
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids.
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the human body. It is composed of around 270 bones at birth – this total decreases to around 206 bones by adulthood after some bones get fused together. The bone mass in the skeleton makes up about 14% of the total body weight and reaches maximum mass between the ages of 25 and 30. The human skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton is formed by the vertebral column, the rib cage, the skull and other associated bones. The appendicular skeleton, which is attached to the axial skeleton, is formed by the shoulder girdle, the pelvic girdle and the bones of the upper and lower limbs.

Polydactyly is a birth defect that results in extra fingers or toes. The hands are more commonly involved than the feet. Extra fingers may be painful, affect self-esteem, or result in clumsiness.

Hypophosphatasia (; also called deficiency of alkaline phosphatase, phosphoethanolaminuria, or Rathbun's syndrome; sometimes abbreviated HPP) is a rare, and sometimes fatal, inherited metabolic bone disease. Clinical symptoms are heterogeneous, ranging from the rapidly fatal, perinatal variant, with profound skeletal hypomineralization, respiratory compromise or vitamin B6 dependent seizures to a milder, progressive osteomalacia later in life. Tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) deficiency in osteoblasts and chondrocytes impairs bone mineralization, leading to rickets or osteomalacia. The pathognomonic finding is subnormal serum activity of the TNSALP enzyme, which is caused by one of 388 genetic mutations identified to date, in the gene encoding TNSALP. Genetic inheritance is autosomal recessive for the perinatal and infantile forms but either autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant in the milder forms.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

Gorham's disease, also known as Gorham vanishing bone disease and phantom bone disease, is a very rare skeletal condition of unknown cause. It is characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of distended, thin-walled vascular or lymphatic channels within bone, which leads to resorption and replacement of bone with angiomas and/or fibrosis.
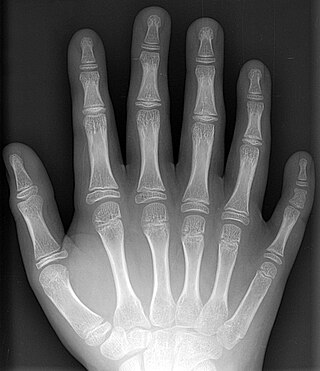
Supernumerary body parts are most commonly a congenital disorder involving the growth of an additional part of the body and a deviation from the body plan. Body parts may be easily visible or hidden away, such as internal organs.
Metaphyseal dysplasia, or Pyle disease, is a disorder of the bones. It is a rare disease in which the outer part of the shafts of long bones is thinner than normal and there is an increased chance of fractures. Its hallmark feature is an abnormality of the long bones in the arms and legs in which the ends (metaphyses) of the bones are abnormally broad; the shape of the bones resembles a boat oar or paddle. The broad metaphyses are due to enlargement of the spongy inner layer of bone. Although trabecular bone is expanded, the dense outermost layer of bone is thinner than normal. As a result, the bones are fragile and fracture easily. The bone abnormalities in the legs commonly cause knock knees in affected individuals.
Monostotic fibrous dysplasia is a form of fibrous dysplasia where only one bone is involved. It comprises a majority of the cases of fibrous dysplasia.

Keutel syndrome (KS) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by abnormal diffuse cartilage calcification, hypoplasia of the mid-face, peripheral pulmonary stenosis, hearing loss, short distal phalanges (tips) of the fingers and mild mental retardation. Individuals with KS often present with peripheral pulmonary stenosis, brachytelephalangism, sloping forehead, midface hypoplasia, and receding chin. It is associated with abnormalities in the gene coding for matrix gla protein, MGP. Being an autosomal recessive disorder, it may be inherited from two unaffected, abnormal MGP-carrying parents. Thus, people who inherit two affected MGP alleles will likely inherit KS.

Pycnodysostosis is a lysosomal storage disease of the bone caused by a mutation in the gene that codes the enzyme cathepsin K. It is also known as PKND and PYCD.
Eleventh finger may refer to:

Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a condition characterized by abnormal calcification/bone formation (hyperostosis) of the soft tissues surrounding the joints of the spine, and also of the peripheral or appendicular skeleton. In the spine, there is bone formation along the anterior longitudinal ligament and sometimes the posterior longitudinal ligament, which may lead to partial or complete fusion of adjacent vertebrae. The facet and sacroiliac joints tend to be uninvolved. The thoracic spine is the most common level involved. In the peripheral skeleton, DISH manifests as a calcific enthesopathy, with pathologic bone formation at sites where ligaments and tendons attach to bone.
Fibrocartilaginous mesenchymoma of bone (FCMB) is an extremely rare tumor first described in 1984. About 26 cases have been reported in literature, with patient ages spanning from 9 to 25 years, though a case in a male infant aged 1 year and 7 months has been reported. Quick growth and bulky size are remarkable features of this tumor.

Constriction ring syndrome (CRS) is a congenital disorder with unknown cause. Because of the unknown cause there are many different, and sometimes incorrect, names. It is a malformation due to intrauterine bands or rings that produce deep grooves in extremities such as fingers and toes. In rare cases the constriction ring can form around other parts of the fetus and cause amputation or even intrauterine death. The anatomy proximal to the site of constriction is developmentally normal. CRS can be associated with other malformations, with club foot being most common. The precise configuration of the bands, lymphedema, and character of the amputations are not predictable and vary with each individual patient. Also, more than one extremity is usually affected, and it is rare for only one ring to present as an isolated malformation with no other manifestation of this syndrome.
Tuberculous dactylitis, also known as spina ventosa, is a skeletal manifestation of tuberculosis, one of the commonest forms of bacterial osteitis. It affects children more often than adults. The first radiological description of the condition is credited to Feilchenfeld in 1896; however, the first histological description was given by Rankin in 1886. The Swedish botanist and physician Carl von Linne was the first to mention the condition by the name spina ventosa.

Vertebral hemangiomas or haemangiomas (VHs) are a common vascular lesion found within the vertebral body of the thoracic and lumbar spine. These are predominantly benign lesions that are often found incidentally during radiology studies for other indications and can involve one or multiple vertebrae. Vertebral hemangiomas are a common etiology estimated to be found in 10-12% of humans at autopsy. They are benign in nature and frequently asymptomatic. Symptoms, if they do occur, are usually related to large hemangiomas, trauma, the hormonal and hemodynamic changes of pregnancy (causing intra-spinal bleeding), or osseous expansion and extra-osseous extension into surround soft tissues or epidural region of the spinal canal.
Dieterich's disease, also known as avascular necrosis of the metacarpal head, is an extremely rare condition characterized by temporary or permanent loss of blood supply to the metacarpal head of the metacarpal bone, resulting in loss of bone tissue. The five metacarpal bones are long bones located between the carpals of the wrist and phalanges of the fingers. Collectively, the metacarpals are referred to as the "metacarpus."

Kirner's deformity, also known as dystelephangy, is an uncommon genetic hand malformation which is characterized by a radial and volar curvature of the distal phalange of the fifth (pinky) finger. It is merely cosmetic and doesn't affect hand function.

Schneckenbecken dysplasia is a rare pre-natally fatal hereditary autosomal recessive condition which affects the bones and pre-natal growth.













