Related Research Articles
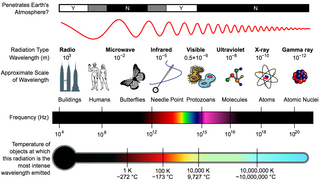
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.

The hertz is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz).

Infrared is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light and shorter than radio waves. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal infrared that is emitted from terrestrial sources and shorter-wavelength near-infrared that is part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.

An optical spectrometer is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the irradiance of the light but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a unit directly proportional to the photon energy, such as reciprocal centimeters or electron volts, which has a reciprocal relationship to wavelength.

The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm . The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well.

In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons. The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the quantization of plasma oscillations, just like phonons are quantizations of mechanical vibrations. Thus, plasmons are collective oscillations of the free electron gas density. For example, at optical frequencies, plasmons can couple with a photon to create another quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton.
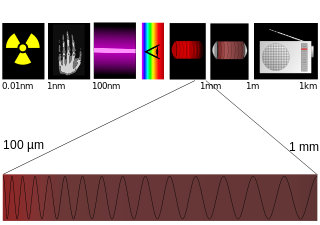
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency (THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the ITU-designated band of frequencies from 0.3 to 3 terahertz (THz), although the upper boundary is somewhat arbitrary and is considered by some sources as 30 THz. One terahertz is 1012 Hz or 1000 GHz. Wavelengths of radiation in the terahertz band correspondingly range from 1 mm to 0.1 mm = 100 µm. Because terahertz radiation begins at a wavelength of around 1 millimeter and proceeds into shorter wavelengths, it is sometimes known as the submillimeter band, and its radiation as submillimeter waves, especially in astronomy. This band of electromagnetic radiation lies within the transition region between microwave and far infrared, and can be regarded as either.

The point spread function (PSF) describes the response of a focused optical imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is the system's impulse response; the PSF is the impulse response or impulse response function (IRF) of a focused optical imaging system. The PSF in many contexts can be thought of as the extended blob in an image that represents a single point object, that is considered as a spatial impulse. In functional terms, it is the spatial domain version of the optical transfer function (OTF) of an imaging system. It is a useful concept in Fourier optics, astronomical imaging, medical imaging, electron microscopy and other imaging techniques such as 3D microscopy and fluorescence microscopy.
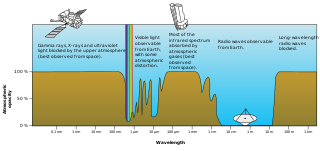
The radio window is a range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that penetrate the Earth's atmosphere. Typically, the lower limit of the radio window's range has a value of about 10 MHz ; the best upper limit achievable from optimal terrestrial observation sites is equal to approximately 1 THz.

In physics, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) is a spectroscopic technique in which the properties of matter are probed with short pulses of terahertz radiation. The generation and detection scheme is sensitive to the sample's effect on both the amplitude and the phase of the terahertz radiation.

Polymethylpentene (PMP), also known as poly(4-methyl-1-pentene), is a thermoplastic polyolefin. It is used for gas-permeable packaging, autoclavable medical and laboratory equipment, microwave components, and cookware. It is commonly called TPX, which is a trademark of Mitsui Chemicals.
Photomixing is the generation of continuous wave terahertz radiation from two lasers. The beams are mixed together and focused onto a photomixer device which generates the terahertz radiation. It is technologically significant because there are few sources capable of providing radiation in this waveband, others include frequency multiplied electronic/microwave sources, quantum cascade laser and ultrashort pulsed lasers with photoconductive switches as used in terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. The advantages of this technique are that it is continuously tunable over the frequency range from 300 GHz to 3 THz, and spectral resolutions in the order of 1 MHz can be achieved. However, the achievable power is on the order of 10−8 W.
Terahertz tomography is a class of tomography where sectional imaging is done by terahertz radiation. Terahertz radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a frequency between 0.1 and 10 THz; it falls between radio waves and light waves on the spectrum; it encompasses portions of the millimeter waves and infrared wavelengths. Because of its high frequency and short wavelength, terahertz wave has a high signal-to-noise ratio in the time domain spectrum. Tomography using terahertz radiation can image samples that are opaque in the visible and near-infrared regions of the spectrum. Terahertz wave three-dimensional (3D) imaging technology has developed rapidly since its first successful application in 1997, and a series of new 3D imaging technologies have been proposed successively.

Electro-optic rectification (EOR), also referred to as optical rectification, is a non-linear optical process that consists of the generation of a quasi-DC polarization in a non-linear medium at the passage of an intense optical beam. For typical intensities, optical rectification is a second-order phenomenon which is based on the inverse process of the electro-optic effect. It was reported for the first time in 1962, when radiation from a ruby laser was transmitted through potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) and potassium dideuterium phosphate (KDdP) crystals.

The Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Leibniz-Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik (FBH) is a research institute, which is a member of the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Scientific Community. The institute is located in Berlin at the Wissenschafts- und Wirtschaftsstandort Adlershof (WISTA), its research activity is applied science in the fields of III-V electronics, photonics, integrated quantum technology and III-V technology

A terahertz metamaterial is a class of composite metamaterials designed to interact at terahertz (THz) frequencies. The terahertz frequency range used in materials research is usually defined as 0.1 to 10 THz.
Terahertz nondestructive evaluation pertains to devices, and techniques of analysis occurring in the terahertz domain of electromagnetic radiation. These devices and techniques evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.

TeraView Limited, or TeraView, is a company that designs terahertz imaging and spectroscopy instruments and equipment for measurement and evaluation of pharmaceutical tablets, nanomaterials, ceramics and composites, integrated circuit chips and more.
Terahertz spectroscopy detects and controls properties of matter with electromagnetic fields that are in the frequency range between a few hundred gigahertz and several terahertz. In many-body systems, several of the relevant states have an energy difference that matches with the energy of a THz photon. Therefore, THz spectroscopy provides a particularly powerful method in resolving and controlling individual transitions between different many-body states. By doing this, one gains new insights about many-body quantum kinetics and how that can be utilized in developing new technologies that are optimized up to the elementary quantum level.

Anisotropic terahertz microspectroscopy (ATM) is a spectroscopic technique in which molecular vibrations in an anisotropic material are probed with short pulses of terahertz radiation whose electric field is linearly polarized parallel to the surface of the material. The technique has been demonstrated in studies involving single crystal sucrose, fructose, oxalic acid, and molecular protein crystals in which the spatial orientation of molecular vibrations are of interest.
References
- ↑ Erik Bründermann; Heinz-Wilhelm Hübers; Maurice FitzGerald Kimmitt (18 April 2012). Terahertz Techniques. Springer. p. 56. ISBN 978-3-642-02592-1.
- ↑ Bründermann, Erik; Hübers, Heinz-Wilhelm; Kimmitt, Maurice F. (2012). Terahertz Techniques. Springer Series in Optical Sciences. Vol. 151. pp. 51–101. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02592-1_3. ISBN 978-3-642-02591-4. ISSN 0342-4111.