
In organic chemistry, a Schiff base is a compound with the general structure R1R2C=NR3. They can be considered a sub-class of imines, being either secondary ketimines or secondary aldimines depending on their structure. Anil refers to a common subset of Schiff bases: imines derived from anilines. The term can be synonymous with azomethine which refers specifically to secondary aldimines.

Terpyridine is a heterocyclic compound derived from pyridine. It is a white solid that is soluble in most organic solvents. The compound is mainly used as a ligand in coordination chemistry.

Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 500,000 tonnes produced in 1998. Ethylenediamine is the first member of the so-called polyethylene amines.
Salicylic aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4OH(CHO). Along with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, it is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. This colorless oily liquid has a bitter almond odor at higher concentration. Salicylaldehyde is a precursor to coumarin and a variety of chelating agents.
Transmetalation (alt. spelling: transmetallation) is a type of organometallic reaction that involves the transfer of ligands from one metal to another. It has the general form:
Bis(oxazoline) ligands (often abbreviated BOX ligands) are a class of privileged chiral ligands containing two oxazoline rings. They are typically C2‑symmetric and exist in a wide variety of forms; with structures based around CH2 or pyridine linkers being particularly common (often generalised BOX and PyBOX respectively). The coordination complexes of bis(oxazoline) ligands are used in asymmetric catalysis. These ligands are examples of C2-symmetric ligands.

Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.

Salcomine is a coordination complex derived from the salen ligand and cobalt. The complex, which is planar, and a variety of its derivatives are carriers for O2 as well as oxidation catalysts.
Dioxygen complexes are coordination compounds that contain O2 as a ligand. The study of these compounds is inspired by oxygen-carrying proteins such as myoglobin, hemoglobin, hemerythrin, and hemocyanin. Several transition metals form complexes with O2, and many of these complexes form reversibly. The binding of O2 is the first step in many important phenomena, such as cellular respiration, corrosion, and industrial chemistry. The first synthetic oxygen complex was demonstrated in 1938 with cobalt(II) complex reversibly bound O2.

In chemistry, a template reaction is any of a class of ligand-based reactions that occur between two or more adjacent coordination sites on a metal center. In the absence of the metal ion, the same organic reactants produce different products. The term is mainly used in coordination chemistry. The template effects emphasizes the pre-organization provided by the coordination sphere, although the coordination modifies the electronic properties of ligands.

Jacobsen's catalyst is the common name for N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediaminomanganese(III) chloride, a coordination compound of manganese and a salen-type ligand. It is used as an asymmetric catalyst in the Jacobsen epoxidation, which is renowned for its ability to enantioselectively transform prochiral alkenes into epoxides. Before its development, catalysts for the asymmetric epoxidation of alkenes required the substrate to have a directing functional group, such as an alcohol as seen in the Sharpless epoxidation. This compound has two enantiomers, which give the appropriate epoxide product from the alkene starting material.
Cyclodiphosphazanes are saturated four membered P2N2 ring systems and one of the major classes of cyclic phosphazene compounds. Bis(chloro)cyclodiphosphazanes, (cis-[ClP(μ-NR)]2) are important starting compounds for synthesizing a variety of cyclodiphosphazane derivatives by nucleophilic substitution reactions; are prepared by reaction of phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) with a primary amine (RNH2) or amine hydrochlorides (RNH3Cl).

DuPhos is a class of organophosphorus compound that are used ligands for asymmetric synthesis. The name DuPhos is derived from (1) the chemical company that sponsored the research leading to this ligand's invention, DuPont and (2) the compound is a diphosphine ligand type. Specifically it is classified as a C2-symmetric ligand, consisting of two phospholanes rings affixed to a benzene ring.

A metal salen complex is a coordination compound between a metal cation and a ligand derived from N,N′-bis(salicylidene)ethylenediamine, commonly called salen. The classical example is salcomine, the complex with divalent cobalt Co2+, usually denoted as Co(salen). These complexes are widely investigated as catalysts and enzyme mimics.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.
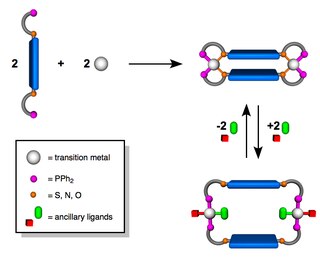
The Weak-Link Approach (WLA) is a supramolecular coordination-based assembly methodology, first introduced in 1998 by the Mirkin Group at Northwestern University. This method takes advantage of hemilabile ligands -ligands that contain both strong and weak binding moieties- that can coordinate to metal centers and quantitatively assemble into a single condensed ‘closed’ structure. Unlike other supramolecular assembly methods, the WLA allows for the synthesis of supramolecular complexes that can be modulated from rigid ‘closed’ structures to flexible ‘open’ structures through reversible binding of allosteric effectors at the structural metal centers. The approach is general and has been applied to a variety of metal centers and ligand designs including those with utility in catalysis and allosteric regulation.
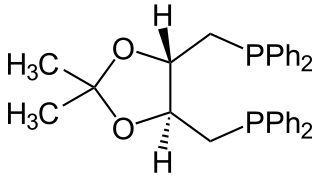
DIOP is an organophosphorus compound that is used as a chiral ligand in asymmetric catalysis. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Diimines are organic compounds containing two imine (RCH=NR') groups. Common derivatives are 1,2-diimines and 1,3-diimines. These compounds are used as ligands, but they are also precursors to other organic compounds.
In homogeneous catalysis, C2-symmetric ligands refer to ligands that lack mirror symmetry but have C2 symmetry. Such ligands are usually bidentate and are valuable in catalysis. The C2 symmetry of ligands limits the number of possible reaction pathways and thereby increases enantioselectivity, relative to asymmetrical analogues. C2-symmetric ligands are a subset of chiral ligands. Chiral ligands, including C2-symmetric ligands, combine with metals or other groups to form chiral catalysts. These catalysts engage in enantioselective chemical synthesis, in which chirality in the catalyst yields chirality in the reaction product.

Salpn is the common name for a chelating ligand, properly called N,N′-bis(salicylidene)-1,2-propanediamine, used as a motor oil additive.

















