Related Research Articles

Kavad I was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 488 to 531, with a two or three-year interruption. A son of Peroz I, he was crowned by the nobles to replace his deposed and unpopular uncle Balash.

Peroz I was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 459 to 484. A son of Yazdegerd II, he disputed the rule of his elder brother and incumbent king Hormizd III, eventually seizing the throne after a two-year struggle. His reign was marked by war and famine. Early in his reign, he successfully quelled a rebellion in Caucasian Albania in the west, and put an end to the Kidarites in the east, briefly expanding Sasanian rule into Tokharistan, where he issued gold coins with his likeness at Balkh. Simultaneously, Iran was suffering from a seven-year famine. He soon clashed with the former subjects of the Kidarites, the Hephthalites, who possibly had previously helped him to gain his throne. He was defeated and captured twice by the Hephthalites and lost his recently acquired possessions.

Yazdegerd II, was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 438 to 457. He was the successor and son of Bahram V.

Balash was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 484 to 488. He was the brother and successor of Peroz I, who had been defeated and killed by a Hephthalite army.

Jamasp was Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 496 to 498/9. He was a son of Peroz I and younger brother of Kavad I. Jamasp was installed on the Sasanian throne upon the deposition of the latter by the nobility and clergy.

The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Europe as the Chionites, and may even be considered as identical to the Chionites. The 5th century Byzantine historian Priscus called them Kidarite Huns, or "Huns who are Kidarites". The Huna/Xionite tribes are often linked, albeit controversially, to the Huns who invaded Eastern Europe during a similar period. They are entirely different from the Hephthalites, who replaced them about a century later.
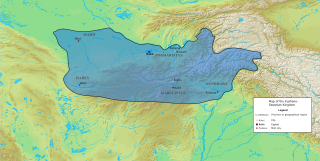
Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom is a historiographic term used by modern scholars to refer to a branch of the Sasanian Persians who established their rule in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries CE at the expense of the declining Kushans. They captured the provinces of Sogdiana, Bactria and Gandhara from the Kushans in 225 CE. The Sasanians established governors for the Sasanian Empire, who minted their own coinage and took the title of Kushanshas, i.e. "Kings of the Kushans". They are sometimes considered as forming a "sub-kingdom" inside the Sasanian Empire. This administration continued until 360-370 CE, when the Kushano-Sasanians lost much of its domains to the invading Kidarite Huns, whilst the rest was incorporated into the imperial Sasanian Empire. Later, the Kidarites were in turn displaced by the Hephthalites. The Sasanians were able to re-establish some authority after they destroyed the Hephthalites with the help of the Turks in 565, but their rule collapsed under Arab attacks in the mid 7th century.

The Hephthalite–Sasanian War of 484 was a military confrontation that took place in 484 between an invading force of the Sasanian Empire under the command of Peroz I and a smaller army of the Hephthalite Empire under the command of Khushnavaz. The battle was a catastrophic defeat for the Sasanian forces who were almost completely wiped out. Peroz, the Sassanid king, was killed in the action.

The Battle of Gol-Zarriun, also Battle of Bukhara, took place in c. 560 when the Sasanian Empire allied with the First Turkic Khaganate against the Hephthalite Empire.

The Hephthalite–Sasanian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Hephthalites and the Sasanian Empire.

Sukhra was an Iranian nobleman from the House of Karen, who was the de facto ruler of the Sasanian Empire from 484 to 493. He was active during the reign of shah Peroz I, Balash and Kavad I. He is often confused with his father Zarmihr Hazarwuxt and son Zarmihr Karen.
Zarmihr Hazarwuxt was an Iranian military leader from the House of Karen, who served as the marzban of Sasanian Armenia briefly in 483.
Gushnaspdād, known in Byzantine sources as Gousanastadēs (Γουσαναστάδης), was a Sasanian nobleman, who was kanarang during the reign of Balash, and Kavad I.
Shapur Mihran, known in Armenian sources as Shapuh Mihran, was a Sasanian nobleman from the House of Mihran. He served as the marzban of Persian Armenia briefly in 482.

Harev, was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, that lay within the kust of Khorasan. The province bordered Kushanshahr in the west, Abarshahr in the east, Marv in the north, and Sakastan in the south.

Sukhra's Hephthalite campaign took place in 484 between the Hephthalites and the Sasanian Empire.

Peroz I Kushanshah was Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 245 to 275. He was the successor of Ardashir I Kushanshah. He was an energetic ruler, who minted coins in Balkh, Herat, and Gandhara. Under him, the Kushano-Sasanians further expanded their domains into the west, pushing the weakened Kushan Empire to Mathura in North India.

Faghanish was a Hephthalite prince, who was the ruler of Chaghaniyan in the mid-6th century. Originally a subordinate of the Hephthalite king, he became a vassal of the Sasanian Empire in c. 560 after the Hephthalite Empire was broken into several minor kingdoms when they suffered a crushing defeat to a combined Sasanian-Turkic army at Gol-Zarriun.

Hind was the name of a southeastern Sasanian province lying near the Indus River. The boundaries of the province are obscure. The Austrian historian and numismatist Nikolaus Schindel has suggested that the province may have corresponded to the Sindh region, where the Sasanians notably minted unique gold coins of themselves. According to the modern historian C. J. Brunner, the province possibly included—whenever jurisdiction was established—the areas of the Indus River, including the southern part of Punjab.
References
- ↑ Rezakhani 2017, p. 128.
- ↑ Rezakhani 2017, pp. 128–129.
- ↑ Schindel 2013, pp. 136–141.