Background
Both ancient and modern Iranian peoples mostly descend from the Proto-Indo-Iranians, common ancestors respectively of the Proto-Iranians and Proto-Indo-Aryans, this people possibly was the same of the Sintashta-Petrovka culture. Proto-Iranians separated from the Proto-Indo-Aryans early in the 2nd-millennium BCE. These peoples probably called themselves by the name "Aryans", which was the basis for several ethnonyms of Iranian and Indo-Aryan peoples or for the entire group of peoples which shares kin and similar cultures. [1]
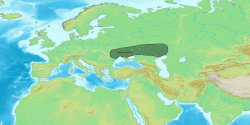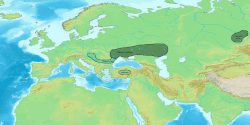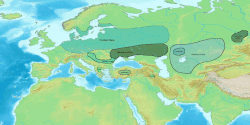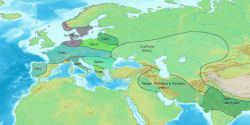
Iranian peoples first appear in Assyrian records in the 9th century BCE. In Classical Antiquity, they were found primarily in Scythia (in Central Asia, Eastern Europe, the Balkans and the Northern Caucasus) and Persia (in Western Asia). They divided into "Western" and "Eastern" branches from an early period, roughly corresponding to the territories of Persia and Scythia, respectively. By the 1st millennium BCE, Medes, Persians, Bactrians and Parthians populated the Iranian plateau, while others such as the Scythians, Sarmatians, Cimmerians and Alans populated the steppes north of the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, as far as the Great Hungarian Plain in the west. The Saka tribes remained mainly in the far-east, eventually spreading as far east as the Ordos Desert. [1]
Ancient Iranian peoples spoke languages that were the ancestors of modern Iranian languages, these languages form a sub-branch of the Indo-Iranian sub-family, which is a branch of the family of the wider Indo-European languages. [1]
Ancient Iranian peoples lived in many regions and, at about 200 BC, they had as farthest geographical points dwelt by them: to the west the Great Hungarian Plain (Alföld), east of the Danube river (where they formed an enclave of Iranian peoples), Ponto-Caspian steppe in today's southern Ukraine, Russia and far western Kazakhstan, and to the east the Altay Mountains western and northwestern foothills and slopes and also western Gansu, Ordos Desert, and western Inner Mongolia, in northwestern China(Xinjiang), to the north southern West Siberia and southern Ural Mountains (Riphean Mountains?) and to the south the northern coasts of the Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea.: [1] [2] : 348 The geographical area dwelt by ancient Iranian peoples was therefore vast (at the end of the 1st Millennium BC they dwelt in an area of several million square kilometers or miles thus roughly corresponding to half or slightly less than half of the geographical area that all Indo-European peoples dwelt in Eurasia). [1]
During Late Antiquity, in a process that lasted until Middle Age, the Iranian populations of Scythia and Sarmatia, in the western (Ponto-Caspian) and central (Kazakh) Eurasian Steppe and most of Central Asia (that once formed a large geographic area dwelt by Iranian peoples), started to be conquered by other non-Iranian peoples and began to be marginalized, assimilated or expelled mainly as result of the Turkic peoples conquests and migrations that resulted in the Turkification of the remaining Iranian ethnic groups in Central Asia and the western Eurasian steppe. Germanic, Slavic and later Mongolian conquests and migrations also contributed to the decline of the Iranian peoples in these regions. By the 10th century, the Eastern Iranian languages were no longer spoken in many of the territories they were once spoken, with the exception of Pashto in Central Asia, Ossetic in the Northern Caucasus and Pamiri languages in Badakhshan. Most of Central Asia and the western Eurasian steppe was almost completely Turkified. However, in most of the southern regions, corresponding to the Iranian Plateau and mountains, more densely populated, Iranian peoples continued to be most of the population and remained so until modern times. [1]
Various Persian empires flourished throughout Antiquity, however, they fell to the Islamic conquest in the 7th century, although other Persian empires formed again later.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.