
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.
Butanol (also called butyl alcohol) is a four-carbon alcohol with a formula of C4H9OH, which occurs in five isomeric structures (four structural isomers), from a straight-chain primary alcohol to a branched-chain tertiary alcohol; all are a butyl or isobutyl group linked to a hydroxyl group (sometimes represented as BuOH, n-BuOH, i-BuOH, and t-BuOH). These are n-butanol, 2 stereoisomers of sec-butanol, isobutanol and tert-butanol. Butanol is primarily used as a solvent and as an intermediate in chemical synthesis, and may be used as a fuel. Biologically produced butanol is called biobutanol, which may be n-butanol or isobutanol.

Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties. BHT is widely used to prevent free radical-mediated oxidation in fluids and other materials, and the regulations overseen by the U.S. F.D.A.—which considers BHT to be "generally recognized as safe"—allow small amounts to be added to foods. Despite this, and the earlier determination by the National Cancer Institute that BHT was noncarcinogenic in an animal model, societal concerns over its broad use have been expressed. BHT has also been postulated as an antiviral drug, but as of March 2020, use of BHT as a drug is not supported by the scientific literature and it has not been approved by any drug regulatory agency for use as an antiviral.

Methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE), also known as methyl tert-butyl ether and tert-butyl methyl ether, is an organic compound with a structural formula (CH3)3COCH3. MTBE is a volatile, flammable, and colorless liquid that is sparingly soluble in water. Primarily used as a fuel additive, MTBE is blended into gasoline to increase knock resistance and reduce unwanted emissions.
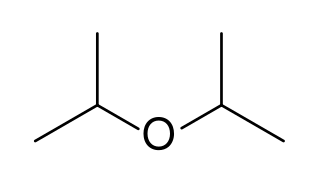
Diisopropyl ether is secondary ether that is used as a solvent. It is a colorless liquid that is slightly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. It is used as an extractant and an oxygenate gasoline additive. It is obtained industrially as a byproduct in the production of isopropanol by hydration of propylene. Diisopropyl ether is sometimes represented by the abbreviation DIPE.

Isobutylene (or 2-methylpropene) is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH3)2C=CH2. It is a four-carbon branched alkene (olefin), one of the four isomers of butylene. It is a colorless flammable gas, and is of considerable industrial value.

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.
Oxygenated chemical compounds contain oxygen as a part of their chemical structure. The term usually refers to oxygenated chemical compounds added to fuels. Oxygenates are usually employed as gasoline additives to reduce carbon monoxide and soot that is created during the burning of the fuel. Compounds related to soot, such as polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and nitrated PAHs, are also reduced.
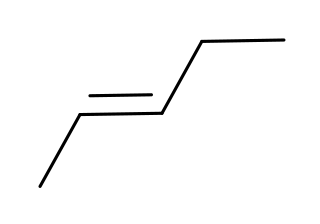
Pentenes are alkenes with the chemical formula C
5H
10. Each contains one double bond within its molecular structure. Six different compounds are in this class, differing from each other by whether the carbon atoms are attached linearly or in a branched structure, and whether the double bond has a cis or trans form.
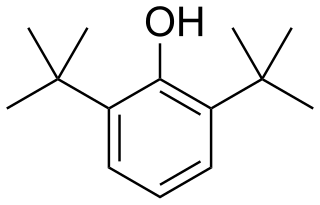
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colorless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizers and antioxidants for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels.
tert-Butyl chloride is the organochloride with the formula (CH3)3CCl. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It is sparingly soluble in water, with a tendency to undergo hydrolysis to the corresponding tert-butyl alcohol. It is produced industrially as a precursor to other organic compounds.
tert-Butyl isocyanide is an organic compound with the formula Me3CNC (Me = methyl, CH3). It is an isocyanide, commonly called isonitrile or carbylamine, as defined by the functional group C≡N-R. tert-Butyl isocyanide, like most alkyl isocyanides, is a reactive colorless liquid with an extremely unpleasant odor. It forms stable complexes with transition metals and can insert into metal-carbon bonds.

Alkylphenols are a family of organic compounds obtained by the alkylation of phenols. The term is usually reserved for commercially important propylphenol, butylphenol, amylphenol, heptylphenol, octylphenol, nonylphenol, dodecylphenol and related "long chain alkylphenols" (LCAPs). Methylphenols and ethylphenols are also alkylphenols, but they are more commonly referred to by their specific names, cresols and xylenols.
tert-Butyl bromide (also referred to as 2-bromo-2-methylpropane) is an organic compound with the formula Me3CBr (Me = methyl). The molecule features a tert-butyl group attached to a bromide substituent. This organobromine compound is used as a standard reagent in synthetic organic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid.

tert-Butylthiol, also known as 2-methylpropane-2-thiol, 2-methyl-2-propanethiol, tert-butyl mercaptan (TBM), and t-BuSH, is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)3CSH. This thiol is used as an odorant for natural gas, which is otherwise odorless. It may also have been used as a flavoring agent.

2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenol (2,4,6-TTBP) is a phenol symmetrically substituted with three tert-butyl groups and thus strongly sterically hindered. 2,4,6-TTBP is a readily oxidizable aromatic compound and a weak acid. It oxidizes to give the deep-blue 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenoxy radical. 2,4,6-TTBP is related to 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, which is widely used as an antioxidant in industrial applications. These compounds are colorless solids.
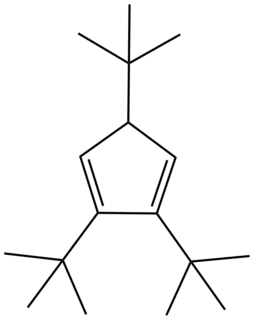
In the area of organometallic chemistry, a bulky cyclopentadienyl ligand is jargon for a ligand of the type C
5H
5−nR−
n where R is a branched alkyl and n = 3 or 4. Representative examples are the tetraisopropyl derivative C
5HiPr−
4 and the tris(tert-butyl) derivative 1,2,4-C
5H
2tBu−
3. These ligands are so large that their complexes behave differently from the pentamethylcyclopentadienyl analogues. Because they cannot closely approach the metal, these bulky ligands stabilize high spin complexes, such as (C5H2tBu3)2Fe2I2. These large ligands stabilize highly unsaturated derivatives such as (C5H2tBu3)2Fe2N2.

4-tert-Butylphenol is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CC6H4OH. It is one of three isomeric tert-butyl phenols. It is a white solid with a distinct phenolic odor. It dissolves in basic water.

2-tert-Butyl phenol is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3CC6H4OH. It is one of three isomeric tert-butyl phenols. It is a colorless oil that dissolves in basic water. It can be prepared by acid-catalyzed alkylation of phenol with isobutene.


















