is an indoor shopping centre in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. It lies 3 miles (5 km) north-east of Sheffield city centre, and 2 miles (3 km) from Rotherham town centre. It is the largest shopping centre in Yorkshire, and currently the twelfth-largest in the United Kingdom. As of 2021, plans for an extension are currently under consideration, for completion in the 2020s, which would make Meadowhall the 11th biggest shopping centre in the United Kingdom.

The South Yorkshire Supertram, sometimes referred to as the Sheffield Supertram, is a tram and tram-train network covering Sheffield and Rotherham in South Yorkshire, England. The network is owned and operated by the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority (SYMCA).

Sheffield station is a combined railway station and tram stop in Sheffield, England; it is the busiest station in South Yorkshire, and the second busiest in Yorkshire & the Humber, after Leeds. Adjacent is the Sheffield Supertram stop.

The Penistone Line is operated by Northern Trains in the West Yorkshire Metro and Travel South Yorkshire areas of northern England. It connects Huddersfield and Sheffield via Penistone and Barnsley, serving many rural communities. Metrocards can be used for travel between Huddersfield and Denby Dale and intermediate stations.

The Wakefield line is a railway line and service in the West Yorkshire Metro and South Yorkshire Passenger Transport Executive areas of northern England. The Wakefield line is coloured yellow on maps and publications by West Yorkshire Metro. The line was electrified in 1989, between Leeds & Wakefield Westgate, as part of the programme to electrify the East Coast Main Line.

The Dearne Valley line is the name given to a railway line in the north of England running from York to Sheffield via Pontefract Baghill and Moorthorpe. The route was built over several years and consists of lines built by several railway companies.

Meadowhall Interchange is a transport interchange located in north-east Sheffield, consisting of a combined heavy rail station, tram stop and bus and coach station. The second-busiest heavy rail station in the city in terms of passenger numbers, Meadowhall Interchange provides connections between National Rail services, the Sheffield Supertram light rail network, intercity coach services and the city bus network.

The Leeds Supertram was a proposed light rail/tram system in Leeds and West Yorkshire in England. It would have been a three-line, 17-mile (27 km) system with 50 stations. It received provisional government approval in 2001, and was specifically for corridors ill-served by the existing heavy rail network. Supertram would have been 75% funded from the public sector, with final contracts for construction and a 27-year operating concession due to have been awarded in 2003. By 2004, disquiet about rising costs had caused the scheme to be scaled back, and it was finally cancelled in 2005 by the Transport Secretary, Alistair Darling.

Rotherham Central railway station is in Rotherham, South Yorkshire, England. The station was originally named "Rotherham", becoming "Rotherham and Masborough" in January 1889 and finally "Rotherham Central" on 25 September 1950.

Parkgate is a suburb of Rotherham, South Yorkshire, England. It has since been consumed by its neighbour, Rawmarsh and is in the ward of Rawmarsh from which it has been indistinguishable since the early 20th century.

Transport in Sheffield, England is developed around the city's unusual topography and medieval street plan. Once an isolated town, the transport infrastructure changed dramatically in the 19th and 20th centuries. The city now has road and rail links with the rest of the country, and road, bus and trams for local transport.

South Yorkshire Passenger Transport Executive (SYPTE) was the passenger transport executive for South Yorkshire. It was responsible for implementing policies set by the South Yorkshire Passenger Transport Authority (SYPTA) and for operation of the Authority's bus fleet from its formation in 1974 until its dissolution in 2023, when its assets and duties were transferred to the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority.

Tinsley railway station was a railway station in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England, opened in March 1869. This station was designed by the company architect John Holloway Sanders. The station served the growing community of Tinsley and the workers at the nearby steelworks which had moved to or had been founded in the lower Don Valley following major changes in manufacturing methods in the mid - late 19th century. The station, opened by the South Yorkshire Railway, was built on the line between Sheffield Victoria and Barnsley and became a junction station with the opening of the line from Tinsley Junction to the original Rotherham station by the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway. The station was located by the main Sheffield to Rotherham road in Tinsley, now on the Sheffield side of M1, Junction 34 in Tinsley.
The Sheffield District Rail Rationalisation Plan was a series of linked railway civil engineering projects, station and line closures and train route changes that took place in and around Sheffield, South Yorkshire. The majority of these changes took place in the 1960s and early 1970s, however the plan, by now much modified in the face of rapidly dwindling freight traffic, was not fully realised until the 1980s.
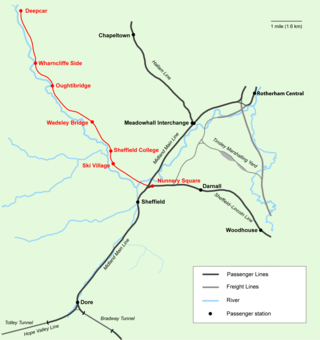
Don Valley Railway first formed as a heritage rail project in September 2003 to operate on the freight rail line between Stocksbridge Steel Works and Sheffield following the route of the former Woodhead Line between Deepcar and Sheffield, The project is developed by Don Valley Railway Ltd., a not-for-profit company and registered charity based in Stocksbridge, South Yorkshire. Original plans to operate heritage rail services for the dual purpose of providing infrastructure for tourism over the weekends, alongside regular commuter services have now shifted towards concentrating on the development of a viable commuter service - though with help of outside assistance heritage plans could be revised. In 2023, the Department for Transport announced that the Don Valley Line will be restored for passenger use.

The Siemens-Duewag Supertram is a fleet of 25 trams built by Siemens-Duewag of Düsseldorf, Germany in 1992 for use on the South Yorkshire Supertram light rail network in England. They were the only trams in use on the network until the entry into service of British Rail Class 399 tram-trains in 2017. As of May 2024, 24 of the fleet are operational, with one currently out of service. Tram 105 was involved in a road traffic collision (RTC) and has arrived back at the depot after repairs, but has not yet returned to service.

The British Rail Class 399 Citylink is a type of rail vehicle built by Vossloh on its Citylink platform for operation by Sheffield Supertram. Primarily a low-floor tram, it is also capable of being used on the National Rail network; the Class 399 is the first such tram-train to see operational use in the United Kingdom.

The Stadler Citylink is a series of tram-trains manufactured by Stadler Rail at its Valencia factory since 2011. The design was introduced by Vossloh España before their takeover by Stadler Rail in 2015. They are currently used in Germany, Hungary, Mexico, Spain and the United Kingdom, with more on order in Austria. Stadler opened a new factory in the United States in 2016, which is in the process of building up to 80 Citylink vehicles for service in Salt Lake City beginning in 2028.

Bus Rapid Transit North is a bus rapid transit scheme introduced by the South Yorkshire Passenger Transport Executive in England. It consists of one route operated by First South Yorkshire between Sheffield and Rotherham.
Public transport in South Yorkshire, England mainly consists of three modes: bus, tram and train. Passengers can switch between these modes of transport at various interchanges operated by the South Yorkshire Combined Mayoral Authority.



















