
The European Environment Agency (EEA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) which provides independent information on the environment.
Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.

The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an independent International research institute located in Laxenburg, near Vienna in Austria, founded as an East-West scientific cooperation initiative during the Cold War. Through its research programs and initiatives, the institute conducts policy-oriented interdisciplinary research into issues too large or complex to be solved by a single country or academic discipline. These include climate change, energy security, population aging, and sustainable development. The results of IIASA research and the expertise of its researchers are made available to policymakers worldwide to help them make informed and evidence-based policies.
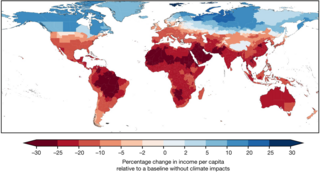
Economic analysis of climate change is about using economic tools and models to calculate the magnitude and distribution of damages caused by climate change. It can also give guidance for the best policies for mitigation and adaptation to climate change from an economic perspective. There are many economic models and frameworks. For example, in a cost–benefit analysis, the trade offs between climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation are made explicit. For this kind of analysis, integrated assessment models (IAMs) are useful. Those models link main features of society and economy with the biosphere and atmosphere into one modelling framework. The total economic impacts from climate change are difficult to estimate. In general, they increase the more the global surface temperature increases.
LADSS, or land allocation decision support system, is an agricultural land-use planning tool developed at The Macaulay Institute. More recently the term LADSS is used to refer to the research of the team behind the original planning tool.

Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to the effects of climate change. These can be both current or expected impacts. Adaptation aims to moderate or avoid harm for people, and is usually done alongside climate change mitigation. It also aims to exploit opportunities. Humans may also intervene to help adjustment for natural systems. There are many adaptation strategies or options. They can help manage impacts and risks to people and nature. The four types of adaptation actions are infrastructural, institutional, behavioural and nature-based options.
The work of the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research – UFZ covers both basic research and applied research.

The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research is a German government-funded research institute addressing crucial scientific questions in the fields of global change, climate impacts, and sustainable development. Ranked among the top environmental think tanks worldwide, it is one of the leading research institutions and part of a global network of scientific and academic institutions working on questions of global environmental change. It is a member of the Leibniz Association, whose institutions perform research on subjects of high relevance to society.

Jacqueline Myriam McGlade is a British-born Canadian marine biologist and environmental informatics professor. Her research concerns the spatial and nonlinear dynamics of ecosystems, climate change and scenario development. She is currently professor of resilience and sustainable development at the University College London Institute for Global Prosperity and Faculty of Engineering, UK, and professor at Strathmore University in the Institute for Public Policy and Governance, Kenya.

The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) was a study led by Pavan Sukhdev from 2007 to 2011. It is an international initiative to draw attention to the global economic benefits of biodiversity. Its objective is to highlight the growing cost of biodiversity loss and ecosystem degradation and to draw together expertise from the fields of science, economics and policy to enable practical actions. TEEB aims to assess, communicate and mainstream the urgency of actions through its five deliverables—D0: science and economic foundations, policy costs and costs of inaction, D1: policy opportunities for national and international policy-makers, D2: decision support for local administrators, D3: business risks, opportunities and metrics and D4: citizen and consumer ownership.

The European green infrastructure is an important part of the new (post-2010) EU strategy for biodiversity and biodiversity policy.
Natural capital accounting is the process of calculating the total stocks and flows of natural resources and services in a given ecosystem or region. Accounting for such goods may occur in physical or monetary terms. This process can subsequently inform government, corporate and consumer decision making as each relates to the use or consumption of natural resources and land, and sustainable behaviour.

The Sustainable Mekong Research Network (SUMERNET) is a network of organizations committed to the sustainable development of the Greater Mekong Region. Launched in 2005, SUMERNET supports policy-relevant research and outreach activities to inform and engage policy-makers, planners and stakeholders. Within this context, it pursues an evolving agenda in response to questions and policy issues that arise in the region. Current research themes are climate-compatible development, regional economic integration, and ecosystem services and local development. The network works on a range of issues including natural ecosystems governance, floods and natural disasters, climate change and adaptation, and transboundary resource flows.
Climate resilience is a concept to describe how well people or ecosystems are prepared to bounce back from certain climate hazard events. The formal definition of the term is the "capacity of social, economic and ecosystems to cope with a hazardous event or trend or disturbance". For example, climate resilience can be the ability to recover from climate-related shocks such as floods and droughts. Methods of coping include suitable responses to maintain relevant functions of societies and ecosystems. To increase climate resilience means one has to reduce the climate vulnerability of people and countries. Efforts to increase climate resilience include a range of social, economic, technological, and political strategies. They have to be implemented at all scales of society, from local community action all the way to global treaties.

The contributions of women in climate change have received increasing attention in the early 21st century. Feedback from women and the issues faced by women have been described as "imperative" by the United Nations and "critical" by the Population Reference Bureau. A report by the World Health Organization concluded that incorporating gender-based analysis would "provide more effective climate change mitigation and adaptation."

Nature-based solutions describe the development and use of nature (biodiversity) and natural processes to address diverse socio-environmental issues. These issues include climate change mitigation and adaptation, human security issues such as water security and food security, and disaster risk reduction. The aim is that resilient ecosystems provide solutions for the benefit of both societies and biodiversity. The 2019 UN Climate Action Summit highlighted nature-based solutions as an effective method to combat climate change. For example, nature-based systems for climate change adaptation can include natural flood management, restoring natural coastal defences, and providing local cooling.
Ecosystem-based adaptation encompasses a broad set of approaches to adapt to climate change. They all involve the management of ecosystems and their services to reduce the vulnerability of human communities to the impacts of climate change. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) defines EBA as "the use of biodiversity and ecosystem services as part of an overall adaptation strategy to help people to adapt to the adverse effects of climate change".
Susana Mourato is a professor of environmental economics at the London School of Economics and Political Science. She holds a leader position at the Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment.
James Hall, is Professor of Climate and Environmental Risks and former director of the Environmental Change Institute at the University of Oxford. He is director of research at the School of Geography and the Environment, Senior Research Fellow at the Department of Engineering Science and Fellow of Linacre College. Hall is a member of the UK Prime Minister's Council for Science and Technology, commissioner of the National Infrastructure Commission, and is chair of the Science and Advisory Committee of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis. He was appointed as a Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering in 2010. He was a member of the Adaptation Sub-Committee of the UK Climate Change Committee from 2009 to 2019. He was appointed as vice-president of the Institution of Civil Engineers in 2021 with a view to become president in 2024.











