Related Research Articles

Petroleum is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture. It consists mainly of hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The term petroleum refers both to naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil, as well as to petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil.

The economy of Qatar is one of the highest in the world based on GDP per capita, ranking generally among the top ten richest countries on world rankings for 2015 and 2016 data compiled by the World Bank, the United Nations, and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The country's economy has grown despite sanctions by its neighbors, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Mainly because the country exports primarily to Japan, South Korea, India and China, making the sanctions effectively redundant as neither Saudi Arabia nor the United Arab Emirates have imposed trading penalties such as tariffs or embargoes on any of these countries for trading with Qatar, or offering incentives such as discounts for their own energy exports to reduce Qatari exports.

A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than 2,175,000 miles (3,500,000 km) of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The United States had 65%, Russia had 8%, and Canada had 3%, thus 76% of all pipeline were in these three countries. The main attribute to pollution from pipelines is caused by corrosion and leakage.

The Hubbert peak theory says that for any given geographical area, from an individual oil-producing region to the planet as a whole, the rate of petroleum production tends to follow a bell-shaped curve. It is one of the primary theories on peak oil.

Peak oil is the point when global oil production reaches its maximum rate, after which it will begin to decline irreversibly. The main concern is that global transportation relies heavily on gasoline and diesel. Transitioning to electric vehicles, biofuels, or more efficient transport could help reduce oil demand.

The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation, and marketing of petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline (petrol). Petroleum is also the raw material for many chemical products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, synthetic fragrances, and plastics. The industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream, and downstream. Upstream regards exploration and extraction of crude oil, midstream encompasses transportation and storage of crude, and downstream concerns refining crude oil into various end products.

Colin J. Campbell was a British petroleum geologist who predicted that oil production would peak by 2007. He claimed the consequences of this are uncertain but drastic, due to the world's dependency on fossil fuels for the vast majority of its energy. His theories have received wide attention but are disputed and have not significantly changed governmental energy policies at this time. To deal with declining global oil production, he proposed the Rimini protocol.
Oil depletion is the decline in oil production of a well, oil field, or geographic area. The Hubbert peak theory makes predictions of production rates based on prior discovery rates and anticipated production rates. Hubbert curves predict that the production curves of non-renewing resources approximate a bell curve. Thus, according to this theory, when the peak of production is passed, production rates enter an irreversible decline.
Oil India Limited (OIL) is a central public sector undertaking engaged in the business of exploration, development and production of crude oil and natural gas, transportation of crude oil and production of liquid petroleum gas. The central public sector undertaking is a Maharatna, with the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas overseeing its operations. Headquartered in Duliajan, Assam, the company has its offices in Duliajan, Noida, Guwahati and Jodhpur.

The petroleum industry in Azerbaijan produced about 33 million tonnes of oil and 35 billion cubic meters of gas in 2022. Azerbaijan is one of the birthplaces of the oil industry.
Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli or Azeri–Chirag–Deepwater Gunashli is a complex of oil fields in the Caspian Sea, about 120 kilometres (75 mi) off the coast of Azerbaijan. It consists of the Azeri and Chirag oil fields, and the deepwater portion of the Gunashli oil field. An overall estimate of the area of the development is 432.4 square kilometres (167.0 sq mi). It is developed by the Azerbaijan International Operating Company, a consortium of international oil companies, and operated by BP on behalf of the consortium. The ACG fields have estimated recoverable reserves of about 5 to 6 billion barrels of petroleum. Peak oil production of 885,000 barrels per day (140,700 m3/d) was reached in 2010. However by the first quarter of 2024 production had fallen to 339,000 barrels per day (53,900 m3/d), or approximately one-third of peak value, as the development continued terminal decline. As of 2021, ACG oil accounted for 95% of all Azerbaijani oil exports.
The Canadian petroleum industry arose in parallel with that of the United States. Because of Canada's unique geography, geology, resources and patterns of settlement, however, it developed in different ways. The evolution of the petroleum sector has been a key factor in the history of Canada, and helps illustrate how the country became quite distinct from her neighbour to the south.

While the local use of oil goes back many centuries, the modern petroleum industry along with its outputs and modern applications are of a recent origin. Petroleum's status as a key component of politics, society, and technology has its roots in the coal and kerosene industry of the late nineteenth century. One of the earliest instances of this is the refining of paraffin from crude oil. Abraham Gesner developed a process to refine a liquid fuel from coal, bitumen and oil shale; it burned more cleanly and was cheaper than whale oil. James Young in 1847 noticed a natural petroleum seepage when he distilled a light thin oil suitable for use as lamp oil, at the same time obtaining a thicker oil suitable for lubricating machinery. The world's first refineries and modern oil wells were established in the mid-nineteenth century. While petroleum industries developed in several countries during the nineteenth century, the two giants were the United States and the Russian Empire, specifically that part of it that today forms the territory of independent Azerbaijan. Together, these two countries produced 97% of the world's oil over the course of the nineteenth century.

Norway is a large energy producer, and one of the world's largest exporters of oil. Most of the electricity in the country is produced by hydroelectricity. Norway is one of the leading countries in the electrification of its transport sector, with the largest fleet of electric vehicles per capita in the world.

Petroleum has been a major industry in the United States since the 1859 Pennsylvania oil rush around Titusville, Pennsylvania. Commonly characterized as "Big Oil", the industry includes exploration, production, refining, transportation, and marketing of oil and natural gas products. The leading crude oil-producing areas in the United States in 2023 were Texas, followed by the offshore federal zone of the Gulf of Mexico, North Dakota and New Mexico.

Leduc No. 1 was a major crude oil discovery made near Leduc, Alberta, Canada, on February 13, 1947. It provided the geological key to Alberta's most prolific conventional oil reserves and resulted in a boom in petroleum exploration and development across Western Canada. The discovery transformed the Alberta economy; oil and gas supplanted farming as the primary industry and resulted in the province becoming one of the richest in the country. Nationally, the discovery allowed Canada to become self-sufficient within a decade and ultimately a major exporter of oil.
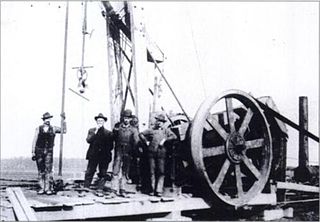
The Indiana gas boom was a period of active drilling and production of natural gas in the Trenton Gas Field, in the US state of Indiana and the adjacent northwest part of Ohio. The boom began in the early 1880s and lasted into the early 20th century.

Offshore oil and gas in the Gulf of Mexico is a major source of oil and natural gas in the United States. The western and central Gulf of Mexico, which includes offshore Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama, is one of the major petroleum-producing areas of the United States. Oil production from US federal waters in the Gulf of Mexico reached an all-time annual high of 1.65 million barrels per day in 2017. Oil production is expected to continue the upward trend in 2018 and 2019, based on ten new oil fields which are planned to start production in those years. According to the Energy Information Administration, "Gulf of Mexico federal offshore oil production accounts for 15% of total U.S. crude oil production and federal offshore natural gas production in the Gulf accounts for 5% of total U.S. dry production."

The Goose Creek Oil Field is a large oil field in Baytown, Texas, on Galveston Bay. Discovered in 1903, and reaching maximum production in 1918 after a series of spectacular gushers, it was one of the fields that contributed to the Texas Oil Boom of the early 20th century. The field was also the location of the first offshore wells in Texas, and the second group of offshore wells in the United States. Consequences of the development of the Goose Creek field included an economic boom and associated influx of workers, the founding and fast growth of Baytown, and the building of the adjacent Baytown Refinery, which is now the 2nd largest oil refinery in the United States with a capacity of 584,000 barrels per day. The field remains active, having produced over 150 million barrels (24,000,000 m3) of oil in its 100-year history.

The petroleum industry in Ohio dates from 1859. Ohio continues to produce significant quantities of oil and gas, having produced more than 1 billion barrels of oil and 9 trillion cubic feet of natural gas since 1860. Unconventional resources, primarily in eastern Ohio, are likely to increase production in Ohio.
References
- ↑ Jean-Marc Lador (2007). The Petroconsultants Adventure. Geneva, Roulet et Cie SA pp 84.
- ↑ "World Oil Reserves--The Problem of Reliable Data".
- ↑ Colin Campbell (2008) The first ever oil database, the history of Petroconsultants. "The first ever oil database, the history of Petroconsultants | ASPO International | the Association for the Study of Peak Oil and Gas". Archived from the original on 2011-06-06. Retrieved 2011-02-08.
- ↑ http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0EIN/is_1996_Oct_10/ai_18754886/ [ bare URL ]