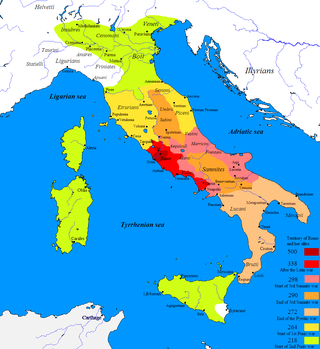
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.

Samnium is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were Safinim for the country and Safineis for the people. The language of these endonyms and of the population was the Oscan language. However, not all the Samnites spoke Oscan, and not all the Oscan-speakers lived in Samnium.

The Samnites were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
Ausona was a 4th-century BC city in the central Italian region of Latium. It was one of the three cities possessed by the tribe of the Ausones and its name seems to imply that it was their chief city or metropolis. It is only once mentioned in history: during the Second Samnite War, when—the Ausones having revolted against the Romans—all three of their cities were betrayed into the hands of the Roman consuls, and their inhabitants put to the sword without mercy. No subsequent notice is found of Ausona; but it is supposed to have been situated on the banks of the little river still called Ausente, which flows into the Liris near its mouth. The plain below the modern village of Le Fratte, near the sources of this little stream, is still known as the Piano dell'Ausente; and some remains of a Roman town have been discovered there.

Isernia is a town and comune in the southern Italian region of Molise, and the capital of the province of Isernia.

Arpino is a comune (municipality) in the province of Frosinone, in the Latin Valley, region of Lazio in central Italy, about 100 km SE of Rome. Its Roman name was Arpinum. The town produced two consuls of the Roman republic: Gaius Marius and Marcus Tullius Cicero.

The Battle of Mount Gaurus, 343 BC, was the first battle of the First Samnite War and also the first battle fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites. The battle is described by the Roman historian Livy as part of Book Seven of his history of Rome, Ab Urbe Condita Libri, where he narrates how the Roman consul Marcus Valerius Corvus won a hard-fought battle against the Samnites at Mount Gaurus, near Cumae, in Campania. Modern historians however believe that most, if not all, of the detail in Livy's description has been invented by him or his sources.

The Battle of Lautulae was a battle fought in 315 BC during the Second Samnite War, opposing the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who defeated the Romans.
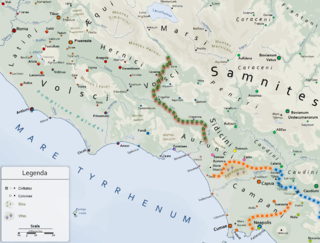
The Hirpini were an ancient Samnite tribe of Southern Italy. While generally regarded as having been Samnites, sometimes they are treated as a distinct and independent nation. They inhabited the southern portion of Samnium, in the more extensive sense of that name, roughly the area now known as Irpinia from their name—a mountainous region bordering on Basilicata towards the south, on Apulia to the east, and on Campania towards the west. No marked natural boundary separated them from these neighboring nations, but they occupied the lofty masses and groups of the central Apennines, while the plains on each side, and the lower ranges that bounded them, belonged to their more fortunate neighbors. The mountain basin formed by the three tributaries of the Vulturnus —the Tamarus, Calor, and Sabatus, which, with their valleys, unite near Beneventum, surrounded on all sides by lofty and rugged ranges of mountains—is the center and heart of their territory. They occupied the Daunian Mountains to the north, while its more southern portion comprised the upper valley of the Aufidus and the lofty group of mountains where that river takes its rise.

Latium adiectum or Latium Novum was a region of Roman Italy between Monte Circeo and the river Garigliano, south of and immediately adjacent to Old Latium, hence its name of attached Latium.

The (Second) Latin War was a conflict between the Roman Republic and its neighbors, the Latin peoples of ancient Italy. It ended in the dissolution of the Latin League and incorporation of its territory into the Roman sphere of influence, with the Latins gaining partial rights and varying levels of citizenship.

Mirabello Sannitico is a small town in the province of Campobasso, Molise, southern Italy. The population is about 2,100 inhabitants. It has an agrarian-based culture and history, dating back to at least the 12th century. Nearby towns include Campobasso to the northwest and Vinchiaturo to the southwest. The Tappino River flows on either side of the town on the north and south.

The Frentani were an Italic tribe occupying the tract on the southeast coast of the Italian peninsula from the Apennines to the Adriatic, and from the frontiers of Apulia to those of the Marrucini. They were bounded on the west by the Samnites, with whom they were closely connected, and from whom they were originally descended. Hence Scylax assigns the whole of this line of coast, from the frontiers of Apulia to those of Picenum, to the Samnites. Their exact limits are less clearly defined, and there is considerable discrepancy in the statements of ancient geographers: Larinum, with its territory, being by some writers termed a city of the Frentani, while the more general opinion included it in Apulia, and thus made the river Tifernus the limit of the two countries. The northern boundary of the Frentani is equally uncertain; both Strabo and Ptolemy concur in fixing it at the river Sagrus, while Pliny extends their limits as far as the Aternus, and, according to Mela, they possessed the mouths both of that river and the Matrinus. The latter statement is certainly inaccurate; and Strabo distinctly tells us that the Marrucini held the right bank of the Aternus down to its mouth, while the Vestini possessed the left bank; hence, the former people must have intervened between the Frentani and the mouth of the Aternus. Pliny's account is, however, nearer the truth than that of Strabo and Ptolemy; for it is certain that Ortona and Anxanum, both of which are situated considerably to the north of the Sagrus, were Frentanian cities. The latter is indeed assigned by Ptolemy to that people, while Strabo also terms Ortona the port or naval station of the Frentani, but erroneously places it to the south of the river Sagrus. Hence, their confines must have approached within a few miles of the Aternus, though without actually abutting upon that river. On the west, they were probably not separated from the Samnites by any well-marked natural boundary, but occupied the lower slopes of the Apennines as well as the hilly country extending from thence to the sea, while the more lofty and central ridges of the mountains were included in Samnium.
"Ausones", the original name and the extant Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, to denote the particular tribe which Livy called the Aurunci, but later it was applied to all Italians, and Ausonia became a poetic term, in Greek and Latin, for Italy itself.
The Caraceni or Caricini or Carricini were a tribe of the Italic Samnites. According to Salmon, their name comes from the Celtic carreg- and car- <Rock>. According to Ptolemy, they inhabited the most northern part of Samnium, bordering on the Peligni and the Frentani; but more especially the upper valley of the Sagrus. The only city that he assigns to them is Aufidena. Zonaras describes them as possessing a town or stronghold, which was taken by the Roman consuls Q. Gallus and C. Fabius with difficulty. Aufidena has been identified with the modern Castel di Sangro, which seems, from the inscriptions and other remains discovered there, to have been an ancient town.
The Caudini were a Samnite tribe that lived among the mountains ringing Campania and in the valleys of the Isclero and Volturnus rivers. Their capital was at Caudium, but it seems certain that the appellation was not confined to the citizens of Caudium and its immediate territory.

The Capture of Neapolis took place during the Second Samnite War in 327 BC, when the Romans seized the city of Neapolis from the Samnites, an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium. The city's fall is attributed to treachery committed by some of its citizens.
The military campaigns of the Samnite Wars were an important stage in Roman expansion in the Italian Peninsula.

The Battle of Saticula, 343 BC, was the second of three battles described by the Roman historian Livy, in Book Seven of his history of Rome, Ab Urbe Condita, as taking place in the first year of the First Samnite War. According to Livy's extensive description, the Roman commander, the consul Aulus Cornelius Cossus was marching from Saticula when he was almost trapped by a Samnite army in a mountain pass. His army was only saved because one of his military tribunes, Publius Decius Mus, led a small group of men to seize a hilltop, distracting the Samnites and allowing the consul to escape. During the night Decius and his men were themselves able to escape. The next day the reunited Romans attacked the Samnites and completely routed them. Several other ancient authors also mention Decius' heroic acts. Modern historians are however sceptical of the historical accuracy of Livy's account, and have in particular noted the similarities with how a military tribune is said to have saved Roman army in 258 BC during the First Punic War.
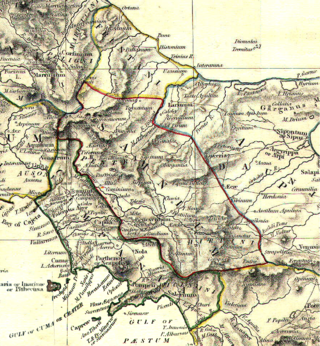
The Sidicini were one of the Italic peoples of ancient Italy. Their territory extended northward from their capital, Teanum Sidicinum, along the valley of the Liri river up to Fregellae, covering around 3,000 square kilometres in total. They were neighbors of the Samnites and Campanians, and allies of the Ausones and Aurunci. Their language was a part of the Osco-Umbrian linguistic family.















