Related Research Articles

A dictator is a political leader who possesses absolute power. A dictatorship is a state ruled by one dictator or by a polity. The word originated as the title of a Roman dictator elected by the Roman Senate to rule the republic in times of emergency. Like the terms "tyrant" and "autocrat", dictator came to be used almost exclusively as a non-titular term for oppressive rule. In modern usage the term dictator is generally used to describe a leader who holds or abuses an extraordinary amount of personal power.

The goliards were a group of generally young clergy in Europe who wrote satirical Latin poetry in the 12th and 13th centuries of the Middle Ages. They were chiefly clerics who served at or had studied at the universities of France, Germany, Spain, Italy, and England, who protested against the growing contradictions within the church through song, poetry and performance. Disaffected and not called to the religious life, they often presented such protests within a structured setting associated with carnival, such as the Feast of Fools, or church liturgy.

Peronism, also known as justicialism, is an Argentine ideology and movement based on the ideas, doctrine and legacy of Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th- and 21st-century Argentine politics. Since 1946, Peronists have won 10 out of the 14 presidential elections in which they have been allowed to run. Peronism is defined through its three flags, which are: "economic independence", "social justice" and "political sovereignty".
In Irish and Scottish mythology, Uathach was Scáthach's daughter and thus the niece of her rival and sister Aífe. Cú Chulainn, who had recently arrived at Scáthach's fortress-home Dún Scáith to be her pupil, accidentally broke one of Uathach's fingers, and Uathach's suitor, Cochar Croibhe, challenged him to single combat despite Uathach's protests. Cú Chulainn killed him and became Uathach's lover.

The Justicialist Party is a major political party in Argentina, and the largest branch within Peronism. Following the 2023 presidential election, it has been the largest party in the opposition against President Javier Milei.

A caudillo is a type of personalist leader wielding military and political power. There is no precise English translation for the term, though it is often used interchangeably with "military dictator," "warlord" and "strongman". The term is historically associated with Spain and Hispanic America, after virtually all of the regions in the latter won independence in the early nineteenth century.
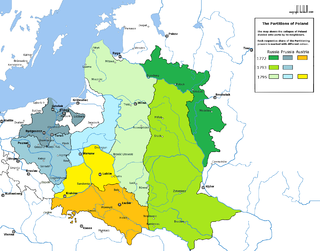
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polish–Lithuanian national sovereignty until 1918. The partition was the result of the Kościuszko Uprising and was followed by a number of Polish–Lithuanian uprisings during the period.

Miksa Fenyő was a Hungarian writer and intellectual, served as a member of parliament in the early 1930s, and was appointed as a Minister of Trade and Commerce under the short-lived government cabinet of Prime Minister János Hadik in 1918.
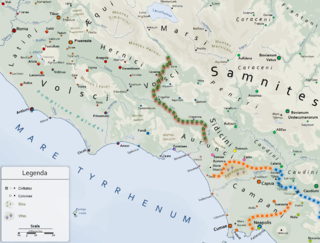
"Ausones", the original name and the extant Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, to denote the particular tribe which Livy termed the Aurunci, but later it was applied to all Italians, and Ausonia became a poetic term, in Greek and Latin, for Italy itself.

The Federalist Party was the nineteenth century Argentine political party that supported federalism. It opposed the Unitarian Party that claimed a centralised government of Buenos Aires Province, with no participation of the other provinces of the custom taxes benefits of the Buenos Aires port. The federales supported the autonomy of the provincial governments and the distribution of external commerce taxes among the provinces.

The Kentucky Democratic Party is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Kentucky. It is currently the minority party in the state, as the rival Republican Party of Kentucky overwhelmingly dominates in the state legislature, congressional delegation, and presidential elections. However, the party does currently control the governorship and lieutenant governorship, and maintains some strength in local elections.

Kirchnerism is an Argentine political movement based on ideals formed by the supporters of spouses Néstor Kirchner and Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, who consecutively served as Presidents of Argentina. Although considered a branch of Peronism, it is opposed by some factions of Peronists and generally considered to fall into the category of left-wing populism. It is considered a representative of the socialism of the 21st century, although similarly to Peronism and in contrast to other left-wing ideologies, it is highly nationalist and populist rather than class-based.
Madí is an international abstract art movement initiated in Buenos Aires in 1946 by the Hungarian-Argentinian artist and poet Gyula Kosice, and the Uruguayans Carmelo Arden Quin and Rhod Rothfuss.

The Arinos River is a river in Brazil. It is located east of, and empties into, the Juruena River. Some of the Suyá Indians, a Gê-speaking people of central Brazil, migrated from the state of Maranhão to this river.

A reja ("grille") is a decorative screen of iron.
A right-wing dictatorship, sometimes also referred to as a rightist dictatorship or right-wing authoritarianism, is an authoritarian or sometimes totalitarian regime following right-wing policies. Right-wing dictatorships are typically characterized by appeals to traditionalism, the protection of law and order and often the advocacy of nationalism, and justify their rise to power based on a need to uphold a conservative status quo. Examples of right-wing dictatorships may include anti-communist ones, such as Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, Estado Novo, Francoist Spain, the Chilean Junta, the Greek Junta, the Brazilian military dictatorship, the Argentine Junta, Republic of China under Chiang Kai-shek, South Korea when it was led by Syngman Rhee, Park Chung Hee, and Chun Doo-hwan, a number of military dictatorships in Latin America during the Cold War, and those that agitate anti-Western sentiments, such as Russia under Vladimir Putin.
The Institute for the Study of Economic and Social Development (IEDES) is an autonomous part of the University of Paris 1 Panthéon Sorbonne, focusing on multidisciplinary research into societies in the South.
Populism refers to a range of political stances that emphasise the idea of "the people" and often juxtapose this group against "the elite". This article focuses on populism in Latin America.
Socialism in Argentina has taken many different shapes throughout Argentina's history. Many of the country's leaders have had a socialist ideology as their political framework within Argentina and more broadly, throughout Latin America. As a result of this history, on the international podium they are recognised for their socialist history and leadership. Argentina's alignment with socialist ideology particularly during the Peronist years has further contributed to this global sentiment. Whilst there has been a history of many different socialist parties the main one to consider is the Socialist Party (Argentina). Although the history of Socialism in Argentina can be traced to specific dates, it is important to view the role it has played as part to the influence of international phenomenon such as World War I, World War II and The Malvinas War. Today, Socialism in Argentina is visible in the contemporary administrations of Néstor Kirchner and his wife and later president Cristina Fernandez de Kirchner.
References
- ↑ personalismo. (2009). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved July 02, 2009, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/452992/personalismo
- ↑ Harding, Robert C. (2006). The History of Panama. Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-03898-3.
- ↑ personalismo. (2009). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved July 02, 2009, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/452992/personalismo
- ↑ personalismo. (2009). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved July 02, 2009, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/452992/personalismo