
The Hell Gate Bridge, originally the New York Connecting Railroad Bridge or the East River Arch Bridge, is a 1,017-foot (310 m) steel through arch railroad bridge in New York City. The bridge crosses the Hell Gate, a strait of the East River, between Astoria in Queens and Randalls and Wards Islands in Manhattan.

The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
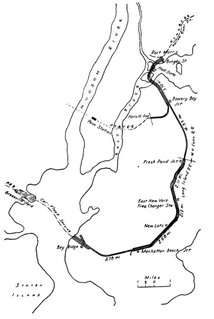
The New York Connecting Railroad or NYCR is a rail line in the borough of Queens in New York City. It links New York City and Long Island by rail directly to the North American mainland. Amtrak, CSX, Canadian Pacific Railway, Providence and Worcester Railroad and New York and Atlantic Railway (NYAR) currently use the line. It runs from the Hell Gate Bridge over the East River to Fresh Pond Junction yard in Glendale. It was completed in 1917. Amtrak uses the northernmost section of the line from Sunnyside Junction in the Woodside section of Queens to the Hell Gate Bridge into the Bronx from which it follows the line north to Boston.

The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over 398 miles of track to 137 different stations, with 58 stations on the north side with the remaining 79 stations on the south. It is operated under contract by Keolis, which took over operations on July 1, 2014 from the Massachusetts Bay Commuter Railroad Company (MBCR).

The Old Colony Railroad (OC) was a major railroad system, mainly covering southeastern Massachusetts and parts of Rhode Island. It operated from 1845 to 1893. Old Colony trains ran from Boston to points such as Plymouth, Fall River, New Bedford, Newport, Providence, Fitchburg, Lowell and Cape Cod. For many years the Old Colony Railroad Company also operated steamboat and ferry lines, including those of the Fall River Line with express train service from Boston to its wharf in Fall River where passengers boarded luxury liners to New York City. The company also briefly operated a railroad line on Martha's Vineyard, as well as the freight-only Union Freight Railroad in Boston. The OC was named after the "Old Colony", the nickname for the Plymouth Colony.

The New York and New England Railroad was a major railroad connecting southern New York State with Hartford, Connecticut, Providence, Rhode Island, and Boston, Massachusetts. It operated under that name from 1873 to 1893. Prior to 1873 it was known as the Boston, Hartford and Erie Railroad, which had been formed by several smaller railroads dating back to 1846. After bankruptcy in 1893, the New York and New England Railroad was reorganized and became known as the New England Railroad before its 1898 lease to the competing New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad. Today, most of the original New York and New England lines have been abandoned; however a portion in Massachusetts is now part of the MBTA's Franklin Line providing commuter rail service to South Station in Boston. The Connecticut Southern Railroad operates freight service on a small portion of the former NY&NE line near East Hartford and Manchester, Connecticut. Other portions in Connecticut and Rhode Island have been converted to rail trails.

The Newburgh, Dutchess and Connecticut Railroad, originally the Dutchess and Columbia Railroad and affectionately "The Never Did and Couldn't", is a link in the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad system in New York state.
The Housatonic Railroad is a Class III railroad operating in southwestern New England. It was chartered in 1983 to operate a short section of ex-New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in northwestern Connecticut, and has since expanded north and south, as well as west into New York State.

Founded in 1996, the Naugatuck Railroad is a common carrier railroad owned by the Railroad Museum of New England and operated by Naugatuck Railroad on tracks leased by Naugatuck Railroad from the Connecticut Department of Transportation. The original Naugatuck Railroad was a railroad chartered to operate through south central Connecticut in 1845, with the first section opening for service in 1849. In 1887 the line was leased by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, and became wholly owned by 1906. At its greatest extent the Naugatuck ran from Bridgeport north to Winsted. Today's Naugatuck Railroad runs from Waterbury to the end of track in Torrington, Connecticut. From Waterbury south to the New Haven Line, Metro-North Railroad operates commuter service on the Waterbury Branch.

The Waterbury Branch is a branch of the Metro-North Railroad New Haven Line, running north from a junction in the Devon section of Milford to Waterbury. Originally built as the Naugatuck Railroad, it once continued north to Winsted. The part north of Waterbury is now leased from CDOT by the Railroad Museum of New England, which operates excursion trains from Thomaston station through their operating subsidiary Naugatuck Railroad ; this name was chosen in homage of the original railroad. The trackage ends in Torrington but Metro North service on the branch ends at Waterbury. There are conceptual plans to extend service from its current terminus in Waterbury to Hartford via Bristol and New Britain. Currently, riders that want to continue to New Britain and Hartford have to transfer to an express bus operated by CTtransit at Waterbury. Except for one weekday morning peak train that operates from Waterbury to Stamford, all trains on this branch operate as shuttles between Waterbury and Bridgeport.

The New York, Providence and Boston Railroad, normally called the Stonington Line, was a major part of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad between New London, Connecticut and Providence, Rhode Island. It is now part of Amtrak's high-speed Northeast Corridor.

The East Side Railroad Tunnel is on the East Side of Providence, Rhode Island. It was opened on November 16, 1908, at a cost of $2 million. It runs 5,080 feet (1,550 m), under College Hill, from Gano Street to Benefit Street and is currently abandoned and sealed, but a project has been suggested to reuse it for either rail or bus use.

The Franklin Line, part of the MBTA Commuter Rail system, runs from Boston's South Station in a southwesterly direction toward Franklin, Massachusetts, utilizing the Northeast Corridor before splitting off onto the namesake Franklin Branch. Most Franklin Line trains connect to the Providence/Stoughton Line at Readville, though some weekday trains use the Dorchester Branch to access South Station. Most weekday trains, and all weekend trains, bypass Hyde Park and Plimptonville. Several weekday trains originate at Norwood Central or Walpole. Trains only serve Foxboro from Boston during special events at Gillette Stadium, but regular service is proposed.

The Naugatuck station is a commuter rail stop on the Waterbury Branch of the Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, located in Naugatuck, Connecticut, United States. All service on the Waterbury Branch is shuttle service to Bridgeport running on very light frequencies ; travel time to Bridgeport is 43 minutes.

Westerly is a passenger rail station on the Northeast Corridor located just north of downtown Westerly, Rhode Island. It is served by Amtrak's Northeast Regional.

The Valley Railroad is a heritage railway based in Connecticut on tracks of the Connecticut Valley Railroad, which was founded in 1868. It operates the Essex Steam Train and the Essex Clipper Dinner Train.

The Hyannis Transportation Center (HTC) is an intermodal transportation center in Hyannis, Massachusetts operated by the Cape Cod Regional Transit Authority (CCRTA). It is the terminus for several CCRTA bus lines and its CapeFLYER passenger train that operates on summer weekends between Boston South Station and Hyannis. It also used by the Plymouth and Brockton Street Railway and Peter Pan Bus Lines intercity bus services. The Cape Cod Central Railroad uses a separate station building across the tracks for its excursion services. A rail yard used by the Cape Cod Central is located north of the station, along with a former roundhouse.

Downtown New Britain is a bus rapid transit station and the terminus of the CTfastrak line, located just south of Route 72 off Columbus Boulevard and Main Street in New Britain, Connecticut. It opened with the line on March 28, 2015. The station consists of one side platform and one island platform, each of which has a number of bus bays for CTfastrak local and express services plus local CT Transit buses which do not use the busway. The station is located at the site of New Britain's former railroad station, which saw service from 1850 to 1960.

Forestville station is a former train station located off 171 Central Street in the Forestville village of Bristol, Connecticut. It was built in 1881 by the New York and New England Railroad, and was a key element of the prosperity of the village, benefiting from many daily passenger rail stops. Service to the area ended in 1960. The station, now repurposed to other uses, was added to the National Register of Historic Places on April 19, 1978 as Forestville Passenger Station.
The Ashtabula, Carson & Jefferson Railroad or Ashtabula, Carson & Jefferson Scenic Railroad is a Class III railroad that operates from a junction in Carson to Jefferson in Ashtabula County, Ohio. ACJR operates freight along with a tourist operation. The main commodities hauled on the line are fertilizer, paper for corrugated boxes, and plastic pellets used in injection molding.




















