Related Research Articles

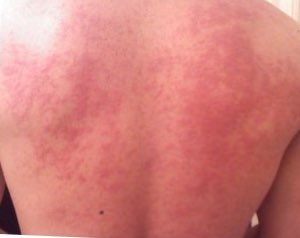
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are a number of conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.
A radioallergosorbent test (RAST) is a blood test using radioimmunoassay test to detect specific IgE antibodies in order to determine the substances a subject is allergic to. This is different from a skin allergy test, which determines allergy by the reaction of a person's skin to different substances.
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes.
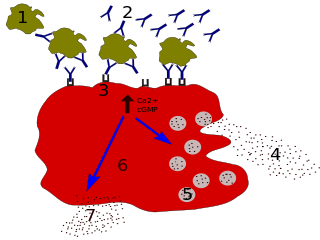
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis, and Fasciola hepatica. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms.
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. This typically occurs within minutes to several hours of exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis. A food intolerance and food poisoning are separate conditions, not due to an immune response.
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is the autoantibody that was first found in rheumatoid arthritis. It is defined as an antibody against the Fc portion of IgG and different RFs can recognize different parts of the IgG-Fc. RF and IgG join to form immune complexes that contribute to the disease process.
Omalizumab, sold under the brand name Xolair, is a medication used to treat asthma, nasal polyps, and urticaria.

X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a rare genetic disorder discovered in 1952 that affects the body's ability to fight infection. As the form of agammaglobulinemia that is X-linked, it is much more common in males. In people with XLA, the white blood cell formation process does not generate mature B cells, which manifests as a complete or near-complete lack of proteins called gamma globulins, including antibodies, in their bloodstream. B cells are part of the immune system and normally manufacture antibodies, which defend the body from infections by sustaining a humoral immunity response. Patients with untreated XLA are prone to develop serious and even fatal infections. A mutation occurs at the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) gene that leads to a severe block in B cell development and a reduced immunoglobulin production in the serum. Btk is particularly responsible for mediating B cell development and maturation through a signaling effect on the B cell receptor BCR. Patients typically present in early childhood with recurrent infections, in particular with extracellular, encapsulated bacteria. XLA is deemed to have a relatively low incidence of disease, with an occurrence rate of approximately 1 in 200,000 live births and a frequency of about 1 in 100,000 male newborns. It has no ethnic predisposition. XLA is treated by infusion of human antibody. Treatment with pooled gamma globulin cannot restore a functional population of B cells, but it is sufficient to reduce the severity and number of infections due to the passive immunity granted by the exogenous antibodies.

Selective immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency (SIgAD) is a genetic immunodeficiency, a type of hypogammaglobulinemia. People with this deficiency lack immunoglobulin A (IgA), a type of antibody that protects against infections of the mucous membranes lining the mouth, airways, and digestive tract. It is defined as an undetectable serum IgA level in the presence of normal serum levels of IgG and IgM, in persons older than 4 years. It is the most common of the primary antibody deficiencies. Most such persons remain healthy throughout their lives and are never diagnosed.
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a condition characterised by an exaggerated response of the immune system to the fungus Aspergillus. It occurs most often in people with asthma or cystic fibrosis. Aspergillus spores are ubiquitous in soil and are commonly found in the sputum of healthy individuals. A. fumigatus is responsible for a spectrum of lung diseases known as aspergilloses.

Wheat allergy is an allergy to wheat which typically presents itself as a food allergy, but can also be a contact allergy resulting from occupational exposure. Like all allergies, wheat allergy involves immunoglobulin E and mast cell response. Typically the allergy is limited to the seed storage proteins of wheat. Some reactions are restricted to wheat proteins, while others can react across many varieties of seeds and other plant tissues. Wheat allergy is rare. Prevalence in adults was found to be 0.21% in a 2012 study in Japan.
Skin allergy testing comprises a range of methods for medical diagnosis of allergies that attempts to provoke a small, controlled, allergic response.
Talizumab (TNX-901) is a humanized monoclonal antibody that was under development by Tanox in Houston, Texas as a new-concept therapeutic for allergic diseases. The unique anti-IgE antibody was designed to target immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IgE-expressing B lymphocytes specifically, without binding to IgE already bound by the high affinity IgE receptors on mast cells and basophils. Talizumab was tested in clinical trials at National Jewish Medical and Research Center and other medical centers and allergy clinics across the U. S. and shown to be able to prevent allergic reactions to accidental exposure to peanuts, which is contained in many kinds of foods.
Tanox was a biopharmaceutical company based in Houston, Texas. The company was founded by two biomedical research scientists, Nancy T. Chang and Tse Wen Chang in March 1986 with $250,000, which was a large part of their family savings at that time. Both Changs grew up and received college education in chemistry in National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan and obtained Ph.D. degrees from Harvard University. For postdoctoral training, Tse Wen shifted to immunology and did research with Herman N. Eisen at the Center for Cancer Research, M.I.T. The two Changs successively became research managers and worked with a range of monoclonal antibody projects in Centocor, Inc. based in Malvern, Pennsylvania, from 1981 to 1985. The Changs were recruited by Baylor College of Medicine toward the end of 1985 and offered faculty positions in the Division of Molecular Virology. Soon after their arrival, they were encouraged by a high-ranking Baylor official and local business leaders to start a biotech venture in Houston. This was in a period of time when the economy of Houston was in slump as the result of the collapse of the oil industry.

Alain L. de Weck,, was a Swiss immunologist and allergist. His main scientific contributions were in the area of characterization and prevention of drug allergy. He was the founding director of the Institute of Clinical Immunology at the University of Bern from 1971 to 1993 and authored or co-authored over 600 peer-reviewed publications. He is the recipient of a number of patents that led to commercial allergy products and services. He served as president of international scientific organizations such as the International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS) and the International Association for Allergy and Clinical Immunology (IAACI) and was founder and later CEO of the Centre Médical des Grand-Places (CMG) company, acquired by Heska of Fort Collins in 1997. In later years he continued his research at the University of Navarra in Spain and wrote on a wide range of topics such as the distinction between science and pseudo-science, the emergence of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and comparative health care policy.

Nancy Tang Chang, née Tang Nanshan, is a biochemist who cofounded Tanox in 1986 to address medical needs in the areas of allergy, asthma, inflammation and diseases affecting the human immune system. Tanox took an innovative approach in developing an asthma drug that focused on the allergy-related basis of asthma, Xolair. In June 2003, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Xolair, the first biotech product cleared for treating those with asthma related to allergies. Tanox was also active in the development of TNX-355, an antibody for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. In 2007, Tanox was sold to Genentech for $919 million. Dr. Chang grew Tanox from an idea to a substantial publicly traded company, doing innovative science. Following her success with Tanox, she has become an angel investor in health-care entrepreneurships and performs philanthropic work in community health-education projects.
HYCOR Biomedical is an American corporation specializing in the manufacture and supply of high-quality in vitro diagnostic products for blood testing for allergies. The company has offices in Garden Grove, California, and Amsterdam, Netherlands. HYCOR Biomedical mainly produces tests and equipment relating to Allergy. Current equipment released by HYCOR includes the fully-automated NOVEOS Immunoanalyzer that uses only 4 microliters of sample per test, paramagnetic microparticles as a solid phase, chemiluminescence and fluorescence methodology for high sensitivity, and liquid ready-to-use reagents. The HYTEC 288 Plus EIA system continues to serve laboratories around the world. The NOVEOS system is the first BIG change in routine allergy testing in over 20 years, capturing the attention of laboratories looking to reduce interference issues that they face with other products, and those looking to improve the patient and clinician experience by reducing the amount of sample needed to perform testing.
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies to treat a number of health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, Kawasaki disease, certain cases of HIV/AIDS and measles, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and certain other infections when a more specific immunoglobulin is not available. Depending on the formulation it can be given by injection into muscle, a vein, or under the skin. The effects last a few weeks.
Stig Gunnar Olof Johansson, professionally often abbreviated S. G. O. Johansson, is a Swedish immunologist. He is credited, along with Ishizaka's team, and Hans Bennich, for the discovery of immunoglobulin E (IgE), a kind of antibody or immunoglobulin that mediates immunity to parasites and also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity and allergic diseases. Their joint paper was published in April 1969.
Teruko "Terry" Ishizaka was a Japanese scientist and immunologist who along with her husband Kimishige Ishizaka discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) in 1966. Their work was regarded as a major breakthrough in the understanding of allergy, and for this work she received the 1972 Passano Award and the 1973 Gairdner Foundation International Award. She was known in the science world for her generosity and collaborative spirit.
References
- Saarinen U M, et al. Lancet 1995;346:1065-1069
- De Backer. Am J Respir 1996;153:A336