Twelve O'Clock High is a 1949 American war film directed by Henry King and based on the novel of the same name by Sy Bartlett and Beirne Lay, Jr. It stars Gregory Peck as Brig. General Frank Savage. Hugh Marlowe, Gary Merrill, Millard Mitchell, and Dean Jagger also appear in supporting roles.

Eglin Air Force Base is a United States Air Force (USAF) base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about three miles (5 km) southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.

Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), the 1st Special Operations Wing (1 SOW), the USAF Special Operations School (USAFSOS) and the Air Combat Command's (ACC) 505th Command and Control Wing. It was named for First Lieutenant Donald Wilson Hurlburt, who died in a crash at Eglin. The installation is nearly 6,700 acres (27 km2) and employs nearly 8,000 military personnel.

Dobbins Air Reserve Base or Dobbins ARB is a United States Air Force reserve air base located in Marietta, Georgia, a suburb about 20 miles (32 km) northwest of Atlanta. Originally known as Dobbins Air Force Base, it was named in honor of Captain Charles M. Dobbins, a World War II C-47 pilot who died near Sicily.

Gunter Annex is a United States Air Force installation located in the North-northeast suburbs of Montgomery, Alabama. The base is named after former Montgomery mayor William Adams Gunter. Until 1992 it was known as Gunter Air Force Base or Gunter Air Force Station. It has been a military training base since its opening in 1940.

Dothan Regional Airport is a public airport in Dale County, Alabama, United States, seven miles northwest of Dothan, a city mostly in Houston County.

Duke Field, also known as Eglin AFB Auxiliary Field #3, is a military airport located three miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Crestview, in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States.
During World War II, Kansas was a major United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) training center for pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers. Kansas was favored because it has excellent, year-round flying conditions. The sparsely populated land made ideal locations for gunnery, bombing, and training ranges.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in California for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters and bombers.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Florida for antisubmarine defense in the western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico and for training pilots and aircrews of USAAF fighters, attack planes, and light and medium bombers. After early 1944, heavy bomber crews also trained in the State. However two major operations in Florida were the School of Applied Tactics and the air Proving Grounds which tested and developed new capabilities.

Mareeba Airfield is an airfield located 4.3 nautical miles south of Mareeba, Queensland, Australia. Built in 1942 as a US Army Air Force base during World War II, the airfield had two runways, with a complement of taxiways, hardstands and a containment area. After the war, much of the airfield reverted to agricultural use, while the southern runway remains as an active airfield.

Cross City Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force facility, located 1.6 miles (2.6 km) east of Cross City, Florida.

Taylor Field, now an industrial park, was an airport and military airfield located near Ocala, Florida. It was closed in 1962 and replaced by Ocala International Airport-Jim Taylor Field.

Naval Outlying Landing Field Choctaw is the United States Navy's designation for an auxiliary airfield that was originally constructed during World War II as Eglin Field Auxiliary Field # 10. It is located 16.6 miles northeast of Pensacola, Florida.

Wagner Field,, is a component of Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. It is located northeast of the main base, 13.9 miles northeast of Valparaiso, Florida.
Eglin Air Force Base, a United States Air Force base located southwest of Valparaiso, Florida, was established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base. It is named in honor of Lieutenant Colonel Frederick I. Eglin, who was killed in a crash of his Northrop A-17 pursuit aircraft on a flight from Langley to Maxwell Field, Alabama.

Pierce Field,, is a satellite airfield located northeast of the Main Base, 5.5 miles north-northeast of Valparaiso, Florida.

Piccolo Field,, is a closed United States Air Force field. It is located 9.3 miles northwest of Valparaiso, Florida.
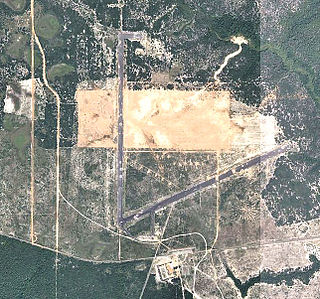
Baldsiefen Field,, is a closed United States Air Force field. It is located 10.2 miles east of Valparaiso, Florida.

Biancur Field,, , is a satellite airfield located northwest of the Main Base, 5.9 miles north-northeast of Valparaiso, Florida. It is also known as site "Test Site B6".