Epidemiology
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2021) |
Pathergy is a skin condition in which a minor trauma such as a bump or bruise leads to the development of skin lesions or ulcers that may be resistant to healing. Pathergy can also lead to ulcerations at the site of surgical incisions. Pathergy is seen with both Behçet's disease and pyoderma gangrenosum. [1] A highly similar phenomenon known as the Koebner phenomenon occurs in autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus, among others.
Doctors looking toward a diagnosis of Behçet's disease may attempt to induce a pathergy reaction with a test known as a "skin prick test". [2] The inflammation and ulceration that occurs as a result of pathergy in pyoderma gangrenosum often responds to systemic steroid therapy.
The pathergy reaction is a unique feature of Behçet's disease and, according to the International Study Group for Behcet's Disease, is among the major criteria required for the diagnosis. Different positive pathergy reaction rates in BD have been reported worldwide. When BD-positive groups are studied for pathergy reaction, the pathergy-positive and pathergy-negative BD groups showed a similar male: female ratio, age at disease onset, and mean disease duration. They also exhibited similar HLA-B51 levels and a similar frequency of oral ulcerations in close family members. The mucocutaneous manifestations, systemic disease expression, and severity score were similar in patients with and without the pathergy reaction. The presence of a positive pathergy reaction is not associated with an increased risk for specific mucocutaneous or systemic manifestations of the disease, and probably does not predict a more severe disease course. [3]
It is also important to note that, while a positive pathergy reaction helps to confirm a specific Behçet's disease diagnosis, a negative reaction does not invalidate a BD diagnosis, because the disease process has to be active at the time of the skin prick test to produce a pathergy reaction. Differences in positive/negative pathergy and severity of the reaction depend on disease activity, ethnicity, type of needle used for the prick test, among other factors. [2]
Pathergy test is done both orally and cutaneous.
Orally, the lower lip is the site of testing. Appearance of any ulcer or papule indicates a positive pathergy reaction.
Cutaneous sites are the flexor forearm.
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2021) |

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer.

An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation.

A mouth ulcer (aphtha) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause. Rarely, a mouth ulcer that does not heal may be a sign of oral cancer. These ulcers may form individually or multiple ulcers may appear at once. Once formed, an ulcer may be maintained by inflammation and/or secondary infection.

Chancroid is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection characterized by painful sores on the genitalia. Chancroid is known to spread from one individual to another solely through sexual contact. However, there have been reports of accidental infection through the hand.

Granuloma inguinale is a bacterial disease caused by Klebsiella granulomatis characterized by genital ulcers. It is endemic in many less-developed regions. It is also known as donovanosis, granuloma genitoinguinale, granuloma inguinale tropicum, granuloma venereum, granuloma venereum genitoinguinale, lupoid form of groin ulceration, serpiginous ulceration of the groin, ulcerating granuloma of the pudendum, and ulcerating sclerosing granuloma. Oral manifestations are also notably seen. The lesions of oral cavity are usually secondary to active genital lesions.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

CREST syndrome, also known as the limited cutaneous form of systemic sclerosis (lcSSc), is a multisystem connective tissue disorder. The acronym "CREST" refers to the five main features: calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia.

Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term canker sore is also used, mainly in North America, although it may also refer to other types of mouth ulcers. The cause is not completely understood but involves a T cell-mediated immune response triggered by a variety of factors which may include nutritional deficiencies, local trauma, stress, hormonal influences, allergies, genetic predisposition, certain foods, dehydration, some food additives, or some hygienic chemical additives like SDS.
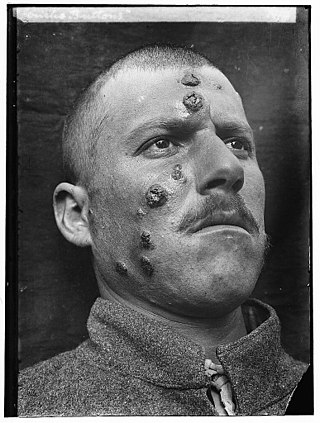
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about thirty species of Leishmania that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.

Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare, inflammatory skin disease where painful pustules or nodules become ulcers that progressively grow. Pyoderma gangrenosum is not infectious.

Gingivostomatitis is a combination of gingivitis and stomatitis, or an inflammation of the oral mucosa and gingiva. Herpetic gingivostomatitis is often the initial presentation during the first ("primary") herpes simplex infection. It is of greater severity than herpes labialis which is often the subsequent presentations. Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis is the most common viral infection of the mouth.

Sweet syndrome (SS), or acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a skin disease characterized by the sudden onset of fever, an elevated white blood cell count, and tender, red, well-demarcated papules and plaques that show dense infiltrates by neutrophil granulocytes on histologic examination.

Pemphigoid is a group of rare autoimmune blistering diseases of the skin, and mucous membranes. As its name indicates, pemphigoid is similar in general appearance to pemphigus, but, unlike pemphigus, pemphigoid does not feature acantholysis, a loss of connections between skin cells.

The Koebner phenomenon or Köbner phenomenon, also called the Koebner response or the isomorphic response, attributed to Heinrich Köbner, is the appearance of skin lesions on lines of trauma. The Koebner phenomenon may result from either a linear exposure or irritation. Conditions demonstrating linear lesions after a linear exposure to a causative agent include: molluscum contagiosum, warts and toxicodendron dermatitis. Warts and molluscum contagiosum lesions can be spread in linear patterns by self-scratching ("auto-inoculation"). Toxicodendron dermatitis lesions are often linear from brushing up against the plant. Causes of the Koebner phenomenon that are secondary to scratching rather than an infective or chemical cause include vitiligo, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen nitidus, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and keratosis follicularis.
A genital ulcer is an open sore located on the genital area, which includes the vulva, penis, perianal region, or anus. Genital ulcers are most commonly caused by infectious agents. However, this is not always the case, as a genital ulcer may have noninfectious causes as well.

PAPA syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterised by its effects on skin and joints. The acronym PAPA stands for pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum and acne.
Cryofibrinogenemia refers to a condition classified as a fibrinogen disorder in which a person's blood plasma is allowed to cool substantially, causing the (reversible) precipitation of a complex containing fibrinogen, fibrin, fibronectin, and, occasionally, small amounts of fibrin split products, albumin, immunoglobulins and other plasma proteins.

Behçet's disease (BD) is a type of inflammatory disorder which affects multiple parts of the body. The most common symptoms include painful sores on the mucous membranes of the mouth and other parts of the body, inflammation of parts of the eye, and arthritis. The sores can last from a few days, up to a week or more. Less commonly there may be inflammation of the brain or spinal cord, blood clots, aneurysms, or blindness. Often, the symptoms come and go.
Oral manifestations of systematic disease are signs and symptoms of disease occurring elsewhere in the body detected in the oral cavity and oral secretions. High blood sugar can be detected by sampling saliva. Saliva sampling may be a non-invasive way to detect changes in the gut microbiome and changes in systemic disease. Another example is tertiary syphilis, where changes to teeth can occur. Syphilis infection can be associated with longitudinal furrows of the tongue.