Related Research Articles

Neisseria is a large genus of bacteria that colonize the mucosal surfaces of many animals. Of the 11 species that colonize humans, only two are pathogens, N. meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae.
MeNZB was a vaccine against a specific strain of group B meningococcus, used to control an epidemic of meningococcal disease in New Zealand. Most people are able to carry the meningococcus bacteria safely with no ill effects. However, meningococcal disease can cause meningitis and sepsis, resulting in brain damage, failure of various organs, severe skin and soft-tissue damage, and death.

Rino Rappuoli is an Italian immunologist. He is the head of vaccine research and development (R&D) at GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) Vaccines. Previously, he has served as visiting scientist at Rockefeller University and Harvard Medical School and held roles at Sclavo, Vaccine Research and CSO, Chiron Corporation, and Novartis Vaccines.

Neisseria meningitidis, often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs.

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. It has a high mortality rate if untreated but is vaccine-preventable. While best known as a cause of meningitis, it can also result in sepsis, which is an even more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.

Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is a pneumococcal vaccine made with the conjugate vaccine method and used to protect infants, young children, and adults against disease caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). It contains purified capsular polysaccharide of pneumococcal serotypes conjugated to a carrier protein to improve antibody response compared to the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of the conjugate vaccine in routine immunizations given to children.
Eculizumab, sold under the brand name Soliris among others, is a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody used to treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, generalized myasthenia gravis, and neuromyelitis optica. In people with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, it reduces both the destruction of red blood cells and need for blood transfusion, but does not appear to affect the risk of death. Eculizumab was the first medication approved for each of its uses, and its approval was granted based on small trials. It is given by intravenous infusion. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody functioning as a terminal complement inhibitor. It binds to the complement C5 protein and inhibits activation of the complement system, a part of the body's immune system. This binding prevents the breakdown of red blood cells in the bloodstream in people with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome.

Hepatitis B vaccine is a vaccine that prevents hepatitis B. The first dose is recommended within 24 hours of birth with either two or three more doses given after that. This includes those with poor immune function such as from HIV/AIDS and those born premature. It is also recommended that health-care workers be vaccinated. In healthy people, routine immunization results in more than 95% of people being protected.

The Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine, also known as Hib vaccine, is a vaccine used to prevent Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection. In countries that include it as a routine vaccine, rates of severe Hib infections have decreased more than 90%. It has therefore resulted in a decrease in the rate of meningitis, pneumonia, and epiglottitis.

JN-International Medical Corporation (JNIMC) is a U.S.-based biopharmaceutical corporation which since 1998 has been focused on developing vaccines and diagnostics for infectious disease for developing countries. This private corporation was founded in 1998 by Dr. Jeeri R. Reddy with the help of Dr. Kelly F. Lechtenberg in a small rural town, Oakland, Nebraska. From there it grew and expanded until in the year 2000 the corporation moved to Omaha, Nebraska.
NmVac4-A/C/Y/W-135 is the commercial name of the polysaccharide vaccine against the bacterium that causes meningococcal meningitis. The product, by JN-International Medical Corporation, is designed and formulated to be used in developing countries for protecting populations during meningitis disease epidemics.

Jeeri Reddy an American biologist who became an entrepreneur, developing new generation preventive and therapeutic vaccines. He has been an active leader in the field of the biopharmaceutical industry, commercializing diagnostics and vaccines through JN-International Medical Corporation. He is the scientific director and president of the corporation that created the world's first serological rapid tests for Tuberculosis to facilitate acid-fast bacilli microscopy for the identification of smear-positive and negative cases. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV was achieved in South East Asia by the use of rapid tests developed by Reddy in 1999. Reddy through his Corporation donated $173,050 worth of Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs) for malaria in Zambia and actively participated in the prevention of child deaths due to Malaria infections. Reddy was personally invited by the president, George W. Bush, and First Lady Laura Bush to the White House for Malaria Awareness Day sponsored by US President Malaria Initiative (PMI) on Wednesday, April 25, 2007.
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by Neisseria meningitidis. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between 85 and 100% effective for at least two years. They result in a decrease in meningitis and sepsis among populations where they are widely used. They are given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin.
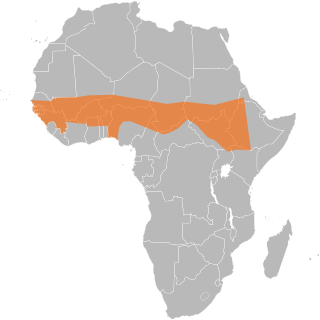
The African meningitis belt is a region in sub-Saharan Africa where the rate of incidence of meningitis is very high. It extends from Senegal to Ethiopia, and the primary cause of meningitis in the belt is Neisseria meningitidis.
MenAfriVac is a vaccine developed for use in sub-Saharan Africa for children and adults between 9 months and 29 years of age against meningococcal bacterium Neisseria meningitidis group A. The vaccine costs less than US$0.50 per dose.
CRM197 is a non-toxic mutant of diphtheria toxin, currently used as a carrier protein for polysaccharides and haptens to make them immunogenic. There is some dispute about the toxicity of CRM197, with evidence that it is toxic to yeast cells and some mammalian cell lines.

A hexavalent vaccine, or 6-in-1 vaccine, is a combination vaccine with six individual vaccines conjugated into one, intended to protect people from multiple diseases. The term usually refers to the children's vaccine that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, haemophilus B, and hepatitis B, which is used in more than 90 countries around the world including in Europe, Canada, Australia, Jordan, and New Zealand.

A vaccine dose contains many ingredients very little of which is the active ingredient, the immunogen. A single dose may have merely nanograms of virus particles, or micrograms of bacterial polysaccharides. A vaccine injection, oral drops or nasal spray is mostly water. Other ingredients are added to boost the immune response, to ensure safety or help with storage, and a tiny amount of material is left-over from the manufacturing process. Very rarely, these materials can cause an allergic reaction in people who are very sensitive to them.
Dan M. Granoff is an infectious disease physician-scientist who was named the 2014 Maurice Hilleman/Merck Laureate by the American Society for Microbiology for outstanding contributions to vaccine discovery and development. Beginning in 2011, Granoff held the Clorox Foundation Endowed Chair and was director of the Center of Immunobiology and Vaccine Development at Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute. His work increased understanding of basic mechanisms of human immunity to encapsulated bacteria, and furthered development of vaccines against Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) and Neisseria meningitidis.
References
- 1 2 "Penbraya". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2023.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Pentavalent Meningococcal Vaccine from Pfizer for Ages 10 to 25 years". Patient Care Online. 24 October 2023. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ↑ "Meningococcal Disease". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 1 September 2023. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ↑ "Approval-first for meningococcal vaccine". European Pharmaceutical Review. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- ↑ "Trumenba". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 9 March 2023.
- ↑ Dhillon S, Pace D (November 2017). "Meningococcal Quadrivalent Tetanus Toxoid Conjugate Vaccine (MenACWY-TT; Nimenrix®): A Review". Drugs. 77 (17): 1881–1896. doi:10.1007/s40265-017-0828-8. PMID 29094312. S2CID 24522214.
- ↑ "Penbraya: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ↑ Beernink PT (March 2020). "Effect of complement Factor H on antibody repertoire and protection elicited by meningococcal capsular group B vaccines containing Factor H binding protein". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 16 (3): 703–712. doi:10.1080/21645515.2019.1664241. PMC 7227650 . PMID 31526219.
- ↑ "Penbraya (meningococcal groups A, B, C, W, and Y vaccine) FDA Approval History". Drugs.com. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ↑ "Penbraya (meningococcal groups A, B, C, W, and Y vaccine) – New vaccine approval". Optum Rx. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- 1 2 "Penbraya EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 19 September 2024. Retrieved 21 September 2024. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.