
A lubricant is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity.

Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, detergents, dispersants, and, for multi-grade oils, viscosity index improvers. The main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to clean the engine from sludge and varnish (detergents). It also neutralizes acids that originate from fuel and from oxidation of the lubricant (detergents), improves the sealing of piston rings, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts.

Synthetic oil is a lubricant consisting of chemical compounds that are artificially modified or synthesised. Synthetic lubricants can be manufactured using chemically modified petroleum components rather than whole crude oil, but can also be synthesized from other raw materials. The base material, however, is still overwhelmingly crude oil that is distilled and then modified physically and chemically. The actual synthesis process and composition of additives is generally a commercial trade secret and will vary among producers.

Jet fuel or aviation turbine fuel is a type of aviation fuel designed for use in aircraft powered by gas-turbine engines. It is colorless to straw-colored in appearance. The most commonly used fuels for commercial aviation are Jet A and Jet A-1, which are produced to a standardized international specification. The only other jet fuel commonly used in civilian turbine-engine powered aviation is Jet B, which is used for its enhanced cold-weather performance.

Gear oil is a lubricant made specifically for transmissions, transfer cases, and differentials in automobiles, trucks, and other machinery. It has high viscosity and usually contains organosulfur compounds. Some modern automatic transaxles do not use a heavy oil at all but lubricate with the lower viscosity hydraulic fluid, which is available at pressure within the automatic transmission. Gear oils account for about 20% of the lubricant market.

Copper electroplating is the process of electroplating a layer of copper onto the surface of a metal object. Copper is used both as a standalone coating and as an undercoat onto which other metals are subsequently plated. The copper layer can be decorative, provide corrosion resistance, increase electrical and thermal conductivity, or improve the adhesion of additional deposits to the substrate.

Petroleum products are materials derived from crude oil (petroleum) as it is processed in oil refineries. Unlike petrochemicals, which are a collection of well-defined usually pure organic compounds, petroleum products are complex mixtures. Most petroleum is converted into petroleum products, which include several classes of fuels.
A corrosion inhibitor or anti-corrosive is a chemical compound added to a liquid or gas to decrease the corrosion rate of a metal that comes into contact with the fluid. The effectiveness of a corrosion inhibitor depends on fluid composition and dynamics. Corrosion inhibitors are common in industry, and also found in over-the-counter products, typically in spray form in combination with a lubricant and sometimes a penetrating oil. They may be added to water to prevent leaching of lead or copper from pipes.
JP-8, or JP8, is a jet fuel, specified and used widely by the US military. It is specified by MIL-DTL-83133 and British Defence Standard 91-87, and similar to commercial aviation's Jet A-1, but with the addition of corrosion inhibitor and anti-icing additives.
AW additives, or antiwear additives, are additives for lubricants to prevent metal-to-metal contact between parts of gears.
In industrial chemistry, a stabilizer or stabiliser is a chemical that is used to prevent degradation. Above all, heat and light stabilizers are added to plastic and rubber materials because they ensure safe processing and protect products against aging and weathering. In particular polyvinyl chloride would not be possible without stabilizers.
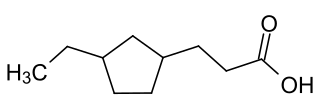
Naphthenic acids (NAs) are mixtures of several cyclopentyl and cyclohexyl carboxylic acids with molecular weights of 120 to well over 700 atomic mass units. The main fractions are carboxylic acids with a carbon backbone of 9 to 20 carbons. McKee et al. claim that "naphthenic acids (NAs) are primarily cycloaliphatic carboxylic acids with 10 to 16 carbons", although acids containing up to 50 carbons have been identified in heavy petroleum.
Oil additives are chemical compounds that improve the lubricant performance of base oil. The manufacturer of many oils can use the same base stock for each formulation and can choose different additives for each use. Additives comprise up to 5% by weight of some oils.
Polymer stabilizers are chemical additives which may be added to polymeric materials to inhibit or retard their degradation. Mainly they protect plastic and rubber products against heat, oxidation, and UV light. The biggest quantity of stabilizers is used for polyvinyl chloride (PVC), as the production and processing of this type of plastic would not be possible without stablizing chemicals. Common polymer degradation processes include oxidation, UV-damage, thermal degradation, ozonolysis, combinations thereof such as photo-oxidation, as well as reactions with catalyst residues, dyes, or impurities. All of these degrade the polymer at a chemical level, via chain scission, uncontrolled recombination and cross-linking, which adversely affects many key properties such as strength, malleability, appearance and colour.

Automotive oil recycling involves the recycling of used oils and the creation of new products from the recycled oils, and includes the recycling of motor oil and hydraulic oil. Oil recycling also benefits the environment: increased opportunities for consumers to recycle oil lessens the likelihood of used oil being dumped on lands and in waterways. For example, one gallon of motor oil dumped into waterways has the potential to pollute one million gallons of water.

Marvel Mystery Oil is an automotive product of the American Marvel Oil Company, founded by Burt Pierce in 1923. It is used as a fuel additive and oil additive, purportedly to function as a corrosion inhibitor, penetrating oil, transmission leak stopper and seal relubricator, despite a lack of scientific evidence supporting such claims.
Honing oil is a liquid, solution or emulsion used to aid in the cutting or grinding of metal, typically by abrasive tools or stones, and may or may not contain oil. It can also be called machining oil,tool oil, cutting fluid, and cutting oil.

Alkenyl succinic anhydrides (ASA) are derivatives of succinic anhydrides. One H of the succinic anhydride ring is replaced with an iso-alkenyl chain (C14 to C22). ASA's are colorless and usually viscous liquids. They are widely used, especially in surface sizing of paper, paperboard, and cardboard, as well as in the hydrophobicization of cellulose fibers. Products treated with it show reduced penetration of aqueous media, such as inks or drinks (like milk or fruit juices).

Salpn is the common name for a chelating ligand, properly called N,N′-bis(salicylidene)-1,2-propanediamine, used as a motor oil additive.












