Related Research Articles

Alexander Theodore "Sasha" Shulgin was an American medicinal chemist, biochemist, organic chemist, pharmacologist, psychopharmacologist, and author. He is credited with introducing 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine to psychologists in the late 1970s for psychopharmaceutical use and for the discovery, synthesis and personal bioassay of over 230 psychoactive compounds for their psychedelic and entactogenic potential.

PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story is a book by Dr. Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin, published in 1991. The subject of the work is psychoactive phenethylamine chemical derivatives, notably those that act as psychedelics and/or empathogen-entactogens. The main title, PiHKAL, is an acronym that stands for "Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved".
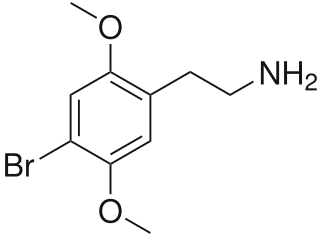
2C-B (4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine) is a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1974. In Shulgin's book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 12–24 mg. As a recreational drug, 2C-B is sold as a white powder sometimes pressed in tablets or gel caps. It is also referred to by a number of street names. The drug is usually taken orally, but can also be insufflated or vaporized. While being primarily a psychedelic it is also a mild entactogen.

2C-T-2 is a psychedelic and entactogenic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in 1981 by Alexander Shulgin, and rated by him as one of the "magical half-dozen" most important psychedelic phenethylamine compounds. The drug has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to those of 2C-T-7.

TIHKAL: The Continuation is a 1997 book written by Alexander Shulgin and Ann Shulgin about a family of psychoactive drugs known as tryptamines. A sequel to PIHKAL: A Chemical Love Story, TIHKAL is an acronym that stands for "Tryptamines I Have Known and Loved".
Uncle Fester is the pen name of Steve Preisler, author of such controversial books as Secrets of Methamphetamine Manufacture, and Silent Death.

3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine is an empathogen-entactogen, psychostimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In terms of pharmacology, MDA acts most importantly as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.
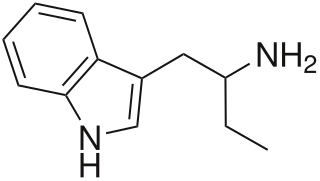
α-Ethyltryptamine, also known as etryptamine, is a psychedelic, stimulant, and entactogenic drug of the tryptamine class. It was originally developed and marketed as an antidepressant under the brand name Monase by Upjohn in the 1960s.
David Earl Nichols is an American pharmacologist and medicinal chemist. Previously the Robert C. and Charlotte P. Anderson Distinguished Chair in Pharmacology at Purdue University, Nichols has worked in the field of psychoactive drugs since 1969. While still a graduate student, he patented the method that is used to make the optical isomers of hallucinogenic amphetamines. His contributions include the synthesis and reporting of escaline, LSZ, 6-APB, 2C-I-NBOMe and other NBOMe variants, and several others, as well as the coining of the term "entactogen".

2C-P is a relatively potent and long acting psychedelic phenethylamine of the 2C family.

Ann Shulgin is an American author and the widow of chemist Alexander Shulgin, with whom she wrote PiHKAL and TiHKAL.

3,4-Methylenedioxyphenylpropan-2-one or piperonyl methyl ketone is a chemical compound consisting of a phenylacetone moiety substituted with a methylenedioxy functional group. It is commonly synthesized from either safrole or its isomer isosafrole via oxidation using the Wacker oxidation or peroxyacid oxidation methods. MDP2P is unstable at room temperature and must be kept in the freezer in order to be preserved properly.

1-Phenyl-2-nitropropene, or simply phenyl-2-nitropropene, or P2NP, as it is commonly referred to, is a chemical compound from the aromatic group of compounds, with the formula C9H9NO2. It is a light-yellow crystalline solid with a distinct smell. Phenyl-2-nitropropene is used in the pharmaceutical industry to manufacture the drug Adderall, an amphetamine mixture used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. P2NP and other similar nitrostyrenes are also employed in the clandestine manufacture of drugs of the amphetamine class, and are listed as drug precursors in many countries.
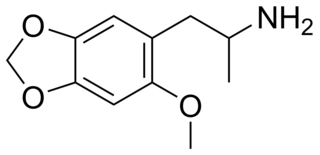
MMDA-2 (2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine) is a psychedelic drug of the amphetamine class. It is closely related to MMDA and MDA.

N-Methyl-2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine is a psychedelic drug of the amphetamine class. It is the N-methylated derivative of MMDA-2, and it is also an analog of MDMA and 6-methyl-MDA.

ALPHA (alpha-ethyl-3,4-methylenedioxybenzylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted benzylamine. It is also the benzylamine analog of 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA). ALPHA was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PIHKAL on the MDA page, the threshold dosage is listed as 10 mg. At mild threshold dosages there are eyes-closed "dreams" with some body tingling, at higher doses was reported to produce a pleasant, positive feeling. This compound is not anoretic at any dose. It lasts about 3 hours. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of ALPHA.

5-Methyl-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (5-Methyl-MDA) is an entactogen and psychedelic designer drug of the amphetamine class. It is a ring-methylated homologue of MDA and a structural isomer of MDMA.

2,3-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (2,3-MDA) or ORTHO-MDA is an amphetamine derivative which is mentioned in PIHKAL as a fairly potent and long-lasting stimulant drug, but with little or none of the entactogenic effects associated with its better-known structural isomer MDA.

1-Methylamino-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane or M-ALPHA is an empathogen, reported by Alexander Shulgin in his book PIHKAL as a positional isomer of MDMA, and subsequently found being sold as a designer drug in the UK in 2010, and reported to the EMCDDA new drug monitoring service. It was described by Alexander Shulgin as similar in action to its demethylated homologue, ALPHA, but with roughly twice the duration and twice the potency.
Drug precursors, also referred to as precursor chemicals or simply precursors, are substances which are known to be used in the illegal manufacture of illicit drugs. Most precursors also have legitimate commercial uses and are legally used in a wide variety of industrial processes and consumer products, such as medicines, flavourings, and fragrances.