Location in Alaska | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Bering Sea |
| Coordinates | 52°55′20″N172°26′35″E / 52.92222°N 172.44306°E Coordinates: 52°55′20″N172°26′35″E / 52.92222°N 172.44306°E |
| Administration | |
Peaked Island is an uninhabited island located in the Aleutian Islands chain in Alaska. [1] It is the westernmost point in the 50 states by direction of travel, and last sunset (at equinox) in U.S. territory. West of it passes the International Date Line, after which come Russian territorial islands.

The Aleutian Islands, also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller ones belonging to both the U.S. state of Alaska and the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying an area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about 1,200 mi (1,900 km) westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and mark a dividing line between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude and the easternmost by longitude. The westernmost U.S. island in real terms, however, is Attu Island, west of which runs the International Date Line. While nearly all the archipelago is part of Alaska and is usually considered as being in the "Alaskan Bush", at the extreme western end, the small, geologically related Commander Islands belong to Russia.

Alaska is a U.S. state in the northwest extremity of North America, just across the Bering Strait from Asia. The Canadian province of British Columbia and territory of Yukon border the state to the east and southeast. Its most extreme western part is Attu Island, and it has a maritime border with Russia to the west across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas—southern parts of the Arctic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. It is the largest U.S. state by area and the seventh largest subnational division in the world. In addition, it is the 3rd least populous and the most sparsely populated of the 50 United States; nevertheless, it is by far the most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel in North America: its population—estimated at 738,432 by the United States Census Bureau in 2015— is more than quadruple the combined populations of Northern Canada and Greenland. Approximately half of Alaska's residents live within the Anchorage metropolitan area. Alaska's economy is dominated by the fishing, natural gas, and oil industries, resources which it has in abundance. Military bases and tourism are also a significant part of the economy.
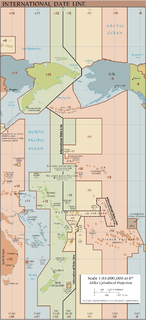
The International Date Line (IDL) is an imaginary line of demarcation on the surface of Earth that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole and demarcates the change of one calendar day to the next. It passes through the middle of the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude but deviating to pass around some territories and island groups.




