Related Research Articles

Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity. Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking microscopic mirror symmetry. Unlike other sources of birefringence which alter a beam's state of polarization, optical activity can be observed in fluids. This can include gases or solutions of chiral molecules such as sugars, molecules with helical secondary structure such as some proteins, and also chiral liquid crystals. It can also be observed in chiral solids such as certain crystals with a rotation between adjacent crystal planes or metamaterials.
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate, is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates.

In chemistry, an enantiomer – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode – is one of two stereoisomers that are non-superposable onto their own mirror image. Enantiomers are much like one's right and left hands, when looking at the same face, they cannot be superposed onto each other. No amount of reorientation in three spatial dimensions will allow the four unique groups on the chiral carbon to line up exactly. The number of stereoisomers a molecule has can be determined by the number of chiral carbons it has. Stereoisomers include both enantiomers and diastereomers.
In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred to as a racemic mixture. Plus and minus forms are called Dextrorotation and levorotation. The D and L enantiomers are present in equal quantities, the resulting sample is described as a racemic mixture or a racemate. Racemization can proceed through a number of different mechanisms, and it has particular significance in pharmacology as different enantiomers may have different pharmaceutical effects.

A meso compound or meso isomer is an optically inactive isomer in a set of stereoisomers, at least two of which are optically active. This means that despite containing two or more stereocenters, the molecule is not chiral. A meso compound is "superimposable" on its mirror image. Two objects can be superimposed if all aspects of the objects coincide and it does not produce a "(+)" or "(-)" reading when analyzed with a polarimeter. The name is derived from the Greek mésos meaning “middle”.

In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality. The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (cheir) 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property.

Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric products in unequal amounts."

In chemistry, specific rotation ([α]) is a property of a chiral chemical compound. It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane-polarized light, per unit distance–concentration product, as the light passes through a sample of a compound in solution. Compounds which rotate the plane of polarization of a beam of plane polarized light clockwise are said to be dextrorotary, and correspond with positive specific rotation values, while compounds which rotate the plane of polarization of plane polarized light counterclockwise are said to be levorotary, and correspond with negative values. If a compound is able to rotate the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light, it is said to be “optically active”.
In stereochemistry, enantiomeric excess (ee) is a measurement of purity used for chiral substances. It reflects the degree to which a sample contains one enantiomer in greater amounts than the other. A racemic mixture has an ee of 0%, while a single completely pure enantiomer has an ee of 100%. A sample with 70% of one enantiomer and 30% of the other has an ee of 40%.
1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol (BINOL) is an organic compound that is often used as a ligand for transition-metal catalysed asymmetric synthesis. BINOL has axial chirality and the two enantiomers can be readily separated and are stable toward racemisation. The specific rotation of the two enantiomers is 35.5° (c = 1 in THF), with the R enantiomer being the dextrorotary one. BINOL is a precursor for another chiral ligand called BINAP. The volumetric mass density of the two enantiomers is 0.62 g cm−3.
Homochirality is a uniformity of chirality, or handedness. Objects are chiral when they cannot be superposed on their mirror images. For example, the left and right hands of a human are approximately mirror images of each other but are not their own mirror images, so they are chiral. In biology, 19 of the 20 natural amino acids are homochiral, being L-chiral (left-handed), while sugars are D-chiral (right-handed). Homochirality can also refer to enantiopure substances in which all the constituents are the same enantiomer, but some sources discourage this use of the term.

Biocatalysis refers to the use of living (biological) systems or their parts to speed up (catalyze) chemical reactions. In biocatalytic processes, natural catalysts, such as enzymes, perform chemical transformations on organic compounds. Both enzymes that have been more or less isolated and enzymes still residing inside living cells are employed for this task. Modern biotechnology, specifically directed evolution, has made the production of modified or non-natural enzymes possible. This has enabled the development of enzymes that can catalyze novel small molecule transformations that may be difficult or impossible using classical synthetic organic chemistry. Utilizing natural or modified enzymes to perform organic synthesis is termed chemoenzymatic synthesis; the reactions performed by the enzyme are classified as chemoenzymatic reactions.
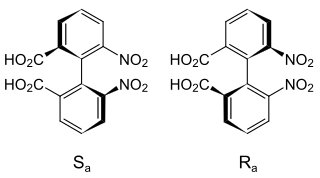
Atropisomers are stereoisomers arising because of hindered rotation about a single bond, where energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual conformers. They occur naturally and are important in pharmaceutical design. When the substituents are achiral, these conformers are enantiomers (atropoenantiomers), showing axial chirality; otherwise they are diastereomers (atropodiastereomers).

Levopropoxyphene is an antitussive. It is an optical isomer of dextropropoxyphene. The racemic mixture is called propoxyphene. Only the dextro-isomer (dextropropoxyphene) has an analgesic effect; the levo-isomer appears to exert only an antitussive effect. It was formerly marketed in the U.S. by Eli Lilly under the tradename Novrad as an antitussive. Unlike many antitussives, it binds poorly to the sigma-1 receptor.
Chiral resolution, or enantiomeric resolution, is a process in stereochemistry for the separation of racemic compounds into their enantiomers. It is an important tool in the production of optically active compounds, including drugs. Another term with the same meaning is optical resolution.

Eligio Perucca was an Italian physics instructor and researcher at the University of Turin in Italy in the early decades of the twentieth century. He later served a professorship at the nearby Polytechnic University of Turin. He discovered an important principle in stereochemistry in 1919, but his contribution was overlooked and forgotten until recently.
The eudysmic ratio represents the difference in pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers of a drug. In most cases where a chiral compound is biologically active, one enantiomer is more active than the other. The eudysmic ratio is the ratio of activity between the two. A eudysmic ratio significantly differing from 1 means that they are statistically different in activity. Eudisimic ratio (ER) reflects the degree of enantioselectivity of the biological systems. For example, (S)-propranolol meaning that (S)-propranolol is 130 times more active as its (R)-enantiomer.

The term chiral describes an object, especially a molecule, which has or produces a non-superposable mirror image of itself. In chemistry, such a molecule is called an enantiomer or is said to exhibit chirality or enantiomerism. The term "chiral" comes from the Greek word for the human hand, which itself exhibits such non-superimposeability of the left hand precisely over the right. Due to the opposition of the fingers and thumbs, no matter how the two hands are oriented, it is impossible for both hands to exactly coincide. Helices, chiral characteristics (properties), chiral media, order, and symmetry all relate to the concept of left- and right-handedness.

Chirality is a property of asymmetry important in several branches of science. The word chirality is derived from the Greek χειρ (kheir), "hand", a familiar chiral object.
Chemical compounds that come as mirror-image pairs are referred to by chemists as chiral or handed molecules. Each twin is called an enantiomer. Drugs that exhibit handedness are referred to as chiral drugs. Chiral drugs that are equimolar (1:1) mixture of enantiomers are called racemic drugs and these are obviously devoid of optical rotation. The most commonly encountered stereogenic unit, that confers chirality to drug molecules are stereogenic center. Stereogenic center can be due to the presence of tetrahedral tetra coordinate atoms (C,N,P) and pyramidal tricoordinate atoms (N,S). The word chiral describes the three-dimensional architecture of the molecule and does not reveal the stereochemical composition. Hence "chiral drug" does not say whether the drug is racemic, single enantiomer or some other combination of stereoisomers. To resolve this issue Joseph Gal introduced a new term called unichiral. Unichiral indicates that the stereochemical composition of a chiral drug is homogenous consisting of a single enantiomer.
References
- ↑ Paul Pfeiffer; Kurt Quehl (1932). "Aktivierung von Komplexsalzen in wäßriger Lösung". Chemische Berichte . 65 (4): 560–565. doi:10.1002/cber.19320650410.
- ↑ E. Perucca "New observations and measurements upon optically active crystals (NaClO3)” Nuovo Cimento1919, volume 18, pp. 112.
- ↑ Chemical & Engineering News, Vol. 86 No. 33, 18 August 2008, p. 38, Recognizing a Pioneer