
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines to applied disciplines. Though more often considered an academic discipline, computer science is closely related to computer programming.
Control Data Corporation (CDC) was a mainframe and supercomputer firm. CDC was one of the nine major United States computer companies through most of the 1960s; the others were IBM, Burroughs Corporation, DEC, NCR, General Electric, Honeywell, RCA, and UNIVAC. CDC was well-known and highly regarded throughout the industry at the time. For most of the 1960s, Seymour Cray worked at CDC and developed a series of machines that were the fastest computers in the world by far, until Cray left the company to found Cray Research (CRI) in the 1970s. After several years of losses in the early 1980s, in 1988 CDC started to leave the computer manufacturing business and sell the related parts of the company, a process that was completed in 1992 with the creation of Control Data Systems, Inc. The remaining businesses of CDC currently operate as Ceridian.

The University of Notre Dame du Lac, known simply as Notre Dame, is a private Catholic research university in Notre Dame, Indiana, north of the city of South Bend. French priest Edward Sorin founded the school in 1842. The main campus covers 1,261 acres in a suburban setting and contains landmarks such as the Golden Dome, the Word of Life mural, Notre Dame Stadium, and the Basilica. Originally for men, the university did not formally accept undergraduate female students until 1972.

The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and modern computing technology and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper or for chalk and slate, with or without the aid of tables.

Project Athena was a joint project of MIT, Digital Equipment Corporation, and IBM to produce a campus-wide distributed computing environment for educational use. It was launched in 1983, and research and development ran until June 30, 1991. As of 2023, Athena is still in production use at MIT. It works as software that makes a machine a thin client, that will download educational applications from the MIT servers on demand.

A flowchart is a type of diagram that represents a workflow or process. A flowchart can also be defined as a diagrammatic representation of an algorithm, a step-by-step approach to solving a task.

Notre Dame Stadium is an outdoor football stadium in Notre Dame, Indiana, the home field of the University of Notre Dame Fighting Irish football team.
Mark E. Dean is an American inventor and computer engineer. He developed the ISA bus, and he led a design team for making a one-gigahertz computer processor chip. He holds three of nine PC patents for being the co-creator of the IBM personal computer released in 1981. In 1995, Dean was named the first ever African-American IBM Fellow.
Frederick Jelinek was a Czech-American researcher in information theory, automatic speech recognition, and natural language processing. He is well known for his oft-quoted statement, "Every time I fire a linguist, the performance of the speech recognizer goes up".

Harm Peter Hofstee is a Dutch physicist and computer scientist who currently is a distinguished research staff member at IBM Austin, USA, and a part-time professor in Big Data Systems at Delft University of Technology, Netherlands.
William A. Goddard was an American engineer and inventor. He earned a degree in physics from Occidental College. Before working in industry, Goddard was a high school science teacher in Los Angeles. He briefly worked in the aerospace industry for North American Aviation, Inc. before becoming an engineer at International Business Machines (IBM). His most acclaimed achievement is co-inventing along with John Lynott United States Patent 3,503,060, which is entitled “Direct Access Magnetic Disc Storage Device”. This invention claims cover modern-day hard disk drives.

The history of IBM research in Israel dates from 1972 with the establishment of the IBM Haifa Research Lab. The research lab is located in a custom-built complex on the University of Haifa campus, with branches in Haifa and Tel Aviv. The staff at the IBM Haifa Research Lab works on projects connected to the topics of healthcare, cloud computing, formal and image and video analytics among others.

Chandrasekaran Mohan is an Indian-born American computer scientist. He was born on 3 August 1955 in Tamil Nadu, India. After growing up there and finishing his undergraduate studies in Chennai, he moved to the United States in 1977 for graduate studies, naturalizing in 2007. In June 2020, he retired from being an IBM Fellow at the IBM Almaden Research Center after working at IBM Research for 38.5 years. Currently, he is a visiting professor at China's Tsinghua University. He is also an Honorary Advisor at the Tamil Nadu e-Governance Agency (TNeGA) in Chennai and an advisor at the Kerala Blockchain Academy in Kerala.

Dharmendra S. Modha is an Indian American manager and lead researcher of the Cognitive Computing group at IBM Almaden Research Center. He is known for his pioneering works in Artificial Intelligence and Mind Simulation. In November 2009, Modha announced at a supercomputing conference that his team had written a program that simulated a cat brain. He is the recipient of multiple honors, including the Gordon Bell Prize, given each year to recognize outstanding achievement in high-performance computing applications. In November 2012, Modha announced on his blog that using 96 Blue Gene/Q racks of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Sequoia supercomputer, a combined IBM and LBNL team achieved an unprecedented scale of 2.084 billion neurosynaptic cores containing 530 billion neurons and 137 trillion synapses running only 1542× slower than real time. In August 2014 a paper describing the TrueNorth Architecture, "the first-ever production-scale 'neuromorphic' computer chip designed to work more like a mammalian brain than" a processor was published in the journal Science. TrueNorth project culminated in a 64 million neuron system for running deep neural network applications.

The Notre Dame Fighting Irish baseball team is the intercollegiate baseball team representing the University of Notre Dame in Notre Dame, Indiana. Notre Dame competes as a member of the Atlantic Coast Conference in the NCAA Division 1 college baseball league. The team is currently coached by Shawn Stiffler and plays its home games at Frank Eck Baseball Stadium, which has a capacity of 1,825. The school has appeared in three College World Series, in 1957, 2002, and 2022 and has won 6 conference titles.

The College of Engineering is a college within the University of Notre Dame. The Dean of the College of Engineering is Patricia J. Culligan, Ph.D. Its graduate school for Engineering is ranked #47 in the USA and #15 for undergraduate.
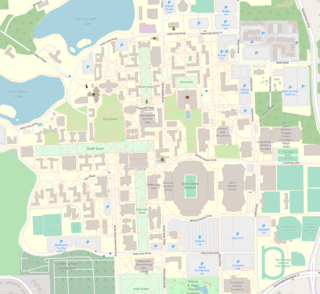
The campus of the University of Notre Dame is located in Notre Dame, Indiana, and spans 1,250 acres comprising around 170 buildings. The campus is consistently ranked and admired as one of the most beautiful university campuses in the United States and around the world, particularly noted for the Golden Dome, the Basilica and its stained glass windows, the quads and the greenery, the Grotto, Touchdown Jesus, its collegiate gothic architecture, and its statues and museums. Notre Dame is a major tourist attraction in northern Indiana; in the 2015–2016 academic year, more than 1.8 million visitors, almost half of whom were from outside of St. Joseph County, visited the campus.
John A. Murphy is an American inventor and computer engineer credited with inventing ARCNET, the first commercial networking system, in 1976. He was working for Datapoint Corporation at the time. His biography appeared in the IT History Society website.
Albert Smiley Hoagland had a long career on the development of hard disk drives (HDD) starting with the IBM RAMAC. From 1956 to 1984, he was with IBM in San Jose, California, and then, from 1984 to 2005, he was the director of the Institute for Information Storage Technology at Santa Clara University. He wrote the first book on Digital Magnetic Recording. Hoagland played a central role in the preservation and restoration of the IBM RAMAC now displayed at the Computer History Museum, Mountain View, California. He died in Portland, Oregon, on 1st October 2022.












