
Components of an electrical circuit are electrically connected if an electric current can run between them through an electrical conductor. An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to create an electrical connection between parts of an electrical circuit, or between different electrical circuits, thereby joining them into a larger circuit.

The XLR connector is a type of electrical connector primarily used in professional audio, video, and stage lighting equipment. XLR connectors are cylindrical in design, with three to seven connector pins, and are often employed for analog balanced audio interconnections, AES3 digital audio, portable intercom, DMX512 lighting control, and for low-voltage power supply. XLR connectors are included to the international standard for dimensions, IEC 61076-2-103. The XLR connector resembles the DIN connector, but is larger, more robust and is physically incompatible with it.

The DIN connector is an electrical connector that was standardized by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the mid 1950's, initially with 3 pins for mono, but when stereo connections and gear appeared in late 1950's, versions with 5 pins or more were launched. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that limits the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, have been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 ; DIN 45322 ; DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 ; and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9.

Schuko is a plug/socket system used in much of Europe and in many countries east of there. It is a registered trademark referring to a system of AC power plugs and sockets that is defined as "CEE 7/3" (sockets) and "CEE 7/4" (plugs). A Schuko plug features two round pins of 4.8 mm diameter for the line and neutral contacts, plus two flat contact areas on the top and bottom side of the plug for protective earth (ground). The socket has a predominantly circular recess which is 17.5 mm deep with two symmetrical round apertures and two earthing clips on the sides of the socket positioned to ensure that the earth is always engaged before live pin contact is made. Schuko plugs and sockets are symmetric AC connectors. They can be mated in two ways, therefore line can be connected to either pin of the appliance plug. As with most types of European sockets, Schuko sockets can accept Europlugs. Schuko plugs are considered a very safe design when used with Schuko sockets, but they can also mate with other sockets to give an unsafe result.

The Electricity Supply Board is a state owned electricity company operating in the Republic of Ireland. While historically a monopoly, the ESB now operates as a commercial semi-state concern in a "liberalised" and competitive market. It is a statutory corporation whose members are appointed by the government of Ireland.

AC power plugs and sockets connect devices to mains electricity to supply them with electrical power. A plug is the connector attached to an electrically-operated device, often via a cable. A socket is fixed in place, often on the internal walls of buildings, and is connected to an AC electrical circuit. Inserting the plug into the socket allows the device to draw power from this circuit.

IEC 60309 is a series of international standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for "plugs, socket-outlets and couplers for industrial purposes". They are also referred to as "pin & sleeve" connectors in North America or as "CeeForm" connectors in the entertainment industry. The maximum voltage allowed by the standard is 1000 V DC or AC; the maximum current, 800 A; and the maximum frequency, 500 Hz. The ambient temperature range is −25 °C to 40 °C.

Industrial and multiphase plugs and sockets provide a connection to the electrical mains rated at higher voltages and currents than household plugs and sockets. They are generally used in polyphase systems, with high currents, or when protection from environmental hazards is required. Industrial outlets may have weatherproof covers, waterproofing sleeves, or may be interlocked with a switch to prevent accidental disconnection of an energized plug. Some types of connectors are approved for hazardous areas such as coal mines or petrochemical plants, where flammable gas may be present.

The Europlug is a flat, non-rewirable two-pole, round-pin domestic AC power plug, rated for voltages up to 250 V and currents up to 2.5 A. It is a compromise design intended to connect low-power Class II appliances safely to the many different forms of round-pin domestic power socket used across Europe. However, it is not compatible with the rectangular-pin BS 1363 sockets found in Cyprus, Gibraltar, Singapore, Malaysia, United Arab Emirates, Hong Kong, Ireland, Malta and the United Kingdom. By the standard, Europlugs must be non-rewirable and must be supplied attached to a power cord; anything else is non-compliant.
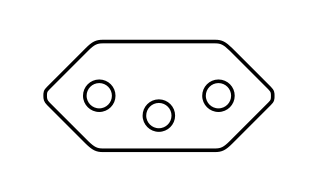
IEC 60906-1 is an international standard designed "to provide a standard for a safe, compact and practical 16 A 250 V AC system of plugs and socket-outlets that could be accepted by many countries as their national standard, even if not in the near future." The standard was originally published by the International Electrotechnical Commission in 1986; the current edition is ed2.0 published in 2009. Although it is almost identical to the Swiss SEV 1011 T12 plug for 10 A 250 V a.c. standardised in 1937, its dimensions are slightly different and its polarization is flipped. As of July 2014, only South Africa has introduced a standard based closely on IEC 60906-1. Brazil used it as the basis for its NBR 14136 standard, but this is not compatible with IEC 60906-1. In 2017 the European Union (EU) published recommendations advising against the harmonisation of domestic plug and socket systems in the EU.

AS/NZS 3112 is the harmonised Australian and New Zealand standard for AC power plugs (male) and sockets (female). The standard is used in Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, Tonga, Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea and several other Pacific island countries, plus in Argentina and China. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) "world plugs" Web site calls this plug Type I.

SAE J1772, also known as a J plug or Type 1 connector after its international standard, IEC 62196 Type 1, is a North American standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles maintained by SAE International under the formal title "SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler".
The IECEE is the IEC System of Conformity Assessment Schemes for Electrotechnical Equipment and Components being a body of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The IEC uses the name IECEE for the IEC System for Conformity Testing and Certification of Electrotechnical Equipment and Components that is better known as the CB System

IEC 62196Plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets – Conductive charging of electric vehicles is a series of international standards that define requirements and tests for plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets for conductive charging of electric vehicles and is maintained by the technical subcommittee SC 23H “Plugs, Socket-outlets and Couplers for industrial and similar applications, and for Electric Vehicles” of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).

Plugs and sockets for electrical appliances not hardwired to mains electricity originated in the United Kingdom in the 1870s and were initially two-pin designs. These were usually sold as a mating pair, but gradually de facto and then official standards arose to enable the interchange of compatible devices. British standards have proliferated throughout large parts of the former British Empire.

The IEC 62196 Type 2 connector is used for charging electric vehicles, mainly within Europe, as it was declared standard by the EU. Based on widespread red IEC 60309 three phase plugs with five pins, which come in different diameters according to maximum current, a single size was selected, as maximum possible power will be communicated to the car via two additional communication pins and by a simple resistor coding within the cable. The onboard charger inside the car has to limit the current accordingly.
There are approximately 20 types in common use around the world, such as AC power plugs and sockets, and many obsolete socket types which are still found in older buildings.
CEE 7 is a standard for alternating-current plugs and sockets. First published in 1951 by the former International Commission on the Rules for the Approval of Electrical Equipment (IECEE), it unified standards produced by several continental European countries. The 2nd edition was published in 1963 and last updated in March 1983. It remains available from the IEC, but they state that "this standard shall not be used alone, it is to be used in addition to IEC 60884-1".

SN 441011, until 2019 SEV 1011, is the Swiss national standard for AC power plug for domestic use and similar purposes. The plug SN 441011 Type 12 and the socket SN 441011 Type 13 are also known internationally as Type J.

The IEC 62196 Type 3 connector is used for charging battery electric vehicles, mainly within France and Italy, as it was one of three AC plug standards described in IEC 62196-2. The Type 3 connector comes in two physical formats, Type 3A for single-phase (230V) and Type 3C for single- and three-phase (400V) alternating current (AC) power. Both have since been superseded by the Type 2 connector, the latter adopted as sole connector in 2013 by the European Union. The Type 1 connector is the corresponding AC connector standard used in North America, Japan, and South Korea.



















