Related Research Articles
The Persians are a Western Iranian ethnic group who comprise the majority of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.

Cambyses II was the second King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 530 to 522 BC. He was the son and successor of Cyrus the Great and his mother was Cassandane. His relatively brief reign was marked by his conquests in North Africa, notably Egypt, which he conquered after his victory over the Egyptian pharaoh Psamtik III at the battle of Pelusium in 525 BC. After having established himself in Egypt, he expanded the empire's holdings in Africa, including the conquest of Cyrenaica. In the spring of 522 BC, Cambyses hurriedly left Egypt to deal with a rebellion in Persia.

Fars province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Shiraz.

Pasargadae was the capital of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great. Today it is an archaeological site located just north of the town of Madar-e-Soleyman and about 90 kilometres (56 mi) to the northeast of the modern city of Shiraz. It is one of Iran's UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is considered to be the location of the Tomb of Cyrus, a tomb previously attributed to Madar-e-Soleyman, the "Mother of Solomon". Currently it is a national tourist site administered by the Iranian culture of world heritage.

Cyrus II of Persia, commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. Hailing from Persis, he brought the Achaemenid dynasty to power by defeating the Median Empire and embracing all of the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanding vastly and eventually conquering most of West Asia and much of Central Asia to create what would soon become the largest polity in human history at the time. The Achaemenid Empire's largest territorial extent was achieved under Darius the Great, whose rule stretched from Southeast Europe in the west to the Indus River valley in the east.
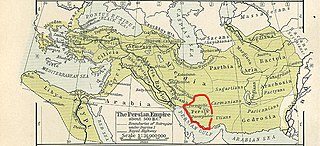
Persis, also called Persia proper, is a historic region in southwestern Iran, roughly corresponding with Fars province. The Persians are thought to have initially migrated either from Central Asia or, more probably, from the north through the Caucasus. They would then have migrated to the current region of Persis in the early 1st millennium BC. The country name Persia was derived directly from the Old Persian Parsa.

Naqsh-e Rostam is an ancient archeological site and necropolis located about 13 km northwest of Persepolis, in Fars province, Iran. A collection of ancient Iranian rock reliefs are cut into the face of the mountain and the mountain contains the final resting place of four Achaemenid kings, notably king Darius the Great and his son, Xerxes. This site is of great significance to the history of Iran and to Iranians, as it contains various archeological sites carved into the rock wall through time for more than a millennium from the Elamites and Achaemenids to Sassanians. It lies a few hundred meters from Naqsh-e Rajab, with a further four Sassanid rock reliefs, three celebrating kings and one a high priest.

Tangeh Bolāghi, also transliterated as Tange-ye Bolāghi, or Bolāghi Gorge, is an archaeologically significant valley consisting of 130 ancient settlements, dating back to the period between 5000 BCE and the Sassanian dynastic era. It is situated in Iran’s southern province of Fars, some 7 kilometres from Pasargadae, Iran. This is the valley of the Polvar River, a tributary to Kor River.

Istakhr was an ancient city in Fars province, five kilometres north of Persepolis in southwestern Iran. It flourished as the capital of the Persian Frataraka governors and Kings of Persis from the third century BC to the early 3rd century AD. It reached its apex under the Sasanian Empire, and was the hometown of the Sasanian dynasty. Istakhr briefly served as the first capital of the Sasanian Empire from 224 to 226 AD and then as principal city, region, and religious centre of the Sasanian province of Pars.
Ariobarzanes, was an Achaemenid prince, satrap and a Persian military commander who led an ambush of the Persian army to resist against the invasion of Macedonian King Alexander the Great at the Battle of the Persian Gate in January 330 BC.

Media is a region of north-western Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Medes. During the Achaemenid period, it comprised present-day Iranian Azerbaijan, Iranian Kurdistan and western Tabaristan. As a satrapy under Achaemenid rule, it would eventually encompass a wider region, stretching to southern Dagestan in the north. However, after the wars of Alexander the Great, the northern parts were separated due to the Partition of Babylon and became known as Atropatene, while the remaining region became known as Lesser Media.

The Achaemenid dynasty was a royal house that ruled the Persian Empire, which eventually stretched from Egypt and Thrace in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east.
Sivand Dam is a dam built in 2007 in Fars province, Iran. Named after the nearby town of Sivand located northwest of Shiraz, it was the center of worldwide concern because of the flooding it would cause in historical and archaeologically rich areas of Ancient Persia and possible harm it may cause to the nearby UNESCO World Heritage Sites of Persepolis and Pasargadae.

The Medo-Persian conflict was a military campaign led by the Median king Astyages against Persis in the mid 6th-century BCE. Classical sources claim that Persis had been a vassal of the Median kingdom that revolted against Median rule, but this is not confirmed by contemporary evidence. After some battles the Persians led by Cyrus the Great emerged victorious, subsequently conquering Median territories and establishing the Achaemenid Empire.

Achaemenid architecture includes all architectural achievements of the Achaemenid Persians manifesting in construction of spectacular cities used for governance and inhabitation, temples made for worship and social gatherings, and mausoleums erected in honor of fallen kings. Achaemenid architecture was influenced by Mesopotamian, Assyrian, Egyptian, Elamite, Lydian, Greek and Median architecture. The quintessential feature of Persian architecture was its eclectic nature with foreign elements, yet producing a unique Persian identity seen in the finished product. Achaemenid architecture is academically classified under Persian architecture in terms of its style and design.

The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire, was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of 5.5 million square kilometres. The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley to the southeast.

Frataraka is an ancient Persian title, interpreted variously as “leader, governor, forerunner”. It is an epithet or title of a series of rulers in Persis from 3rd to mid 2nd century BC, or alternatively between 295 and 220 BC, at the time of the Seleucid Empire, prior to the Parthian conquest of West Asia and Iran. Studies of frataraka coins are important to historians of this period.
The Maspii were an Iranian tribe from Persis or Persia, in modern southwestern Iran. This tribe was one of the three main and leading Persian tribes, alongside the Maraphii and the Pasargadae.
The Maraphii were an Iranian tribe from Persis or Persia, in modern southwestern Iran. This tribe was one of the three main and leading Persian tribes alongside the Maspii and the Pasargadae.
References
- 1 2 "Persis | ancient region, Iran". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2017-08-07.