
The British National Formulary (BNF) is a United Kingdom (UK) pharmaceutical reference book that contains a wide spectrum of information and advice on prescribing and pharmacology, along with specific facts and details about many medicines available on the UK National Health Service (NHS). Information within the BNF includes indication(s), contraindications, side effects, doses, legal classification, names and prices of available proprietary and generic formulations, and any other notable points. Though it is a national formulary, it nevertheless also includes entries for some medicines which are not available under the NHS, and must be prescribed and/or purchased privately. A symbol clearly denotes such drugs in their entry.

Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, and reviewing medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links health sciences with pharmaceutical sciences and natural sciences. The professional practice is becoming more clinically oriented as most of the drugs are now manufactured by pharmaceutical industries. Based on the setting, the pharmacy is classified as a community or institutional pharmacy. Providing direct patient care in the community of institutional pharmacies are considered clinical pharmacy.
The pregnancy category of a medication is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does not include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites in breast milk.

Australian Medicines Handbook (AMH) is a peer-reviewed medicines prescribing guide for Australian health professionals. The handbook is available in paper and digital formats and is supplemented by the AMH Aged Care Companion and the AMH Children's Dosing Companion.
The Royal Pharmaceutical Society is the body responsible for the leadership and support of the pharmacy profession (pharmacists) within England, Scotland, and Wales. It was created along with the General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC) in September 2010 when the previous Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain was split so that representative and regulatory functions of the pharmacy profession could be separated. Membership in society is not a prerequisite for engaging in practice as a pharmacist within the United Kingdom. Its predecessor the Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain was founded on 15 April 1841.

Piroxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class used to relieve the symptoms of painful inflammatory conditions like arthritis. Piroxicam works by preventing the production of endogenous prostaglandins which are involved in the mediation of pain, stiffness, tenderness and swelling. The medicine is available as capsules, tablets and as a prescription-free gel 0.5%. It is also available in a betadex formulation, which allows a more rapid absorption of piroxicam from the digestive tract. Piroxicam is one of the few NSAIDs that can be given parenteral routes.
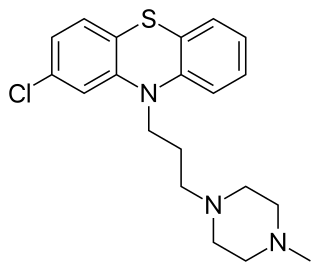
Prochlorperazine, formerly sold under the brand name Compazine among others, is a medication used to treat nausea, migraines and anxiety. It is a less preferred medication for anxiety. It may be taken by mouth, rectally, injection into a vein, or injection into a muscle.
The British Pharmacopoeia (BP) is the national pharmacopoeia of the United Kingdom. It is an annually published collection of quality standards for medicinal substances in the UK, which is used by individuals and organisations involved in pharmaceutical research, development, manufacture and testing.

The British National Formulary for Children (BNFC) is the standard UK paediatric reference for prescribing and pharmacology.
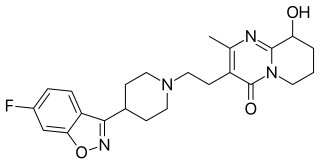
Paliperidone, sold under the trade name Invega among others, is an atypical antipsychotic. It is mainly used to treat schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.

Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference is a reference book published by Pharmaceutical Press listing some 6,000 drugs and medicines used throughout the world, including details of over 180,000 proprietary preparations. It also includes almost 700 disease treatment reviews. It was first published in 1883 under the title Martindale: The Extra Pharmacopoeia. Martindale contains information on drugs in clinical use worldwide, as well as selected investigational and veterinary drugs, herbal and complementary medicines, pharmaceutical excipients, vitamins and nutritional agents, vaccines, radiopharmaceuticals, contrast media and diagnostic agents, medicinal gases, drugs of abuse and recreational drugs, toxic substances, disinfectants, and pesticides.
Pharmaceutical policy is a branch of health policy that deals with the development, provision and use of medications within a health care system. It embraces drugs, biologics, vaccines and natural health products.

Linagliptin, sold under the brand name Tradjenta among others, is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is generally less preferred than metformin and sulfonylureas as an initial treatment. It is used together with exercise and diet. It is not recommended in type 1 diabetes. It is taken by mouth.
At its most basic level, a formulary is a list of medicines. Traditionally, a formulary contained a collection of formulas for the compounding and testing of medication. Today, the main function of a prescription formulary is to specify particular medications that are approved to be prescribed at a particular hospital, in a particular health system, or under a particular health insurance policy. The development of prescription formularies is based on evaluations of efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of drugs.
The Australian Pharmaceutical Formulary (APF) is the national formulary used by pharmacists in Australia, compiled by the Pharmaceutical Society of Australia. New editions of the APF are released every few years, with the latest edition being the 25th.

Irish Medicines Formulary (IMF) is a medicines reference for doctors, nurses, pharmacists and dentists, providing medicines information which is medico-legally relevant in Ireland. It is published in online and print formats, and lists original brands, branded generics and pure generic prescription medicines.
Drug nomenclature is the systematic naming of drugs, especially pharmaceutical drugs. In the majority of circumstances, drugs have 3 types of names: chemical names, the most important of which is the IUPAC name; generic or nonproprietary names, the most important of which are international nonproprietary names (INNs); and trade names, which are brand names. Under the INN system, generic names for drugs are constructed out of affixes and stems that classify the drugs into useful categories while keeping related names distinguishable. A marketed drug might also have a company code or compound code.
EMDEX is the most commonly used reference source of drug and therapeutic information by healthcare professionals in Nigeria. It was first published in 1991 as Nigeria's Essential Drugs (NED) Guide.
EMDEX drug information contents, arrangements and therapeutic recommendations are supported by several references and clinical guidelines notably WHO Model Formulary, WHO ATC Classification System, Nigeria's Essential Medicines List and Standard Treatment Guidelines, etc. The information is regularly reviewed and updated by a select team of healthcare practitioners and academics.
The central objective of EMDEX has been to promote rational use of medicines through provision of independent drug information, and use of clinical guidelines and essential medicines list. It is the largest and up-to-date source of information on drug products approved for use in Nigeria by NAFDAC .
The use of EMDEX as a reference drug manual is endorsed by Pharmacists Council of Nigeria, Nursing & Midwifery Council of Nigeria and major health institutions. It is used both within and outside Nigeria by physicians, dentists, pharmacists, nurse practitioners, and auxiliary health workers at all levels of healthcare delivery. These healthcare providers rely on EMDEX for accuracy and completeness of drug information namely indications, contra-indications, precautions or warnings, adverse effects, dosages, and drug use in special populations like children, elderly, pregnancy & lactation.
EMDEX publications are also in the syllabus of various colleges & schools of medicine, pharmacy & nursing.










