Related Research Articles
The Dutch Language Union is an international regulatory institution that governs issues regarding the Dutch language. It is best known for its spelling reforms which are promulgated by member states, grammar books, the Green Booklet and its support of Dutch language courses and studies worldwide. It was founded on a treaty concluded between the Netherlands and Belgium on 9 September 1980. Suriname has been an associate member of the Taalunie since 2004.

The Coat of arms of Aruba has been officially in use since November 15, 1955, as the recognized national symbol of Aruba.

Gilberto François "Betico" Croes was an Aruban political activist who was a proponent for Aruba's separation from the Netherlands Antilles. This eventually occurred in 1986, but following a car accident on 31 December 1985, Croes lapsed into a coma and never became conscious to see his accomplishment. He is best remembered as "Libertador" (liberator) and as the father of the Aruban people.
Same-sex marriage is legal in Aruba and Curaçao, two constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, in accordance with a ruling from the Supreme Court of the Netherlands issued on 12 July 2024. In September 2021, a lower court in Curaçao ruled that preventing same-sex couples from marrying violates the equality provisions of the Constitution of Curaçao, but left the decision of whether to legalise same-sex marriage up to the Parliament. In December 2022, the Joint Court of Justice of Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, and of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba ruled on appeal that Aruba's and Curaçao's same-sex marriage bans were unconstitutional. The court order was set to go into effect on 7 March 2023 if not appealed to the Supreme Court; however, the governments of both Curaçao and Aruba subsequently appealed. On 12 July 2024, the Supreme Court upheld the lower court ruling, effectively legalizing same-sex marriage in Aruba and Curaçao with immediate effect.

The rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in Aruba, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, have evolved remarkably in the past decades. Both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are legal in Aruba.

The Netherlands Antilles was an autonomous Caribbean country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It was dissolved on 10 October 2010.
The Netherlands Patent Office is the patent office of the Netherlands. It is an agency of the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs. The agency is located in the premises of the European Patent Office (EPO), in Rijswijk, near The Hague. The Netherlands Patent Office grants patents in the Netherlands and deals with European patents validated in the Netherlands. It assumes its functions from the rijksoctrooiwet.

The Kingdom of the Netherlands, commonly known simply as the Netherlands, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united under the monarch of the Netherlands, who functions as head of state. The realm is not a federation; it is a unitary monarchy with its largest subdivision, the eponymous Netherlands, predominantly located in Northwestern Europe and with several smaller island territories located in the Caribbean.

Finland–Netherlands relations are the bilateral relations between the Netherlands and Finland. The Netherlands recognised Finland's independence on 28 January 1918. Diplomatic relations between them were established on 14 August 1918. The Netherlands has an embassy in Helsinki Finland has an embassy in the Hague, Both countries are full members of the COE, EU and NATO. The Netherlands supported Finland's NATO membership during Finland's accession into NATO, which was finalized on 4 April 2023. And Netherlands is Observer bureau of the BEAC, CBSS and AC.

The Caribbean Netherlands is a geographic region of the Netherlands located outside of Europe, in the Caribbean, consisting of three special municipalities. These are the islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba, as they are also known in legislation, or the BES islands for short. The islands are officially classified as public bodies in the Netherlands and as overseas territories of the European Union; as such, European Union law does not automatically apply to them.
The Benelux Court of Justice is a court which is common to the Benelux countries Belgium, Netherlands and Luxembourg. The organisation was established by the treaty of 31 March 1965. The court's budget rests with the Benelux Union and is of 9 judges of the supreme courts as well as 6 judges of the courts of appeal of the three countries. The court is mainly tasked with answering requests for preliminary rulings from the supreme courts regarding regulations which are common to the three countries and serves as a civil service tribunal for personnel of the Benelux Economic Union and the Benelux Organization for Intellectual Property (BOIP), although it may also be tasked with advising the three governments, and with direct judicial tasks following the entry into force in 2016 of a 2012 protocol to the treaty.

A common visa exists since the end of 2010 for the territories of Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten and the Caribbean Netherlands which form together the territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. The visa is not valid for the European part of the Netherlands, which is part of the Schengen Area.
The Convention on the association of the Netherlands Antilles with the European Economic Community is an international agreement amending the Treaty establishing the European Economic Community, with the aim of awarding OCT status to the Netherlands Antilles, which was a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1954 until 2010. A full treaty revision was needed because Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, and Luxembourg wanted to add a protocol on the import of refined petroleum products from the Netherlands Antilles.
The Conventions concerning Employment of Women during the Night are conventions drafted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) which prohibit women from performing industrial work during the night. The first convention was adopted in 1919 and revised versions were adopted in 1934 and 1948. A protocol to the convention was adopted in 1990 allowing for easing of the restriction under conditions. As of April 2011 the conventions had 27, 15, 46 (undenounced) ratifications respectively. The protocol was ratified 5 and denounced by 2.
Patent law in the Netherlands, or simply Dutch patent law, is mainly governed by the Kingdom Patents Act and the European Patent Convention. A patent covering the Netherlands can be obtained through three different routes: through the direct filing of a national patent application with the Netherlands Patent Office, through the filing of a European patent application, or through the filing of an international application under the Patent Cooperation Treaty followed by the entry into European phase of said international application. The Dutch patent has a term of 20 years and has effect in the Netherlands, Curaçao and Sint Maarten. Aruba has its own patent system.

In the Netherlands, from the entry into force of the Advisory Referendum Act on 1 July 2015, until its repeal on 18 February 2018, most types of primary laws could be subjected to a suspensory, non-binding referendum if requested shortly after royal assent and subsequent proclamation. If a law was rejected by more than half of the votes cast, with a mandatory turnout of at least 30%, its entry into force was to be suspended indefinitely and a follow-up law had to be enacted that either repealed the law or provided for its entry into force.
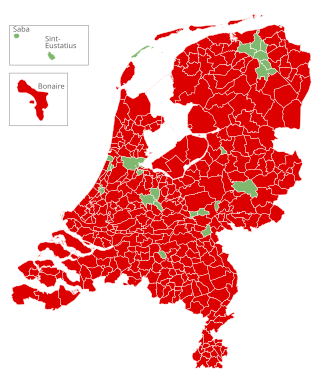
An advisory referendum on the approval of the Ukraine–European Union Association Agreement was held in the Netherlands on 6 April 2016. The referendum question was: "Are you for or against the Approval Act of the Association Agreement between the European Union and Ukraine?"
The Ministry of Justice is the Aruban Ministry responsible for justice, imprisonment and public security. The Ministry was created in 1986, following Aruba's Status aparte" Per an ordinance passed in 2002, the ministry is organized as follows

Netherlands–Sweden relations are the bilateral relations between Sweden and the Netherlands. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe, NATO and the European Union. The Netherlands has an embassy in Stockholm, while Sweden has an embassy in The Hague. the Netherlands strongly supported Sweden's NATO membership during the latter's accession process.

Caha di orgel is a mechanical music instrument that bridges the gap between a barrel piano and an organ.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Overheid, Aruba (2014-01-27). "10.07AB97.029 Octrooiverordening". www.overheid.aw (in Dutch). Retrieved 2023-04-30.
- 1 2 3 Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Netherlands, M.J.M. Verhagen (31 October 2007). "Protocol tot wijziging van de TRIPS-Overeenkomst, met bijlage en aanhangsel bij de bijlage; Genève, 6 december 2005". officielebekendmakingen.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- 1 2 "Patent". Bureau of Intellectual Property Aruba. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- 1 2 "FAQ". Bureau of Intellectual Property Aruba. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ "Patent Cooperation Treaty". overheid.nl. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ "Notice from the European Patent Office concerning the requirements to be observed when filing an international application with the EPO as a PCT receiving Office Annex: Applicability of the PCT to EPC territories". European Patent Office . 31 March 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ "Strasbourg Agreement concerning the international Patent Classification of March 24, 1971". overheid.nl. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ "Contracting Parties > Budapest Treaty > Netherlands". WIPO . Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ "Rijkswet van 17 november 2005, houdende goedkeuring en uitvoering van de op 17 december 1991 te München tot stand gekomen Akte tot herziening van artikel 63 van het Verdrag inzake de verlening van Europese octrooien van 5 oktober 1973 (TRB. 1992, 47), het op 1 juni 2000 te Genève tot stand gekomen Verdrag inzake octrooirecht (TRB. 2001, 120), het op 17 oktober 2000 te Londen tot stand gekomen Verdrag inzake de toepassing van artikel 65 van het Verdrag inzake de verlening van Europese octrooien van 5 oktober 1973 (TRB. 2001, 21) en de op 29 november 2000 te München tot stand gekomen Akte tot herziening van het Verdrag inzake de verlening van Europese octrooien (TRB. 2002, 64)". 17 January 2006.