
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston, Massachusetts is a teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School and one of the founding members of Beth Israel Lahey Health. It was formed out of the 1996 merger of Beth Israel Hospital and New England Deaconess Hospital. Among independent teaching hospitals, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center has ranked in the top three recipients of biomedical research funding from the National Institutes of Health. Research funding totals nearly $200 million annually. BIDMC researchers run more than 850 active sponsored projects and 200 clinical trials. The Harvard-Thorndike General Clinical Research Center, the oldest clinical research laboratory in the United States, has been located on this site since 1973.
Medical tourism is the practice of traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable at home. However, in recent years it may equally refer to those from developed countries who travel to developing countries for lower-priced medical treatments. With differences between the medical agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA), etc., which decide whether a drug is approved in their country or region, or not, the motivation may be also for medical services unavailable or non-licensed in the home country.

Massachusetts General Hospital is a teaching hospital located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the original and largest clinical education and research facility of Harvard Medical School/Harvard University, and houses the world's largest hospital-based research program with an annual research budget of more than $1.2 billion in 2021. It is the third-oldest general hospital in the United States with a patient capacity of 999 beds. Along with Brigham and Women's Hospital, Mass General is a founding member of Mass General Brigham, formerly known as Partners HealthCare, the largest healthcare provider in Massachusetts.
The Joint Commission is a United States-based nonprofit tax-exempt 501(c) organization that accredits more than 22,000 US health care organizations and programs. The international branch accredits medical services from around the world.

The Aga Khan University Hospital (AKUH) in Karachi, established in 1985, is the primary teaching site of the Aga Khan University's (AKU) Faculty of Health Sciences. Founded by the Aga Khan, the hospital provides a broad range of secondary and tertiary care, including diagnosis of disease and team management of patient care.
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory surgery, day surgery, day case surgery, or same-day surgery, is surgery that does not require an overnight hospital stay. The term “outpatient” arises from the fact that surgery patients may enter and leave the facility on the same day. The advantages of outpatient surgery over inpatient surgery include greater convenience and reduced costs.

The American Osteopathic Association (AOA) is the representative member organization for the more than 176,000 osteopathic medical doctors (D.O.s) and osteopathic medical students in the United States. The AOA is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, and is involved in post-graduate training for osteopathic physicians. Beginning in 2015, it began accrediting post-graduate education as a committee within the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education, creating a unified accreditation system for all DOs and MDs in the United States. The organization promotes public health, encourages academic scientific research, serves as the primary certifying body for D.O.s overseeing 18 certifying boards, and is the accrediting agency for osteopathic medical schools through its Commission on Osteopathic College Accreditation. As of October 2015, the AOA no longer owns the Healthcare Facilities Accreditation Program (HFAP), which accredited hospitals and other health care facilities.
Health information management (HIM) is information management applied to health and health care. It is the practice of analyzing and protecting digital and traditional medical information vital to providing quality patient care. With the widespread computerization of health records, traditional (paper-based) records are being replaced with electronic health records (EHRs). The tools of health informatics and health information technology are continually improving to bring greater efficiency to information management in the health care sector.
Due to the near-universal desire for safe and good quality healthcare, there is a growing interest in international healthcare accreditation. Providing healthcare, especially of an adequate standard, is a complex and challenging process. Healthcare is a vital and emotive issue—its importance pervades all aspects of societies, and it has medical, social, political, ethical, business, and financial ramifications. In any part of the world healthcare services can be provided either by the public sector or by the private sector, or by a combination of both, and the site of delivery of healthcare can be located in hospitals or be accessed through practitioners working in the community, such as general medical practitioners and dental surgeons.
The Trent Accreditation Scheme (TAS), now replaced de facto by a number of independent accreditation schemes, such as the QHA Trent Accreditation, was a British accreditation scheme formed with a mission to maintain and continually evaluate standards of quality, especially in health care delivery, through the surveying and accreditation of health care organisations, especially hospitals and clinics, both in the UK and elsewhere in the world.
Hospital accreditation has been defined as “A self-assessment and external peer assessment process used by health care organizations to accurately assess their level of performance in relation to established standards and to implement ways to continuously improve”. Critically, accreditation is not just about standard-setting: there are analytical, counseling and self-improvement dimensions to the process. There are parallel issues in evidence-based medicine, quality assurance and medical ethics, and the reduction of medical error is a key role of the accreditation process. Hospital accreditation is therefore one component in the maintenance of patient safety. However, there is limited and contested evidence supporting the effectiveness of accreditation programs.
Hamad Medical Corporation (HMC) is Qatar’s main not-for-profit health care provider, and is based in Doha. It was established by Emiri Decree No. 35 in 1979. HMC manages several hospitals, as well as emergency, specialized, and ambulatory care centers, and operates both the national ambulance service and a home healthcare service.

The Acıbadem Healthcare Group is a Turkish healthcare institution, operating with 17,000 employees. It comprises 21 hospitals and 16 medical centers. The group consists of a network of general hospitals, medical centers, outpatient clinics, an ophthalmology center and various laboratories.
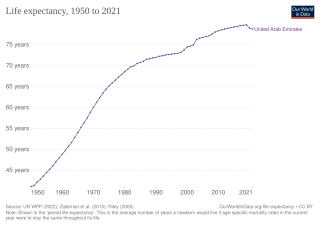
The United Arab Emirates has enacted federal legislation to require universal healthcare, but this has not yet been implemented by all seven emirates. Healthcare is provided for all nationals. While health insurance is set to be mandated for citizens of other countries. Employers are to be required to provide health insurance for expatriate workers. In the UAE employers must also provide health insurance for up to one spouse and three dependents, while in Dubai expats are required to provide insurance for their dependents.
Western Michigan University Homer Stryker M.D. School of Medicine (WMed) is a private medical school in Kalamazoo, Michigan. WMed was established in 2012 and confers the Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree, as well as Master of Science in Biomedical Sciences degree and the Master of Science in Medical Engineering degree. WMed is a collaboration between Western Michigan University and Kalamazoo's two teaching hospitals, Ascension Borgess and Bronson Healthcare. The inaugural class of 54 students started in August 2014.

Wockhardt Hospitals Ltd is an Indian for-profit private hospital network headquartered in Mumbai. The chain of hospitals is owned by the promoters of Wockhardt, a multinational pharmaceutical company. It has six hospitals across four western Indian cities–Mumbai, Nagpur, Nashik and Rajkot.

Dubai Healthcare City (DHCC) is a healthcare free economic zone situated in the Emirate of Dubai, United Arab Emirates. DHCC was launched in 2002 by Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, vice-president and Prime Minister of the UAE and Ruler of Dubai. DHCC was mandated by the government to meet the demand for high-quality, patient-centered healthcare, and the main aim is to attract tourists to Dubai for medical services and treatments.

Voluntary Health Services, popularly known as the VHS Hospital, is a multispecialty tertiary care referral hospital in the south Indian state of Tamil Nadu, reportedly serving the economically weaker sections of the society. It was founded in 1958 by Krishnaswami Srinivas Sanjivi, an Indian physician, social worker and a winner of Padma Shri and Padma Bhushan awards and is run by a charitable non governmental organization of the same name. The hospital is situated along Rajiv Gandhi Salai at Taramani, in Chennai.
The Ahalia Health Heritage and Knowledge Village, managed by the Ahalia International Foundation, is one of the largest edu-health campus in Kerala, India. It is headquartered in the city of Palakkad. The organization, which started as an eye hospital in 2005, now has more than 11 regional eye care branches all over the state.








