Related Research Articles

Asperger syndrome (AS),also known as Asperger's syndrome or Asperger's,is a term formerly used to describe a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication,along with restricted,repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. Asperger syndrome has been merged with other conditions into autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and is no longer considered a diagnosis. It was considered milder than other diagnoses which were merged into ASD due to relatively unimpaired spoken language and intelligence.
The diagnostic category pervasive developmental disorders (PDD),as opposed to specific developmental disorders (SDD),was a group of disorders characterized by delays in the development of multiple basic functions including socialization and communication. It was defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM),and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD).

Lorna Gladys Wing was an English psychiatrist. She was a pioneer in the field of childhood developmental disorders,who advanced understanding of autism worldwide,introduced the term Asperger syndrome in 1976 and was involved in founding the National Autistic Society (NAS) in the UK.
Pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS) is a historic psychiatric diagnosis first defined in 1980 that has since been incorporated into autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-5 (2013).
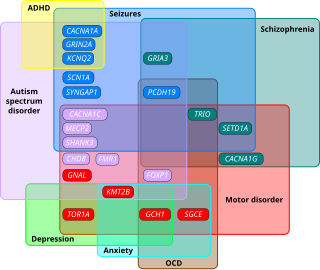
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that begins in early childhood,persists throughout adulthood,and affects two crucial areas of development:social communication and restricted,repetitive patterns of behavior. There are many conditions comorbid to autism spectrum disorder,such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,anxiety disorders,and epilepsy.
High-functioning autism (HFA) was historically an autism classification to describe a person who exhibited no intellectual disability but had some difficulty in communication,emotion recognition,expression,and/or social interaction. However,many in medical and autistic communities have called to stop using the term,finding it simplistic and unindicative of the difficulties some autistic people face.
Nonverbal learning disorder is a proposed category of neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by core deficits in non-verbal skills,especially visual-spatial processing. People with this condition have normal or advanced verbal intelligence and significantly lower nonverbal intelligence. A review of papers found that proposed diagnostic criteria were inconsistent. Proposed additional diagnostic criteria include intact verbal intelligence,and deficits in the following:visuoconstruction abilities,speech prosody,fine motor coordination,mathematical reasoning,visuospatial memory and social skills. NVLD is not recognised by the DSM-5 and is not clinically distinct from learning disorders.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to autism:
The epidemiology of autism is the study of the incidence and distribution of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). A 2022 systematic review of global prevalence of autism spectrum disorders found a median prevalence of 1% in children in studies published from 2012 to 2021,with a trend of increasing prevalence over time. However,the study's 1% figure may reflect an underestimate of prevalence in low- and middle-income countries.
Multiple complex developmental disorder (MCDD) is a research category,proposed to involve several neurological and psychological symptoms where at least some symptoms are first noticed during early childhood and persist throughout life. It was originally suggested to be a subtype of pervasive developmental disorders (PDD) with co-morbid schizophrenia or another psychotic disorder;however,there is some controversy that not everyone with MCDD meets criteria for both PDD and psychosis. The term multiplex developmental disorder was coined by Donald J. Cohen in 1986.
A spectrum disorder is a disorder that includes a range of linked conditions,sometimes also extending to include singular symptoms and traits. The different elements of a spectrum either have a similar appearance or are thought to be caused by the same underlying mechanism. In either case,a spectrum approach is taken because there appears to be "not a unitary disorder but rather a syndrome composed of subgroups". The spectrum may represent a range of severity,comprising relatively "severe" mental disorders through to relatively "mild and nonclinical deficits".
Asperger syndrome (AS) was formerly a separate diagnosis under autism spectrum disorder. Under the DSM-5 and ICD-11,patients formerly diagnosable with Asperger syndrome are diagnosable with Autism Spectrum Disorder. The term is considered offensive by some autistic individuals. It was named after Hans Asperger (1906–80),who was an Austrian psychiatrist and pediatrician. An English psychiatrist,Lorna Wing,popularized the term "Asperger's syndrome" in a 1981 publication;the first book in English on Asperger syndrome was written by Uta Frith in 1991 and the condition was subsequently recognized in formal diagnostic manuals later in the 1990s.

Classic autism,also known as childhood autism,autistic disorder,(early) infantile autism,infantile psychosis,Kanner's autism,Kanner's syndrome,or (formerly) just autism,is a neurodevelopmental condition first described by Leo Kanner in 1943. It is characterized by atypical and impaired development in social interaction and communication as well as restricted,repetitive behaviors,activities,and interests. These symptoms first appear in early childhood and persist throughout life.

Michael Fitzgerald is an Irish professor of child and adolescent psychiatry,specialising in autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Fred Robert Volkmar is a psychiatrist,psychologist,and the Irving B. Harris Professor of Child Psychiatry,Pediatrics,and Psychology at the Yale School of Medicine. From 2006 to 2014,he was the director of the Yale Child Study Center and the head of child psychiatry at Yale New Haven Hospital. Prior to these appointments,he was the director of the Autism Program at the Yale Child Study Center since 1983.
The history of autism spans over a century;autism has been subject to varying treatments,being pathologized or being viewed as a beneficial part of human neurodiversity. The understanding of autism has been shaped by cultural,scientific,and societal factors,and its perception and treatment change over time as scientific understanding of autism develops.
The Ritvo Autism &Asperger Diagnostic Scale (RAADS) is a psychological self-rating scale developed by Dr. Riva Ariella Ritvo. An abridged and translated 14 question version was then developed at the Department of Clinical Neuroscience at the Karolinska Institute,to aid in the identification of patients who may have undiagnosed ASD.
Social (pragmatic) communication disorder (SPCD),also known as pragmatic language impairment (PLI),is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in the social use of verbal and nonverbal communication. Individuals who are defined by the acronym "SPCD" struggle to effectively indulge in social interactions,interpret social cues,and may struggle to use words appropriately in social contexts.

Edward Ross Ritvo was an American psychiatrist known for his research on genetic components of autism. He was a professor emeritus of UCLA's Neuropsychiatric Institute.
References
- 1 2 "Interview with Dr. Peter Szatmari, MD". Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 20 (4): 312–314. November 2011. ISSN 1719-8429. PMC 3222576 . PMID 22114614.
- ↑ "Old Boys". James FitzGerald. Retrieved 2024-01-09.
- ↑ Grant-Oyeye, Lind (2022). "Dr. Peter Szatmari". Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 31 (2): 103–106. ISSN 1719-8429. PMC 9084376 . PMID 35614952.
- ↑ CAIRN: Canadian Autism Intervention Research Network. Peter Szatmari. Archived 2006-06-14 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 11 July 2006.
- ↑ "Peter Szatmari | SickKids Directory". SickKids. Retrieved 2024-01-10.
- ↑ Szatmari, Peter. "Studies in autism/PDD". Archived from the original on October 17, 2007. Retrieved 2006-07-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link). Retrieved on 11 July 2006. - 1 2 Szatmari, P., Brenner, R. and Nagy, J. (1989) Asperger's syndrome: A review of clinical features. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 34, pp. 554-560.
- ↑ McMaster University faculty: Peter Szatmari Archived 2013-04-05 at the Wayback Machine .
- ↑ Genome Canada boosts autism genetics research Archived 2007-02-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Stoddart, K. P. (Editor) (2005). "Children, Youth and Adults with Asperger Syndrome: Integrating Multiple Perspectives." London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. ISBN 1-84310-268-4. p. 239.