Related Research Articles
Aramaic is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, southeastern Anatolia, Eastern Arabia and the Sinai Peninsula, where it has been continually written and spoken in different varieties for over three thousand years.

Etruscan was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually completely superseded by it. The Etruscans left around 13,000 inscriptions that have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Greek, or Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study, with it mostly being referred to as one of the Tyrsenian languages, at times as an isolate, and a number of other less well-known hypotheses.

The Lombards or Longobards were a Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
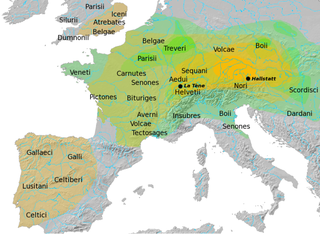
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of its area by the La Tène culture. It is commonly associated with Proto-Celtic speaking populations.

Juno was an ancient Roman goddess, the protector and special counsellor of the state. She was equated to Hera, queen of the gods in Greek mythology and a goddess of love and marriage. A daughter of Saturn and Ops, she was the sister and wife of Jupiter and the mother of Mars, Vulcan, Bellona, Lucina and Juventas. Like Hera, her sacred animal was the peacock. Her Etruscan counterpart was Uni, and she was said to also watch over the women of Rome. As the patron goddess of Rome and the Roman Empire, Juno was called Regina ("Queen") and was a member of the Capitoline Triad, centered on the Capitoline Hill in Rome, and also including Jupiter, and Minerva, goddess of wisdom.

The Duenos inscription is one of the earliest known Old Latin texts, variously dated from the 7th to the 5th century BC. It is inscribed on the sides of a kernos, in this case a trio of small globular vases adjoined by three clay struts. It was found by Heinrich Dressel in 1880 in the valley between Quirinale and Viminale in Rome. The kernos is part of the collection of the Staatliche Museen in Berlin.

Nynetjer is the Horus name of the third pharaoh of the Second Dynasty of Egypt during the Early Dynastic Period. Archaeologically, Nynetjer is the best attested king of the entire dynasty. Direct evidence shows that he succeeded Raneb on the throne. What happened after him is much less clear as historical sources and archaeological evidences point to some breakdown or partition of the state.

Menkauhor Kaiu was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Old Kingdom period. He was the seventh ruler of the Fifth Dynasty at the end of the 25th century BC or early in the 24th century BC.

Djedkare Isesi was a pharaoh, the eighth and penultimate ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt in the late 25th century to mid-24th century BC, during the Old Kingdom. Djedkare succeeded Menkauhor Kaiu and was in turn succeeded by Unas. His relationship to both of these pharaohs remain uncertain, although it is often conjectured that Unas was Djedkare's son, owing to the smooth transition between the two.

The Proto-Sinaitic script is a Middle Bronze Age writing system known from a small corpus of about 30-40 inscriptions and fragments from Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula, as well as two inscriptions from Wadi el-Hol in Middle Egypt. Together with about 20 known Proto-Canaanite inscriptions, it is also known as Early Alphabetic, i.e. the earliest trace of alphabetic writing and the common ancestor of both the Ancient South Arabian script and the Phoenician alphabet, which led to many modern alphabets including the Greek alphabet. According to common theory, Canaanites or Hyksos who spoke a Canaanite language repurposed Egyptian hieroglyphs to construct a different script.

Nyuserre Ini was an Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, the sixth ruler of the Fifth Dynasty during the Old Kingdom period. He is credited with a reign of 24 to 35 years depending on the scholar, and likely lived in the second half of the 25th century BCE. Nyuserre was the younger son of Neferirkare Kakai and queen Khentkaus II, and the brother of the short-lived king Neferefre. He may have succeeded his brother directly, as indicated by much later historical sources. Alternatively, Shepseskare may have reigned between the two as advocated by Miroslav Verner, albeit only for a few weeks or months at the most. The relation of Shepseskare with Neferefre and Nyuserre remains highly uncertain. Nyuserre was in turn succeeded by Menkauhor Kaiu, who could have been his nephew and a son of Neferefre.
The Pillar of the Boatmen is a monumental Roman column erected in Lutetia in honour of Jupiter by the guild of boatmen in the 1st century AD. It is the oldest monument in Paris and is one of the earliest pieces of representational Gallo-Roman art to carry a written inscription.

The Franks Casket is a small Anglo-Saxon whale's bone chest from the early 8th century, now in the British Museum. The casket is densely decorated with knife-cut narrative scenes in flat two-dimensional low-relief and with inscriptions mostly in Anglo-Saxon runes. Generally thought to be of Northumbrian origin, it is of unique importance for the insight it gives into early Anglo-Saxon art and culture. Both identifying the images and interpreting the runic inscriptions has generated a considerable amount of scholarship.

A hammer mill, hammer forge or hammer works was a workshop in the pre-industrial era that was typically used to manufacture semi-finished, wrought iron products or, sometimes, finished agricultural or mining tools, or military weapons. The feature that gave its name to these workshops was the water-driven trip hammer, or set of hammers, used in the process. The shaft, or 'helve', of the hammer was pivoted in the middle and the hammer head was lifted by the action of cams set on a rotating camshaft that periodically depressed the end of the shaft. As it rose and fell, the head of the hammer described an arc. The face of the hammer was made of iron for durability.

Ancient Celtic warfare refers to the historical methods of warfare employed by various Celtic people and tribes from Classical antiquity through the Migration period.

Gothic is an extinct East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text corpus. All others, including Burgundian and Vandalic, are known, if at all, only from proper names that survived in historical accounts, and from loanwords in other, mainly Romance, languages.

Lombardic or Langobardic is an extinct West Germanic language that was spoken by the Lombards, the Germanic people who settled in present-day Italy in the sixth century and established the Kingdom of the Lombards. It was already declining by the seventh century because the invaders quickly adopted the Vulgar Latin spoken by the local population. Many toponyms in modern Lombardy and Greater Lombardy and items of Lombard and broader Gallo-Italic vocabulary derive from Lombardic.

In the European High Middle Ages, the typical sword was a straight, double-edged weapon with a single-handed, cruciform hilt and a blade length of about 70 to 80 centimetres. This type is frequently depicted in period artwork, and numerous examples have been preserved archaeologically.

The Lead Plaque of Magliano, which contains 73 words in the Etruscan language, seems to be a dedicatory text, including as it does many names of mostly underworld deities. It was found in 1882, and dates to the mid 5th century BC. It is now housed in the National Archaeological Museum in Florence.

The Achaemenid royal inscriptions are the surviving inscriptions in cuneiform script from the Achaemenid Empire, dating from the 6th to 4th century BCE. These inscriptions are primary sources for the history of the empire, along with archaeological evidence and the administrative archives of Persepolis. However, scholars are reliant on Greek sources to reconstruct much of Achaemenid history.
References
- ↑ Drboglav, D. (1984): Zagadki latinskih klejm na mečah IX-XIV vekov (Klassifikazija, datirovka i čtenie nadpisej). Moskva.
- ↑ Štereva, I. (1975): Kam vaprosa za mečovete v srednovekovna Balgarija. V: Archeologia, kn. 2, 55-60.
- ↑ Mihailov, St. (1985): Nadpisăt na latinski ezik vărhu meča ot Perniškata krepost. V: Archeologia, kn. 3, 46 sl.
- ↑ Dentschewa, Langobardische (?)…, p. 1.
- Friedrich E. GRÜNZWEIG: Ein Schwert mit Inschrift aus Pernik (Bulgarien), Amsterdamer Beiträge zur älteren Germanistik 61 (2006).
- Dentschewa, Emilia: "Langobardische (?) Inschrift auf einem Schwert aus dem 8. Jahrhundert in bulgarischem Boden". In: Beiträge zur Geschichte der deutschen Sprache und Literatur, Band 128 (2006) Heft 1, S. 1-11.
- Dentschewa, Emilia: "+IHININIhVILPIDHINIhVILPN+ oder die Botschaft eines Schwertes aus der Zeit des Königreichs der Langobarden (?)" In: Archaeologia Bulgarica IX (2005) Heft 2, S. 99-105.