
Honduras is a country in Central America. Honduras borders the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean. Guatemala lies to the west, Nicaragua south east and El Salvador to the south west. Honduras is the second largest Central American republic, with a total area of 112,890 square kilometres (43,590 sq mi).

The geography of Switzerland encompasses the geographical features of Switzerland, a mountainous and landlocked country located in Western and Central Europe. Switzerland's natural landscape is marked by its numerous lakes and mountains. It is surrounded by five countries: Austria and Liechtenstein to the east, France to the west, Italy to the south and Germany to the north. Switzerland has a maximum north–south length of 220 kilometres (140 mi) and an east–west length of about 350 kilometres (220 mi).

Algeria comprises 2,381,740 square kilometres (919,590 sq mi) of land, more than 80% of which is desert, in North Africa, between Morocco and Tunisia. It is the largest country in Africa. Its Arabic name, Al Jazair, is believed to derive from the rocky islands along the coastline of the Mediterranean Sea. The northern portion, an area of mountains, valleys, and plateaus between the Mediterranean and the Sahara Desert, forms an integral part of the section of North Africa known as the Maghreb. This area includes Morocco, Tunisia, and the northwestern portion of Libya known historically as Tripolitania.

Lüneburg Heath is a large area of heath, geest, and woodland in the northeastern part of the state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. It forms part of the hinterland for the cities of Hamburg, Hanover and Bremen and is named after the town of Lüneburg. Most of the area is a nature reserve. Northern Low Saxon is still widely spoken in the region.

The Mascarene Islands or Mascarenes or Mascarenhas Archipelago is a group of islands in the Indian Ocean east of Madagascar consisting of the islands belonging to the Republic of Mauritius as well as the French department of La Réunion. Their name derives from the Portuguese navigator Pedro Mascarenhas, who first visited them in April 1512. The islands share a common geologic origin in the volcanism of the Réunion hotspot beneath the Mascarene Plateau and form a distinct ecoregion with a unique flora and fauna.
UNESCO Biosphere Reserves are environment-protected scientific-research institutions of international status that are created with the intent for conservation in a natural state the most typical natural complexes of biosphere, conducting background ecological monitoring, studying of the surrounding natural environment, its changes under the activity of anthropogenic factors.

Pinus cembra, also known as Swiss pine, Swiss stone pine, Arolla pine, Austrian stone pine, or just stone pine, is a species of pine tree in the subgenus Strobus.

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.

Taï National Park is a national park in Côte d'Ivoire that contains one of the last areas of primary rainforest in West Africa. It was inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 1982 due to the diversity of its flora and fauna. Five mammal species of the Taï National Park are on the Red List of Threatened Species: pygmy hippopotamus, olive colobus monkeys, leopards, chimpanzees, and Jentink's duiker.

Dacrycarpus dacrydioides, commonly known as kahikatea and white pine, is a coniferous tree endemic to New Zealand. A podocarp, it is New Zealand's tallest tree, gaining heights of 60 m over a life span of 600 years. It was first described botanically by the French botanist Achille Richard in 1832 as Podocarpusdacrydioides, and was given its current binomial name Dacrycarpus dacrydioides in 1969 by the American botanist David de Laubenfels. Analysis of DNA has confirmed its evolutionary relationship with other species in the genera Dacrycarpus and Dacrydium.

The Coconino National Forest is a 1.856-million acre United States National Forest located in northern Arizona in the vicinity of Flagstaff, with elevations ranging from 2,600 feet to the highest point in Arizona at 12,633 feet. Originally established in 1898 as the "San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve", the area was designated a U.S. National Forest by Pres. Theodore Roosevelt on July 2, 1908, when the San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve was merged with lands from other surrounding forest reserves to create the Coconino National Forest. Today, the Coconino National Forest contains diverse landscapes, including deserts, ponderosa pine forests, flatlands, mesas, alpine tundra, and ancient volcanic peaks. The forest surrounds the towns of Sedona and Flagstaff and borders four other national forests; the Kaibab National Forest to the west and northwest, the Prescott National Forest to the southwest, the Tonto National Forest to the south, and the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest to the southeast. The forest contains all or parts of nine designated wilderness areas, including the Kachina Peaks Wilderness, which includes the summit of the San Francisco Peaks. The headquarters are in Flagstaff. The Coconino National Forest consists of three districts: Flagstaff Ranger District, Mogollon Rim Ranger District, and Red Rock Ranger District, which have local ranger district offices in Flagstaff, Happy Jack, and Sedona.
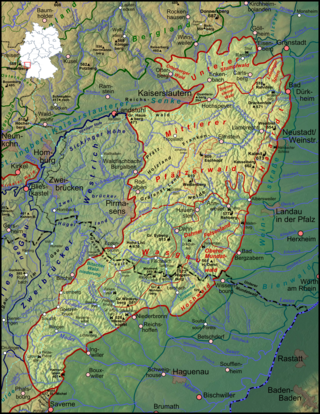
The Palatinate Forest, sometimes also called the Palatine Forest, is a low-mountain region in southwestern Germany, located in the Palatinate in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate. The forest is a designated nature park covering 1,771 km2 and its highest elevation is the Kalmit.

Sixt-Fer-à-Cheval is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department within the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France. It is located at the end of the Giffre Valley.
Germany is a country in Central and Western Europe that stretches from the Alps, across the North European Plain to the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. It is the second-most populous country in Europe after Russia, and is seventh-largest country by area in the continent. The area of Germany ranked 63rd and covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of waters, smaller than Japan but larger than Republic of the Congo.

The Illgraben valley is one of the most geologically unstable regions of Switzerland, and is located south of Leuk in the Canton of Valais.
The flora of the Colorado Plateau and Canyonlands region is generally characterized by plant adaptations to the arid conditions of the region, and a wide variation of plant communities from wide variations in elevation and soil types. The elevation variation results in temperature variation. Differing soil types are largely due to erosion of different sedimentary layers in the canyons, from the layers at lowest point of canyons of the Colorado River network, to the top layers of the plateau. Exceptions to flora adapted to aridity occur in lowland riparian areas, at springs, and in hanging gardens.

The Bryansk Forest Nature Reserve, also known as Bryansky Les, is a nature reserve in Bryansk Oblast, Russia, along the Nerussa River near the Russian border with Ukraine.

In ecology and forestry, yellow pine refers to a number of conifer species that tend to grow in similar plant communities and yield similar strong wood. In the Western United States, yellow pine refers to Jeffrey pine or ponderosa pine. In the Southeastern United States, yellow pine refers to longleaf pine, shortleaf pine, slash pine, or loblolly pine. In the United Kingdom, yellow pine refers to eastern white pine or Scots pine. In New Zealand, it refers to Halocarpus biformis.

Forest of Orléans is a French national forest for the most part and makes up 70% of a French natural region, located in the department of Loiret in the Centre-Val de Loire region.

Rivnenskyi Nature Reserve is a strict nature reserve in the northwest of Ukraine, created to protect and study the representative landscape of the Polesia region. It was established by the President of Ukraine, Leonid Danylovych Kuchma, on April 3, 1999. In accordance with the Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine on August 14, 2003, the reserve was permanently transferred to a land area of 42,288 km2.



















